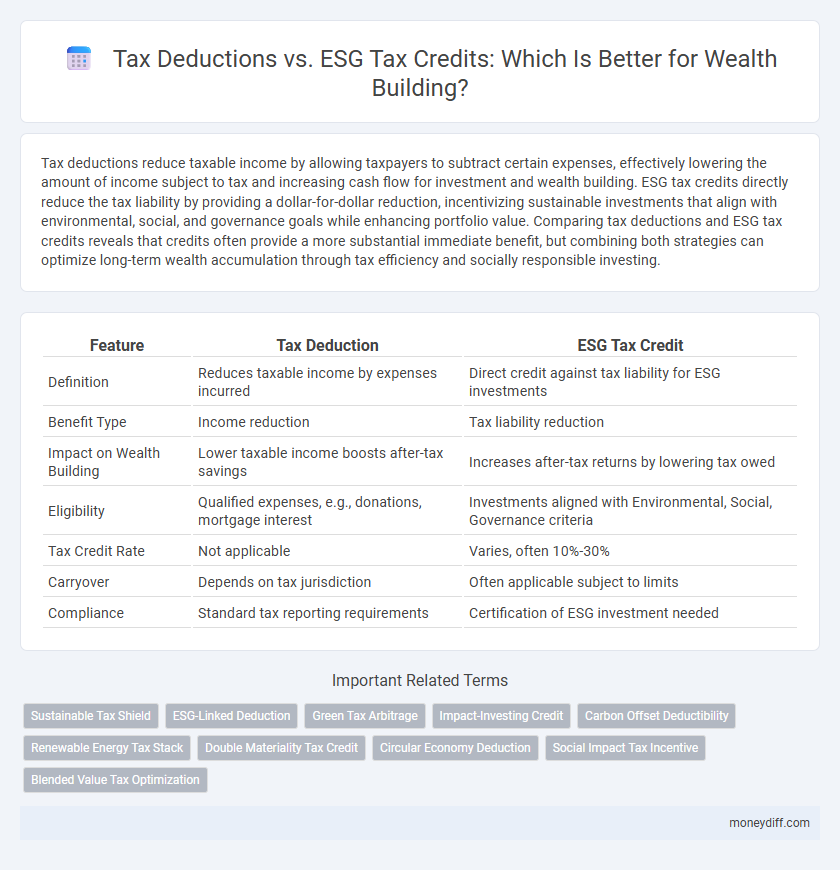
Tax deductions reduce taxable income by allowing taxpayers to subtract certain expenses, effectively lowering the amount of income subject to tax and increasing cash flow for investment and wealth building. ESG tax credits directly reduce the tax liability by providing a dollar-for-dollar reduction, incentivizing sustainable investments that align with environmental, social, and governance goals while enhancing portfolio value. Comparing tax deductions and ESG tax credits reveals that credits often provide a more substantial immediate benefit, but combining both strategies can optimize long-term wealth accumulation through tax efficiency and socially responsible investing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tax Deduction | ESG Tax Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduces taxable income by expenses incurred | Direct credit against tax liability for ESG investments |
| Benefit Type | Income reduction | Tax liability reduction |
| Impact on Wealth Building | Lower taxable income boosts after-tax savings | Increases after-tax returns by lowering tax owed |
| Eligibility | Qualified expenses, e.g., donations, mortgage interest | Investments aligned with Environmental, Social, Governance criteria |
| Tax Credit Rate | Not applicable | Varies, often 10%-30% |
| Carryover | Depends on tax jurisdiction | Often applicable subject to limits |
| Compliance | Standard tax reporting requirements | Certification of ESG investment needed |
Understanding Tax Deductions and ESG Tax Credits
Tax deductions reduce taxable income based on eligible expenses, directly lowering the amount on which taxes are calculated. ESG tax credits offer dollar-for-dollar reductions in tax liability for investments in environmentally and socially responsible projects, enhancing wealth accumulation through government incentives. Understanding the specific eligibility criteria and financial impacts of both helps optimize tax strategies for sustainable wealth building.
