Traditional savings accounts offer easy access and lower minimum balance requirements, making them suitable for everyday saving needs. High-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher interest rates, allowing your savings to grow faster while maintaining liquidity. Choosing between the two depends on your priority for accessibility versus maximizing interest returns.
Table of Comparison
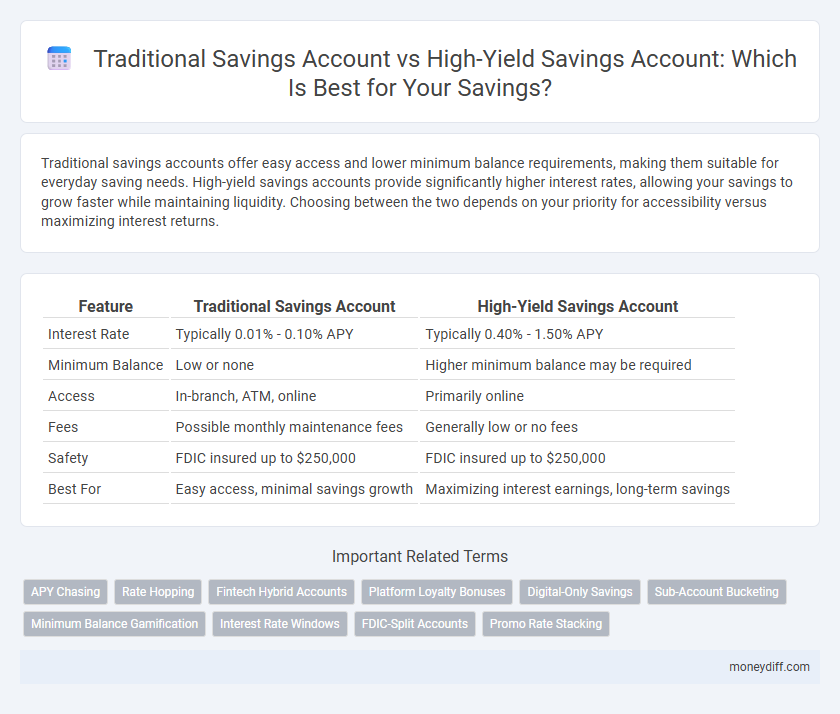
| Feature | Traditional Savings Account | High-Yield Savings Account |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Typically 0.01% - 0.10% APY | Typically 0.40% - 1.50% APY |
| Minimum Balance | Low or none | Higher minimum balance may be required |
| Access | In-branch, ATM, online | Primarily online |
| Fees | Possible monthly maintenance fees | Generally low or no fees |
| Safety | FDIC insured up to $250,000 | FDIC insured up to $250,000 |
| Best For | Easy access, minimal savings growth | Maximizing interest earnings, long-term savings |
Understanding Traditional Savings Accounts
Traditional savings accounts provide a secure method for saving money with easy access and federal insurance protection, typically offering lower interest rates compared to high-yield savings accounts. These accounts are ideal for individuals prioritizing liquidity and minimal risk, as they allow regular deposits and withdrawals without penalties. Understanding the features, such as minimum balance requirements and interest calculation methods, helps savers choose the best option aligned with their financial goals.
What Is a High-Yield Savings Account?
A high-yield savings account offers significantly higher interest rates compared to a traditional savings account, often exceeding 2% APY, which accelerates the growth of your savings. These accounts are usually provided by online banks with lower overhead costs, enabling them to pass on better rates to customers. Unlike traditional savings accounts with minimal interest, high-yield options maximize earnings while maintaining safety and liquidity.
Interest Rates: Traditional vs High-Yield Accounts
Traditional savings accounts typically offer interest rates around 0.01% to 0.10%, making them less effective for growing savings over time. High-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher interest rates, often ranging from 3.00% to 5.00%, allowing savers to earn more substantial returns on their deposits. Choosing a high-yield savings account maximizes interest earnings and accelerates the growth of your savings compared to traditional options.
Account Accessibility and Convenience
Traditional savings accounts offer extensive accessibility through widespread branch networks and ATM access, allowing easy deposits and withdrawals. High-yield savings accounts primarily operate online, providing convenience with higher interest rates but may limit immediate access to funds due to fewer physical locations. Customers seeking quick, in-person transactions often prefer traditional accounts, while those prioritizing digital management and better returns lean towards high-yield options.
Minimum Balance Requirements
Traditional savings accounts typically require low or no minimum balance, making them accessible for everyday savers. High-yield savings accounts often impose higher minimum balance requirements to access the elevated interest rates, which can limit flexibility for small savers. Choosing between the two depends on balancing the need for higher returns against maintaining lower or no minimum balance constraints.
