Social Security provides a guaranteed, lifelong income that adjusts for inflation, serving as a reliable foundation for retirement households. Sidecar Savings offer flexibility and growth potential through investments but come with market risks and require careful management to ensure sustainable withdrawals. Combining Social Security with Sidecar Savings can balance stability and growth, enhancing overall retirement income security.
Table of Comparison
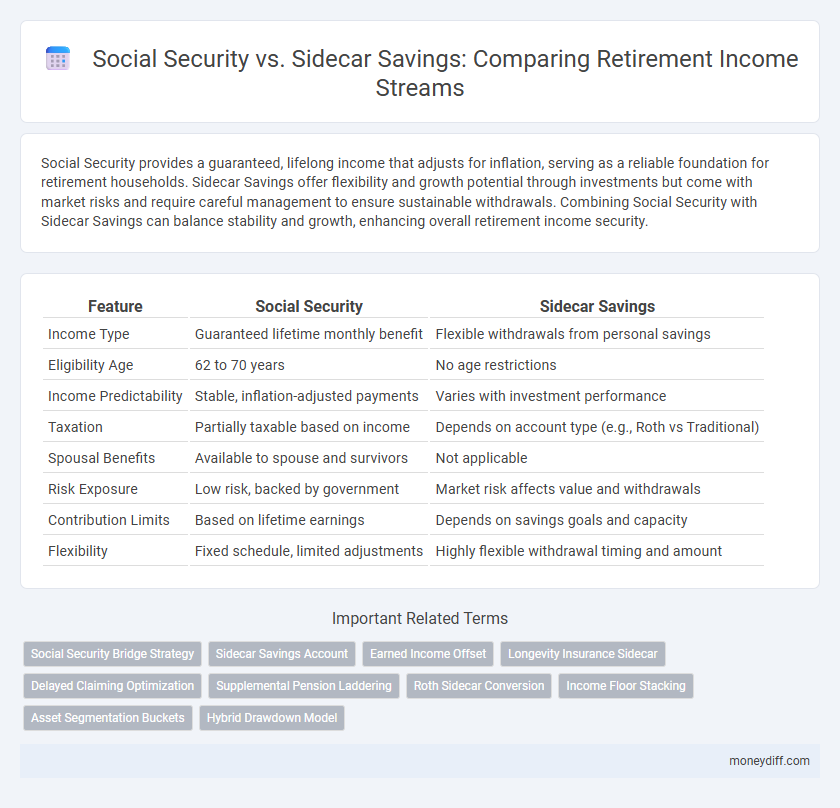
| Feature | Social Security | Sidecar Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Income Type | Guaranteed lifetime monthly benefit | Flexible withdrawals from personal savings |
| Eligibility Age | 62 to 70 years | No age restrictions |
| Income Predictability | Stable, inflation-adjusted payments | Varies with investment performance |
| Taxation | Partially taxable based on income | Depends on account type (e.g., Roth vs Traditional) |
| Spousal Benefits | Available to spouse and survivors | Not applicable |
| Risk Exposure | Low risk, backed by government | Market risk affects value and withdrawals |
| Contribution Limits | Based on lifetime earnings | Depends on savings goals and capacity |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedule, limited adjustments | Highly flexible withdrawal timing and amount |
Understanding Social Security: The Basics
Social Security provides a guaranteed monthly income based on your lifetime earnings and work history, offering a foundation for retirement income that adjusts with inflation. Benefits are calculated using your highest 35 years of earnings, with eligibility starting as early as age 62 and increasing if you delay claiming up to age 70. Understanding the rules around Social Security helps optimize your claim strategy, ensuring you maximize guaranteed income before considering supplemental sources like Sidecar Savings accounts.
What is a Sidecar Savings Account?
A Sidecar Savings Account is a supplemental retirement income strategy designed to enhance financial security beyond Social Security benefits. It functions as a dedicated savings vehicle where individuals contribute funds during their working years to generate additional income during retirement. This approach helps bridge income gaps by providing flexible, tax-advantaged withdrawals separate from Social Security payments.
Key Differences: Social Security vs Sidecar Savings
Social Security provides a guaranteed monthly income based on lifetime earnings and government formulas, ensuring inflation-adjusted benefits throughout retirement. Sidecar savings consist of personal investments or savings accounts offering flexible access and potential growth but carry market risk and no guaranteed payouts. Social Security acts as a foundational income stream, while sidecar savings serve as a supplemental resource to enhance overall retirement security.
Evaluating Retirement Income Reliability
Social Security offers a guaranteed, inflation-adjusted income stream backed by the federal government, providing a reliable foundation for retirement. Sidecar savings, including IRAs and 401(k)s, offer flexibility and growth potential but depend on market performance and withdrawal strategy. Evaluating retirement income reliability requires balancing the steady income from Social Security with the variable but potentially higher returns from sidecar savings.
Pros and Cons of Social Security
Social Security provides a guaranteed, inflation-adjusted income stream for life, offering a reliable financial foundation during retirement with benefits tied to earnings history. However, it may not fully cover all retirement expenses due to increasing life expectancy and potential future funding uncertainties, limiting its ability to serve as the sole income source. Reliance on Social Security alone can also reduce flexibility, as benefit amounts are fixed and withdrawals cannot be adjusted based on individual financial needs or market performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sidecar Savings
Sidecar savings offer flexible access to funds without restrictions on withdrawals, unlike Social Security, which has age-based limits and fixed benefit amounts. These savings provide opportunities for higher growth through diversified investments but carry market risk and require disciplined saving to build sufficient retirement income. Unlike Social Security's guaranteed income, sidecar savings lack longevity protection but can supplement income and cover unexpected expenses.
