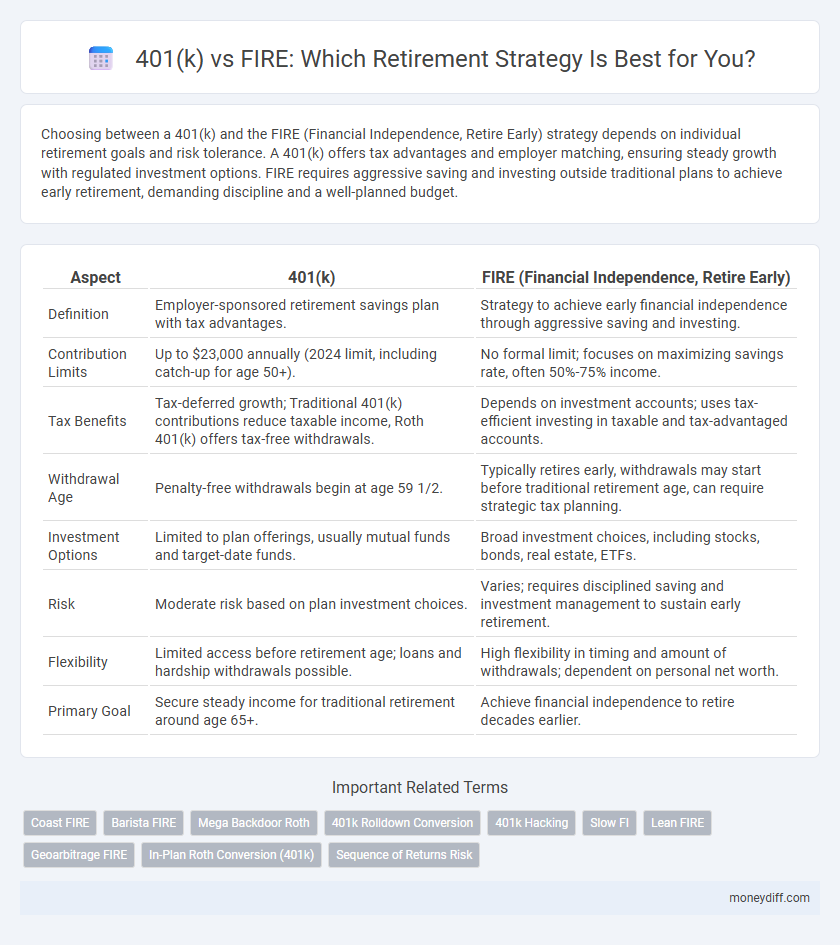
Choosing between a 401(k) and the FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) strategy depends on individual retirement goals and risk tolerance. A 401(k) offers tax advantages and employer matching, ensuring steady growth with regulated investment options. FIRE requires aggressive saving and investing outside traditional plans to achieve early retirement, demanding discipline and a well-planned budget.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | 401(k) | FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employer-sponsored retirement savings plan with tax advantages. | Strategy to achieve early financial independence through aggressive saving and investing. |
| Contribution Limits | Up to $23,000 annually (2024 limit, including catch-up for age 50+). | No formal limit; focuses on maximizing savings rate, often 50%-75% income. |
| Tax Benefits | Tax-deferred growth; Traditional 401(k) contributions reduce taxable income, Roth 401(k) offers tax-free withdrawals. | Depends on investment accounts; uses tax-efficient investing in taxable and tax-advantaged accounts. |
| Withdrawal Age | Penalty-free withdrawals begin at age 59 1/2. | Typically retires early, withdrawals may start before traditional retirement age, can require strategic tax planning. |
| Investment Options | Limited to plan offerings, usually mutual funds and target-date funds. | Broad investment choices, including stocks, bonds, real estate, ETFs. |
| Risk | Moderate risk based on plan investment choices. | Varies; requires disciplined saving and investment management to sustain early retirement. |
| Flexibility | Limited access before retirement age; loans and hardship withdrawals possible. | High flexibility in timing and amount of withdrawals; dependent on personal net worth. |
| Primary Goal | Secure steady income for traditional retirement around age 65+. | Achieve financial independence to retire decades earlier. |
Understanding 401(k) Plans: Basics and Benefits
401(k) plans are employer-sponsored retirement savings accounts allowing employees to contribute pre-tax income, reducing taxable income while growing investments tax-deferred. Contributions often include employer matching, maximizing savings potential and accelerating wealth accumulation. Understanding 401(k) benefits like automatic payroll deductions, diverse investment options, and compound growth is essential for effective retirement planning compared to pursuing FIRE strategies.