Key Differences Between Tax Deductions and ESG Tax Credits
Tax deductions reduce taxable income by allowing a portion of expenses to be subtracted, lowering overall tax liability, whereas ESG tax credits directly reduce the amount of tax owed as incentives for environmentally and socially responsible investments. Tax deductions benefit a wide range of taxpayers by decreasing taxable income, while ESG tax credits specifically target companies and individuals engaging in sustainable practices. Understanding the difference is crucial for strategic wealth building, as ESG tax credits often provide dollar-for-dollar tax savings and promote long-term value aligned with environmental, social, and governance goals.
How Tax Deductions Impact Wealth Accumulation
Tax deductions reduce taxable income, allowing individuals to retain more earnings and invest those savings, which accelerates wealth accumulation over time through compounding growth. By lowering the immediate tax burden, deductions increase disposable income that can be allocated toward high-yield assets or retirement accounts. Effective utilization of tax deductions supports long-term financial goals, enhancing capital growth and overall net worth.
Wealth Building Advantages of ESG Tax Credits
ESG tax credits offer significant wealth-building advantages by directly reducing tax liabilities while promoting sustainable investments that can appreciate over time. Unlike traditional tax deductions, which lower taxable income, ESG tax credits provide dollar-for-dollar tax offsets, enhancing cash flow and investment potential for high-net-worth individuals. Leveraging ESG tax credits accelerates portfolio diversification with socially responsible assets, aligning financial growth with long-term environmental and social governance goals.
Eligibility Criteria for Tax Deductions vs ESG Tax Credits
Tax deductions typically require taxpayers to incur eligible expenses such as mortgage interest, charitable contributions, or business-related costs, lowering taxable income based on documented expenditures. ESG tax credits focus on investments in environmental, social, and governance initiatives, demanding compliance with specific standards like renewable energy projects or socially responsible activities to qualify. Eligibility for tax deductions generally centers on expense documentation and personal or business status, whereas ESG tax credits hinge on meeting defined sustainability criteria and certification from recognized authorities.
Maximizing Wealth: Combining Tax Deductions and ESG Credits
Maximizing wealth involves strategically leveraging both tax deductions and ESG tax credits to reduce taxable income and qualify for incentives that promote sustainable investments. Tax deductions lower immediate tax liabilities by accounting for eligible expenses, while ESG tax credits directly reduce taxes owed by incentivizing eco-friendly business practices and investments. Combining these tools enhances overall tax efficiency, accelerating wealth accumulation through mindful financial planning and socially responsible investing.
Common Tax Deduction Strategies for Investors
Common tax deduction strategies for investors include deducting mortgage interest, property taxes, and investment-related expenses such as advisory fees and interest on loans used for investment purposes. Capital losses can offset capital gains, reducing taxable income and enhancing wealth accumulation over time. Maximizing contributions to retirement accounts and utilizing depreciation deductions on rental properties are also effective methods to minimize tax liability and support long-term wealth building.
ESG Tax Credits: Supporting Sustainability While Growing Wealth
ESG tax credits provide substantial financial incentives for investors and businesses that prioritize environmental, social, and governance criteria, enabling wealth building through sustainable practices. These credits reduce tax liabilities by rewarding investments in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and social impact projects, aligning financial growth with ethical stewardship. Unlike standard tax deductions, ESG tax credits directly offset tax owed, enhancing after-tax returns while promoting long-term sustainability goals.
Tax Planning Tips for Enhancing Long-Term Wealth
Maximizing long-term wealth requires strategic tax planning by balancing tax deductions with ESG tax credits, which provide financial incentives for sustainable investments. Tax deductions reduce taxable income immediately, whereas ESG tax credits directly lower tax liability, making ESG-focused portfolios increasingly advantageous for building wealth. Incorporating both tools within retirement accounts and diversified asset classes optimizes after-tax returns and supports sustainable financial growth.