Diversifying Your Retirement Income Streams
Diversifying your retirement income streams enhances financial security by balancing Social Security benefits with sidecar savings, such as taxable investment accounts or annuities. Social Security provides a guaranteed, inflation-adjusted income base, while sidecar savings offer flexibility and potential for growth to cover unexpected expenses or lifestyle choices. Combining these sources reduces reliance on a single income type, mitigating risks associated with market fluctuations and policy changes.
Impact of Inflation on Retirement Funds
Social Security benefits provide a cost-of-living adjustment (COLA) to help protect retirees from inflation eroding their purchasing power over time. Sidecar savings, such as IRAs or 401(k) accounts, require active investment strategies to outpace inflation and preserve real retirement income. Inflation's impact can diminish fixed income streams, making diversification between Social Security and inflation-protected sidecar savings critical for sustained financial security in retirement.
Tax Implications: Social Security vs Sidecar Savings
Social Security benefits are subject to federal income taxes based on combined income, potentially reducing net retirement income for higher earners. Sidecar savings, such as Roth IRAs or taxable investment accounts, offer varied tax treatments--Roth accounts provide tax-free withdrawals, while taxable accounts incur capital gains taxes upon asset sales. Strategic use of sidecar savings alongside Social Security can optimize tax efficiency, lowering overall tax liabilities during retirement.
Choosing the Best Strategy for Your Retirement Goals
Evaluate Social Security and Sidecar Savings by analyzing income stability, tax implications, and flexibility to align with your retirement goals. Social Security offers guaranteed lifetime benefits adjusted for inflation, while Sidecar Savings provide additional liquidity and investment growth potential. Prioritize a strategy that balances consistent income with opportunities for supplemental savings to optimize financial security throughout retirement.
Related Important Terms
Social Security Bridge Strategy
The Social Security Bridge Strategy leverages early retirement savings, such as sidecar savings, to cover expenses before claiming Social Security benefits at full retirement age, maximizing long-term income potential. This approach optimizes cash flow by minimizing Social Security's early claim penalties and increasing delayed benefit amounts, enhancing overall retirement income security.
Sidecar Savings Account
Sidecar Savings Accounts provide a flexible, tax-efficient supplement to Social Security income, allowing retirees to access funds without penalties before age 59 1/2. This approach enhances financial security by creating a diversified retirement income stream, reducing reliance on Social Security alone.
Earned Income Offset
Social Security benefits are subject to the Earned Income Offset, which reduces payments when retirees earn income above certain thresholds, potentially limiting cash flow. Sidecar Savings accounts provide flexible withdrawal options without income restrictions, making them a valuable complement to Social Security for managing retirement income streams.
Longevity Insurance Sidecar
The Longevity Insurance Sidecar provides a strategic supplement to Social Security by offering a guaranteed income stream that activates at advanced ages, addressing the risk of outliving traditional benefits. This approach enhances retirement security by combining the predictable baseline of Social Security with the flexibility and longevity protection of a Sidecar savings vehicle.
Delayed Claiming Optimization
Delaying Social Security benefits increases monthly payments by up to 8% per year, maximizing guaranteed lifetime income and reducing longevity risk. Sidecar savings provide flexible, tax-advantaged supplemental income, allowing for strategic withdrawals while optimizing Social Security's delayed claiming strategy.
Supplemental Pension Laddering
Social Security provides a guaranteed lifelong income stream indexed to inflation, serving as a foundational base for retirement stability, while Sidecar Savings offer flexible supplemental funds that can be strategically laddered to cover expenses during market downturns or unexpected costs. This Supplemental Pension Laddering approach enhances income diversification, reduces longevity risk, and optimizes tax efficiency by timing withdrawals from taxable, tax-deferred, and tax-free accounts alongside Social Security benefits.
Roth Sidecar Conversion
Roth Sidecar Conversions enhance retirement income streams by allowing tax-free growth and withdrawals, complementing Social Security benefits which are taxable and subject to indexing. Utilizing Roth conversions strategically can reduce future tax liabilities, providing a more flexible and efficient distribution strategy alongside guaranteed Social Security payments.
Income Floor Stacking
Income floor stacking combines guaranteed Social Security benefits with sidecar savings accounts to create a reliable, diversified retirement income stream. This strategy enhances financial security by layering a stable foundation of Social Security with flexible, tax-efficient withdrawals from supplemental savings.
Asset Segmentation Buckets
Social Security provides a guaranteed, inflation-adjusted income stream essential for meeting basic retirement expenses, while Sidecar Savings in segmented asset buckets offer flexibility and growth potential to cover discretionary costs and market fluctuations. This asset segmentation strategy balances the stability of Social Security with the personalized management of side savings, optimizing income diversification and risk mitigation in retirement planning.
Hybrid Drawdown Model
The Hybrid Drawdown Model combines guaranteed Social Security benefits with flexible Sidecar Savings, optimizing retirement income stability and growth potential by balancing predictable payouts and adjustable withdrawals. This approach leverages Social Security's inflation-protected lifetime income alongside tax-efficient sidecar accounts, enhancing financial resilience against market volatility and longevity risk.
Social Security vs Sidecar Savings for retirement income streams. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com