What is the FIRE Movement? Key Principles Explained
The FIRE movement, standing for Financial Independence, Retire Early, emphasizes aggressive saving and investing to achieve early retirement, often decades ahead of traditional timelines. Key principles include maximizing savings rates, reducing expenses, and prioritizing investment in low-cost index funds to build a sustainable passive income. Unlike conventional 401(k) plans tied to employer-sponsored retirement accounts, FIRE advocates for financial freedom through diverse income streams and rigorous financial discipline.
401(k) vs. FIRE: Core Differences in Retirement Strategies
401(k) plans emphasize structured, tax-advantaged savings with employer matching and gradual withdrawals post-retirement, focusing on long-term wealth accumulation within traditional financial frameworks. FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) prioritizes aggressive saving and investing strategies to achieve early retirement, often relying on higher savings rates and more flexible withdrawal timelines. Both strategies demand disciplined financial planning; however, 401(k) focuses on steady growth and risk management while FIRE centers on rapid asset accumulation and lifestyle adjustment.
Tax Advantages: 401(k) Accounts vs. FIRE Approaches
401(k) accounts offer significant tax advantages through pre-tax contributions, tax-deferred growth, and potential employer matching, which collectively enhance retirement savings efficiency. In contrast, FIRE strategies prioritize aggressive savings and early investment, often utilizing tax-advantaged accounts like Roth IRAs and HSAs for tax-free growth and withdrawals. Understanding the distinct tax benefits of 401(k) plans versus diversified FIRE investment vehicles helps optimize long-term retirement income and tax planning.
Contribution Limits and Withdrawal Rules Compared
401(k) plans have annual contribution limits set by the IRS, currently $22,500 for individuals under 50 and $30,000 for those 50 and older, allowing tax-deferred growth until withdrawals begin after age 59 1/2, with penalties for early withdrawal. The FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) strategy prioritizes aggressive saving and investing beyond traditional retirement accounts, often utilizing taxable brokerage accounts where no contribution limits apply but capital gains taxes may affect withdrawal flexibility. Understanding the strict regulatory withdrawal rules of 401(k)s versus the flexible but tax-exposed access in FIRE strategies is critical for optimizing retirement fund availability and minimizing penalties.
Risk Management: Traditional 401(k) vs. Aggressive FIRE Investing
Traditional 401(k) plans offer a balanced risk management approach with diversified portfolios and employer matching contributions, providing a safer, more predictable retirement accumulation. In contrast, FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) strategies often rely on aggressive investing in stocks and alternative assets, which can yield higher returns but come with increased market volatility and potential for significant losses. Evaluating personal risk tolerance and financial goals is essential to choose between the stability of a 401(k) and the high-risk, high-reward nature of FIRE investing.
Flexibility and Accessibility: Drawing Funds in Both Paths
401(k) plans generally impose restrictions and penalties on early withdrawals before age 59 1/2, limiting flexibility in accessing retirement funds. FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) strategies prioritize building accessible investment portfolios and taxable accounts, enabling earlier and penalty-free fund usage. The FIRE approach offers greater control over asset allocation and withdrawal timing compared to traditional 401(k) constraints.
Timeline to Retirement: 401(k) Planning vs. FIRE Acceleration
401(k) planning typically targets retirement at the traditional age of 59 1/2 or later, allowing for steady contributions and tax advantages. FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) aims to accelerate financial freedom, often enabling retirement decades earlier by maximizing savings rates and investment returns. The timeline difference hinges on contribution intensity, investment strategy, and lifestyle choices, with FIRE requiring more aggressive financial discipline to retire before typical 401(k) milestones.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Living with 401(k) vs. FIRE Philosophy
Living with a 401(k) often involves a traditional work-life balance, requiring continued employment until reaching retirement age to maximize contributions and benefits. The FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) philosophy demands significant lifestyle adjustments, prioritizing aggressive saving, frugality, and alternative income streams to achieve early financial independence. These contrasting approaches impact daily spending habits, risk tolerance, and long-term financial planning strategies.
