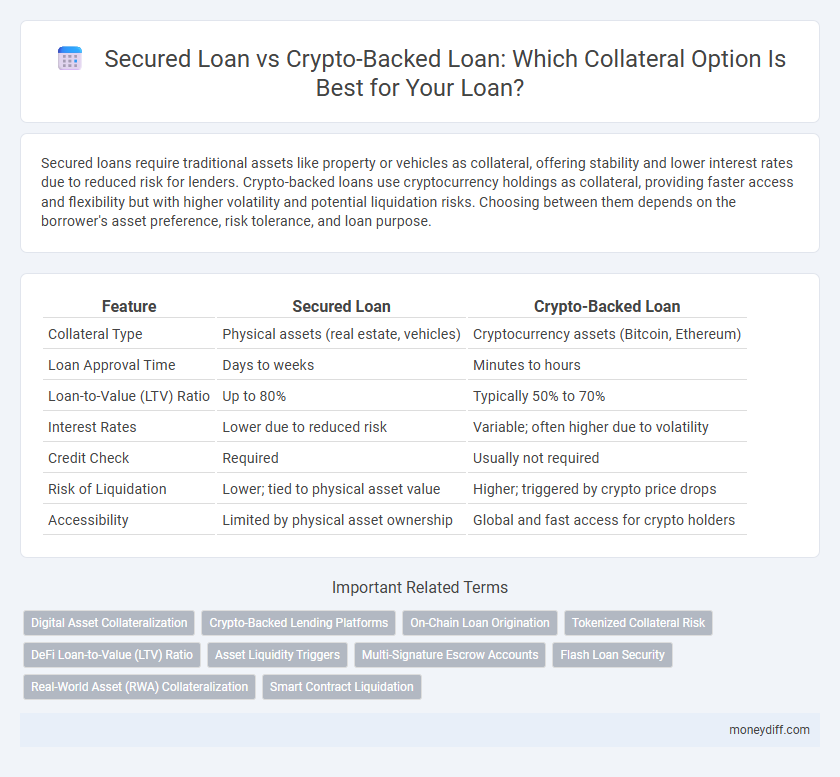
Secured loans require traditional assets like property or vehicles as collateral, offering stability and lower interest rates due to reduced risk for lenders. Crypto-backed loans use cryptocurrency holdings as collateral, providing faster access and flexibility but with higher volatility and potential liquidation risks. Choosing between them depends on the borrower's asset preference, risk tolerance, and loan purpose.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Secured Loan | Crypto-Backed Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Collateral Type | Physical assets (real estate, vehicles) | Cryptocurrency assets (Bitcoin, Ethereum) |
| Loan Approval Time | Days to weeks | Minutes to hours |
| Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio | Up to 80% | Typically 50% to 70% |
| Interest Rates | Lower due to reduced risk | Variable; often higher due to volatility |
| Credit Check | Required | Usually not required |
| Risk of Liquidation | Lower; tied to physical asset value | Higher; triggered by crypto price drops |
| Accessibility | Limited by physical asset ownership | Global and fast access for crypto holders |
Understanding Secured Loans: Traditional Collateral Explained
Secured loans require borrowers to provide traditional collateral such as real estate, vehicles, or savings accounts to reduce lender risk and often secure lower interest rates. The value and liquidity of these tangible assets play a critical role in loan approval and terms, ensuring the lender can recover funds if the borrower defaults. Understanding the appraisal process and collateral requirements helps borrowers strategically leverage assets for favorable loan conditions.
What are Crypto-Backed Loans? A Modern Approach to Borrowing
Crypto-backed loans leverage digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum as collateral, offering borrowers quick access to liquidity without selling their cryptocurrencies. These loans typically feature lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans and maintain ownership of the crypto during the loan term, providing flexibility and potential for asset appreciation. Unlike traditional secured loans that require physical assets or credit checks, crypto-backed loans use blockchain technology to enable transparent and efficient lending processes.
Types of Collateral: Physical Assets vs Digital Assets
Secured loans typically require physical assets such as real estate, vehicles, or savings accounts as collateral, offering lenders tangible security and often lower interest rates. Crypto-backed loans use digital assets like Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other cryptocurrencies as collateral, providing faster approval and access to funds but with higher volatility risk. The choice between physical assets and digital assets impacts loan terms, risk exposure, and asset liquidity in the lending process.
Loan Approval Process: Requirements and Eligibility
Secured loans require tangible assets such as real estate or vehicles as collateral, with loan approval heavily dependent on the borrower's credit score, income verification, and asset appraisal. Crypto-backed loans utilize digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum, prioritizing the value and volatility of the cryptocurrency held, often allowing faster approval without traditional credit checks. Eligibility for secured loans typically involves stringent financial documentation and stable credit history, whereas crypto-backed loans offer flexible requirements but demand sufficient crypto collateral to mitigate market risks.
Interest Rates Comparison: Secured vs Crypto-Backed Loans
Secured loans typically offer lower interest rates due to traditional collateral such as real estate or vehicles, which reduces lender risk. Crypto-backed loans often carry higher interest rates reflecting the volatility and regulatory uncertainty of digital assets used as collateral. Lenders price these risks into crypto-backed loan rates, making them less favorable compared to conventional secured loan interest rates.
Risk Factors: Asset Volatility and Repossession
Secured loans typically use stable physical assets like real estate or vehicles as collateral, reducing the risk of significant value fluctuations and easing the repossession process. Crypto-backed loans involve highly volatile digital assets, where rapid price drops can trigger immediate liquidation or margin calls, increasing borrower risk. The unpredictable nature of cryptocurrency values results in higher chances of collateral loss compared to traditional secured loans.