Fees and Charges Compared
Traditional savings accounts often have low or no monthly maintenance fees but typically offer minimal interest rates, limiting growth potential. High-yield savings accounts usually provide significantly higher interest rates but may impose minimum balance requirements and higher fees if conditions are not met. Evaluating fee structures alongside interest benefits is essential to maximize savings efficiency.
FDIC Insurance and Account Safety
Traditional savings accounts and high-yield savings accounts both offer FDIC insurance up to $250,000 per depositor, ensuring the safety of your funds in the event of bank failure. FDIC insurance guarantees that the principal amount deposited is protected, regardless of the account type, making both options secure choices for savings. While interest rates differ, the fundamental security provided by FDIC insurance makes either account a reliable vehicle for protecting your money.
Ideal Uses for Each Savings Account Type
Traditional savings accounts are ideal for individuals seeking easy access to their funds with minimal risk and lower minimum balance requirements, making them suitable for emergency savings and short-term goals. High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates, perfect for savers focused on maximizing returns over longer periods while maintaining liquidity. Choosing between the two depends on the saver's priority: immediate accessibility with traditional accounts or enhanced growth potential with high-yield accounts.
How to Switch from Traditional to High-Yield Savings
To switch from a traditional savings account to a high-yield savings account, begin by researching institutions offering competitive annual percentage yields (APYs) with minimal fees. Open a high-yield savings account by providing necessary identification and completing the application process online or in-branch. Transfer funds from your traditional account, ensuring automatic deposits and withdrawals are updated to maximize your interest earnings efficiently.
Choosing the Best Account for Your Savings Goals
Traditional savings accounts offer lower interest rates, typically around 0.01% to 0.10% APY, making them suitable for emergency funds or short-term savings with easy access. High-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher returns, often ranging from 3.00% to 5.00% APY, ideal for maximizing growth over longer periods without sacrificing liquidity. Select the account that aligns with your savings goals by balancing interest rates, access to funds, and account fees to optimize your financial growth.
Related Important Terms
APY Chasing
High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher APYs compared to traditional savings accounts, often ranging from 3.5% to 5%, enabling faster growth of your savings through compounded interest. Traditional accounts typically provide APYs below 0.1%, making them less competitive for maximizing returns on deposits.
Rate Hopping
Rate hopping involves moving funds between traditional savings accounts and high-yield savings accounts to maximize interest earnings, as high-yield accounts often offer rates several times higher than traditional accounts, sometimes exceeding 4% APY compared to under 0.1% APY in conventional accounts. Savvy savers take advantage of promotional rates and online banks' offerings, frequently shifting balances to capture the best available returns while maintaining liquidity.
Fintech Hybrid Accounts
Fintech hybrid accounts combine the security of traditional savings accounts with the higher interest rates typically offered by high-yield savings accounts, providing savers with both liquidity and improved returns. These digital-first platforms leverage advanced algorithms and partnerships with multiple banks to optimize interest accrual while maintaining easy access to funds and robust mobile management features.
Platform Loyalty Bonuses
Traditional savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates but may provide platform loyalty bonuses such as fee waivers or small cash rewards to retain customers, while high-yield savings accounts prioritize higher interest earnings with fewer or no loyalty incentives. Evaluating these bonuses alongside interest rates is essential for maximizing overall savings growth on each platform.
Digital-Only Savings
Digital-only savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts, often providing yields up to 5 times greater due to lower overhead costs. These accounts combine ease of access through mobile apps with enhanced compound interest benefits, making them ideal for maximizing savings growth efficiently.
Sub-Account Bucketing
Traditional savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates, making sub-account bucketing a practical strategy to organize funds while maximizing liquidity. High-yield savings accounts enhance growth potential through higher returns, and using sub-account bucketing within them helps manage savings goals efficiently by segmenting funds for various purposes.
Minimum Balance Gamification
Traditional savings accounts typically require lower minimum balances but offer minimal interest rates, limiting potential earnings. High-yield savings accounts often demand higher minimum balances that encourage disciplined saving habits through gamification features like tiered interest rates and reward milestones.
Interest Rate Windows
Traditional savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates ranging from 0.01% to 0.10%, limiting potential growth on deposited funds. High-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher interest rates, often between 3.00% and 4.50%, enabling faster accumulation of savings through compounded returns.
FDIC-Split Accounts
Traditional savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates and FDIC insurance coverage up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank, while high-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher APYs with the same FDIC protection. Utilizing FDIC-split accounts across multiple banks allows savers to maximize insured limits and optimize returns by combining the benefits of both account types.
Promo Rate Stacking
High-yield savings accounts often offer promotional rate stacking, allowing savers to benefit from increased interest rates for a limited time, significantly boosting their earnings compared to traditional savings accounts with fixed low rates. This strategy enhances overall savings growth by leveraging initial bonus rates before reverting to standard APYs.
Traditional Savings Account vs High-Yield Savings Account for savings. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com