Which is Right for You: 401(k), FIRE, or a Hybrid Approach?
Choosing between a 401(k), FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early), or a hybrid approach depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and lifestyle preferences. A 401(k) offers tax advantages and employer matching, ideal for steady, long-term growth and secure retirement planning. The FIRE strategy emphasizes aggressive saving and investing to retire early, while a hybrid approach balances consistent retirement contributions with early wealth accumulation for flexibility.
Related Important Terms
Coast FIRE
Coast FIRE emphasizes building a solid 401(k) balance early, allowing investments to grow passively without further contributions, contrasting with traditional FIRE's aggressive savings and early retirement plans. Leveraging compound interest in a well-managed 401(k) can secure financial independence, enabling individuals to retire comfortably without continuous income streams.
Barista FIRE
Barista FIRE combines part-time work with a 401k to maintain healthcare benefits while gradually building retirement savings, offering a flexible alternative to full financial independence. This strategy leverages steady income and employer contributions to optimize 401k growth, reducing the need to fully rely on early retirement funds.
Mega Backdoor Roth
The Mega Backdoor Roth strategy enhances 401(k) plans by allowing after-tax contributions up to $66,000 annually (2024 limit), enabling high earners to maximize tax-free retirement growth beyond standard Roth IRA limits. This approach complements FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) goals by accelerating tax-advantaged savings, providing greater flexibility and compounded gains before early retirement.
401k Rolldown Conversion
401k rolldown conversion allows individuals to strategically transfer accumulated 401k funds into more flexible accounts, enhancing tax efficiency and liquidity during retirement. This method contrasts with FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) strategies by prioritizing structured, tax-advantaged growth over accelerated withdrawal plans.
401k Hacking
Maximizing retirement savings through 401k hacking involves strategically contributing to employer-sponsored plans to leverage tax advantages and compound growth, outperforming traditional retirement methods. This approach accelerates wealth accumulation compared to FIRE strategies by enabling higher investment limits, employer matching, and tax-deferred growth within the 401k framework.
Slow FI
Slow FI emphasizes steady, long-term growth through consistent 401k contributions, leveraging compound interest and employer matching to build wealth gradually. Unlike aggressive FIRE strategies, Slow FI prioritizes financial security and lifestyle balance, making retirement achievable without drastic lifestyle changes.
Lean FIRE
Lean FIRE emphasizes retiring early with a minimalist lifestyle by maintaining low annual expenses, optimizing 401(k) contributions, and strategically investing to achieve consistent withdrawal rates below 4%. This approach contrasts with traditional 401(k) saving by prioritizing aggressive cost-cutting and flexible income streams to extend financial independence at a lower savings threshold.
Geoarbitrage FIRE
Geoarbitrage FIRE leverages location-independent income and lower cost of living to accelerate retirement beyond traditional 401(k) limits by maximizing purchasing power in affordable regions. Unlike 401(k) plans with tax-deferred growth and contribution caps, Geoarbitrage FIRE strategies emphasize financial independence through strategic geographic relocation and diversified income streams.
In-Plan Roth Conversion (401k)
In-plan Roth conversions within a 401(k) allow individuals to convert pre-tax savings into after-tax Roth funds, enabling tax-free growth and withdrawals during retirement, which can complement FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) strategies by providing tax diversification and greater control over tax liabilities. This approach enhances flexibility in managing retirement income streams and can optimize long-term tax efficiency compared to traditional 401(k) withdrawals.
Sequence of Returns Risk
Sequence of Returns Risk significantly impacts both 401k and FIRE strategies, as early negative market returns can deplete retirement savings faster in FIRE due to early withdrawals. While 401k plans benefit from structured contributions and potential employer matching, FIRE requires careful withdrawal sequencing to mitigate risk and sustain long-term portfolio growth.
401k vs FIRE for retirement. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com