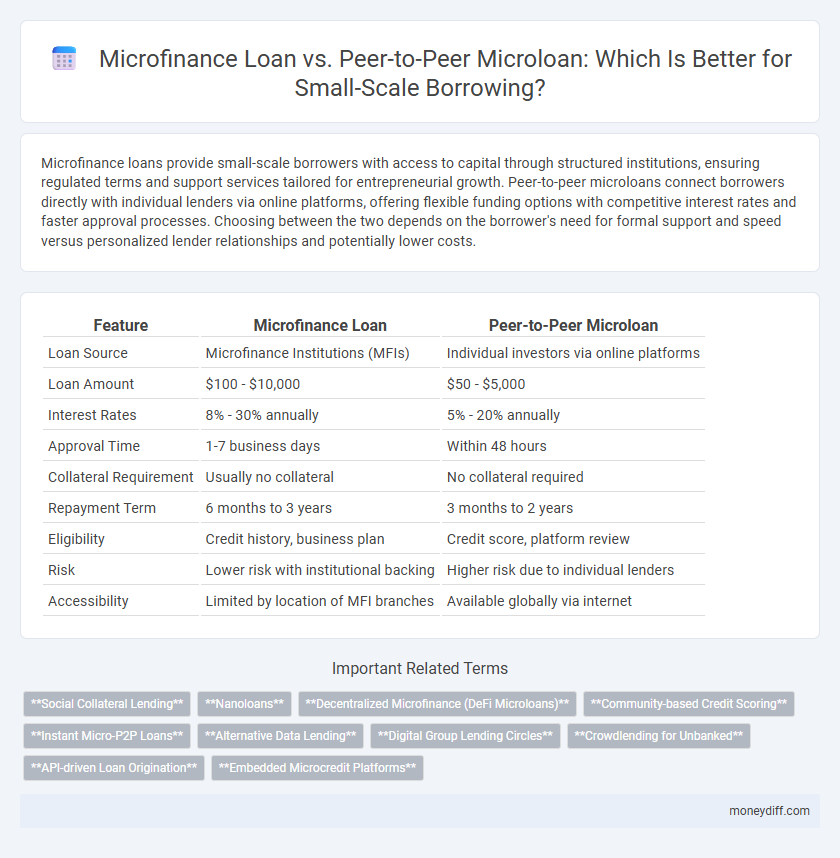
Microfinance loans provide small-scale borrowers with access to capital through structured institutions, ensuring regulated terms and support services tailored for entrepreneurial growth. Peer-to-peer microloans connect borrowers directly with individual lenders via online platforms, offering flexible funding options with competitive interest rates and faster approval processes. Choosing between the two depends on the borrower's need for formal support and speed versus personalized lender relationships and potentially lower costs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Microfinance Loan | Peer-to-Peer Microloan |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Source | Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) | Individual investors via online platforms |
| Loan Amount | $100 - $10,000 | $50 - $5,000 |
| Interest Rates | 8% - 30% annually | 5% - 20% annually |
| Approval Time | 1-7 business days | Within 48 hours |
| Collateral Requirement | Usually no collateral | No collateral required |
| Repayment Term | 6 months to 3 years | 3 months to 2 years |
| Eligibility | Credit history, business plan | Credit score, platform review |
| Risk | Lower risk with institutional backing | Higher risk due to individual lenders |
| Accessibility | Limited by location of MFI branches | Available globally via internet |
Understanding Microfinance Loans: An Overview
Microfinance loans provide small-scale borrowers with access to capital through regulated financial institutions aimed at fostering entrepreneurship and financial inclusion, often featuring fixed interest rates and repayment plans. Peer-to-peer microloans connect borrowers directly with individual lenders via online platforms, offering flexible terms and potentially lower costs but with varying risk levels due to less regulatory oversight. Both lending models address the funding needs of small businesses and entrepreneurs, yet differ in structure, accessibility, and risk management approaches.
What Are Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Microloans?
Peer-to-peer (P2P) microloans are small-scale loans provided directly by individual lenders to borrowers through online platforms, bypassing traditional financial institutions. These loans offer flexible terms and lower interest rates, making them accessible for small-scale entrepreneurs and individuals in underserved markets. P2P microloans leverage digital technology to facilitate transparent transactions and connect borrowers with a diversified pool of lenders globally.
Key Differences Between Microfinance and P2P Microloans
Microfinance loans are typically provided by regulated financial institutions aiming to support underserved small-scale borrowers through structured lending programs, while peer-to-peer (P2P) microloans connect individual lenders directly with borrowers via online platforms, offering more flexible terms. Interest rates in microfinance loans may be higher due to operational costs and risk management, whereas P2P microloans often feature competitive rates driven by lender competition. Credit evaluation in microfinance institutions relies on comprehensive assessments, whereas P2P platforms use alternative data and social underpinnings to assess borrower creditworthiness.