Loan Flexibility and Repayment Terms
Secured loans offer predictable repayment schedules and fixed terms, leveraging tangible assets like property or vehicles as collateral. Crypto-backed loans provide greater flexibility with options for varying loan-to-value ratios and adjustable repayment timelines, using digital assets such as Bitcoin or Ethereum. Borrowers benefit from faster approval and potential interest savings in crypto-backed loans but face market volatility risks impacting collateral value.
Security and Regulation: Protecting Your Assets
Secured loans rely on traditional assets like real estate or vehicles, offering strong regulatory protections and established legal frameworks that safeguard borrowers' collateral. Crypto-backed loans use digital assets as collateral, which introduces higher volatility and less regulatory clarity, increasing risks related to asset valuation and potential loss. Understanding the differences in security measures and regulatory oversight is crucial for protecting your assets in either loan option.
Accessibility: Who Can Apply for Each Loan Type?
Secured loans typically require traditional collateral such as property or vehicles, making them accessible primarily to borrowers with tangible assets and established credit histories. Crypto-backed loans allow access to funds by using digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum as collateral, expanding opportunities to individuals active in the cryptocurrency market without the need for conventional credit checks. This difference in collateral type broadens accessibility for crypto holders, while secured loans remain tied to more conventional borrowing criteria.
Choosing the Right Loan: Key Considerations for Borrowers
When choosing between secured loans and crypto-backed loans, borrowers must evaluate the stability and volatility of their collateral, as traditional assets like real estate offer lower risk compared to fluctuating cryptocurrency values. Interest rates and loan terms vary significantly; secured loans often feature fixed rates and longer repayment periods, while crypto-backed loans may offer faster access but with higher risk and margin calls. Understanding credit requirements and potential liquidation scenarios is crucial to ensure the chosen loan aligns with financial goals and risk tolerance.
Related Important Terms
Digital Asset Collateralization
Secured loans traditionally rely on tangible assets like real estate or vehicles as collateral, whereas crypto-backed loans utilize digital assets such as Bitcoin or Ethereum to secure borrowing, offering faster access and reduced paperwork. Digital asset collateralization introduces enhanced liquidity and flexibility, although it comes with volatility risks that require careful valuation and risk management strategies.
Crypto-Backed Lending Platforms
Crypto-backed lending platforms enable borrowers to use digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum as collateral, offering faster approval and flexible terms compared to traditional secured loans backed by physical assets. These platforms leverage blockchain technology to provide transparent, secure, and decentralized loan services, reducing reliance on credit checks and expanding access to liquidity for crypto holders.
On-Chain Loan Origination
On-chain loan origination leverages blockchain technology to facilitate transparent, automated processing of secured loans and crypto-backed loans, ensuring collateral verification and smart contract enforcement without intermediaries. Unlike traditional secured loans that rely on physical assets, crypto-backed loans utilize digital assets as collateral, enabling faster approval and reduced counterparty risk through real-time on-chain data validation.
Tokenized Collateral Risk
Tokenized collateral in crypto-backed loans introduces unique risks such as market volatility, smart contract vulnerabilities, and regulatory uncertainties, which can lead to rapid collateral value fluctuations and potential liquidation. Traditional secured loans use tangible assets with more stable valuation, reducing exposure to sudden collateral devaluation compared to digital tokens.
DeFi Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio
Secured loans traditionally offer lower Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratios ranging from 50% to 80%, reducing lender risk by backing loans with stable collateral like real estate or vehicles. Crypto-backed loans in DeFi can reach LTV ratios up to 70%, leveraging volatile digital assets whose value fluctuations necessitate over-collateralization to maintain loan security.
Asset Liquidity Triggers
Secured loans rely on traditional assets like real estate or vehicles with predictable liquidity triggers based on market demand and appraisal values, ensuring more stable collateral liquidation in default scenarios. In contrast, crypto-backed loans face high volatility in asset liquidity triggers due to fluctuating cryptocurrency prices and limited market depth, increasing the risk of swift collateral devaluation during margin calls.
Multi-Signature Escrow Accounts
Multi-signature escrow accounts enhance security in secured loans by requiring multiple approvals before funds are released, reducing the risk of fraud or misuse. In crypto-backed loans, these accounts enable decentralized control over collateral, ensuring transparent and tamper-proof management of digital assets.
Flash Loan Security
Secured loans rely on traditional assets like property or vehicles as collateral, offering stable security but slower access to funds; crypto-backed loans use digital assets, enabling faster transactions but increasing risks due to market volatility. Flash loan security emphasizes instant, permissionless borrowing within a single blockchain transaction, demanding robust smart contract safeguards to prevent exploitation and ensure collateral integrity.
Real-World Asset (RWA) Collateralization
Secured loans typically rely on real-world asset (RWA) collateralization such as property, vehicles, or cash deposits, offering lower risk and stable valuation for lenders. Crypto-backed loans use digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum as collateral, which can provide faster approval but involve higher volatility and regulatory uncertainty compared to traditional RWA collateral.
Smart Contract Liquidation
Smart contract liquidation in crypto-backed loans provides automated, transparent enforcement of collateral terms, minimizing default risk and enabling instant asset seizure upon breach. In contrast, secured loans rely on traditional legal processes for collateral liquidation, which are often slower, less efficient, and subject to jurisdictional delays.
Secured Loan vs Crypto-Backed Loan for collateral. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com