Choosing the Best Tax Benefits for Your Wealth Goals
Tax deductions reduce your taxable income directly by lowering the amount subject to tax, while ESG tax credits provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in tax liability for investments in environmental, social, and governance initiatives. Prioritizing ESG tax credits can maximize wealth-building potential through substantial savings on tax bills and supporting sustainable investments. Evaluating your financial goals and consulting a tax advisor helps determine the most advantageous mix of deductions and credits to optimize long-term wealth growth.
Related Important Terms
Sustainable Tax Shield
Tax deduction reduces taxable income by the amount of eligible expenses, lowering overall tax liability, while ESG tax credits directly decrease tax owed by investing in environmental, social, and governance initiatives. Utilizing Sustainable Tax Shield strategies leverages ESG tax credits to enhance wealth building by promoting sustainable investments that yield both financial returns and tax benefits.
ESG-Linked Deduction
ESG-linked tax deductions incentivize environmentally and socially responsible investments by lowering taxable income based on verified ESG expenditures, enhancing wealth building through reduced tax liabilities. Unlike traditional tax deductions, ESG tax credits directly reduce tax owed, offering more immediate financial benefits for sustainable investment activities.
Green Tax Arbitrage
Tax deduction reduces taxable income by lowering the amount subject to taxes, providing immediate savings, while ESG tax credits directly reduce tax liability based on investments in environmentally sustainable initiatives, enhancing long-term wealth building through green tax arbitrage. Leveraging ESG tax credits allows investors to capitalize on government incentives for green projects, turning environmental responsibility into a strategic financial advantage that surpasses traditional tax deductions.
Impact-Investing Credit
Tax deductions reduce taxable income, lowering overall tax liability, while ESG tax credits directly reduce tax owed, providing a dollar-for-dollar benefit that enhances wealth building through impact investing. ESG tax credits specifically incentivize investments in sustainable projects, amplifying financial returns alongside positive social and environmental outcomes.
Carbon Offset Deductibility
Tax deductions for carbon offsets reduce taxable income directly, providing immediate financial benefits, while ESG tax credits offer dollar-for-dollar reductions in tax liability, incentivizing sustainable investments. Understanding the specific offset deductibility rules under IRS Section 45Q and related ESG frameworks is crucial for maximizing wealth-building strategies through environmentally responsible tax planning.
Renewable Energy Tax Stack
Tax deductions reduce taxable income by allowing a direct subtraction of qualified expenses, while ESG tax credits provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in tax liability specifically for investments in renewable energy projects. Leveraging the Renewable Energy Tax Stack, which includes investment tax credits (ITC) and production tax credits (PTC), significantly enhances wealth building by maximizing cash flow and encouraging sustainable, long-term financial growth.
Double Materiality Tax Credit
Double Materiality Tax Credit integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors with financial performance, offering a strategic tax incentive that enhances wealth building through sustainable investments. Unlike traditional tax deductions, these credits provide a direct reduction in tax liability while aligning long-term value creation with corporate responsibility, maximizing both economic and ecological returns.
Circular Economy Deduction
The Circular Economy Deduction offers businesses tax relief by incentivizing sustainable practices such as recycling and resource efficiency, directly reducing taxable income while promoting environmental responsibility. Unlike ESG Tax Credits that target broader environmental, social, and governance goals, this deduction specifically supports wealth building through cost savings and reinvestment opportunities in circular economy initiatives.
Social Impact Tax Incentive
Tax deductions reduce taxable income by allowing individuals or businesses to subtract eligible expenses, while ESG tax credits directly lower tax liability by incentivizing investments in environmental, social, and governance initiatives. Social impact tax incentives encourage wealth building through reduced taxes on projects that promote community development, affordable housing, and social equity, enhancing both financial returns and societal benefits.
Blended Value Tax Optimization
Blended Value Tax Optimization combines traditional tax deductions with ESG tax credits to maximize wealth building by reducing taxable income while supporting sustainable investments. This strategic integration leverages government incentives for environmentally and socially responsible activities, enhancing financial returns alongside positive social impact.
Tax Deduction vs ESG Tax Credit for Wealth Building Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com