Eligibility Criteria: Microfinance Loan vs P2P Microloan
Microfinance loan eligibility often requires borrowers to demonstrate stable income, group membership, or collateral, targeting low-income individuals with limited access to traditional banking. Peer-to-peer (P2P) microloan platforms typically assess credit scores, social reputation, and repayment history, offering more flexible criteria that appeal to small-scale entrepreneurs or freelancers. Differences in eligibility reflect the distinct risk assessment models, with microfinance lenders prioritizing community trust and P2P lenders relying on digital credit evaluation tools.
Application Process: Simplifying Borrowing Steps
Microfinance loans streamline the application process by involving local institutions that often require minimal paperwork and prioritize borrower relationships. Peer-to-peer microloans utilize online platforms to connect lenders directly with borrowers, offering a fully digital application with quick approval times. Both methods simplify borrowing steps but differ in accessibility and procedural formalities.
Interest Rates and Fees: Comparing Loan Costs
Microfinance loans typically offer lower interest rates and more transparent fee structures compared to peer-to-peer microloans, which can have variable rates influenced by individual lenders. Borrowers in microfinance institutions often benefit from subsidized rates and minimal processing fees designed to support small-scale entrepreneurs. Peer-to-peer microloans may entail higher overall costs due to platform fees and the risk premiums set by private investors.
Risk Factors for Small-Scale Borrowers
Microfinance loans typically involve formal institutions with established credit assessment processes, reducing default risk for small-scale borrowers through structured repayment schedules. Peer-to-peer microloans, while offering access to diverse funding sources, carry higher risk due to limited regulatory oversight and variable lender experience. Small-scale borrowers face increased vulnerability to fluctuating interest rates and potential misalignment of loan terms in peer-to-peer platforms compared to the more stable microfinance institutions.
Accessibility and Reach in Underserved Communities
Microfinance loans offer greater accessibility in underserved communities by leveraging established local institutions and tailored financial products designed for low-income borrowers. Peer-to-peer microloans expand reach by connecting individual lenders and borrowers through online platforms, overcoming traditional banking barriers and enabling widespread participation. Both models enhance financial inclusion, but microfinance institutions often provide deeper community engagement and support services crucial for small-scale entrepreneurs.
Impact on Financial Inclusion and Empowerment
Microfinance loans provide structured financial support through institutions targeting underserved small-scale borrowers, significantly improving access to credit and fostering financial inclusion in marginalized communities. Peer-to-peer microloans leverage digital platforms to connect individual lenders and borrowers, enhancing empowerment by offering personalized terms and faster access to funds without traditional banking barriers. Both models contribute to economic empowerment, but peer-to-peer microloans often accelerate inclusion by reducing underwriting constraints and enabling diverse borrower profiles to obtain capital.
Choosing the Right Microloan Option for Your Needs
Microfinance loans offer structured lending through financial institutions with established interest rates and repayment terms, ideal for small-scale borrowers seeking reliability and regulatory oversight. Peer-to-peer microloans connect borrowers directly with individual lenders on digital platforms, providing more flexible terms and potentially lower rates but with varying risk levels. Evaluating factors like loan amount, interest rates, repayment schedules, and platform reputation is essential to choose the microloan that best aligns with your financial needs and repayment capacity.
Related Important Terms
Social Collateral Lending
Social collateral lending in microfinance loans leverages community trust and social networks to reduce default risk, enabling small-scale borrowers without traditional credit history to access funds. Peer-to-peer microloans utilize similar social collateral principles by connecting individual lenders and borrowers directly through online platforms, fostering accountability and repayment through shared social reputations.
Nanoloans
Nanoloans offer a distinct advantage in small-scale borrowing by providing ultra-small loan amounts through microfinance institutions, tailored for immediate, low-risk needs. Peer-to-peer microloans facilitate direct lender-borrower connections, often resulting in flexible terms and competitive interest rates, but Nanoloans prioritize speed and accessibility for underserved individuals.
Decentralized Microfinance (DeFi Microloans)
Decentralized microfinance (DeFi microloans) leverages blockchain technology to offer transparent, secure, and accessible lending without traditional intermediaries, enabling small-scale borrowers to access funds with lower fees and faster approval times compared to conventional microfinance loans. Peer-to-peer microloans on decentralized platforms facilitate direct connections between lenders and borrowers, enhancing financial inclusion while reducing reliance on centralized financial institutions and improving trust through smart contracts.
Community-based Credit Scoring
Community-based credit scoring in microfinance loans leverages local knowledge and social networks to assess borrower reliability, reducing default risks through peer accountability. Peer-to-peer microloans utilize decentralized platforms where creditworthiness is evaluated via community feedback and transaction history, enabling small-scale borrowers to access funds without traditional financial institution barriers.
Instant Micro-P2P Loans
Instant Micro-P2P loans leverage real-time digital platforms to connect small-scale borrowers directly with individual lenders, offering faster approval and fund disbursement compared to traditional microfinance loan processes. This seamless peer-to-peer lending model reduces bureaucratic delays and often provides more flexible terms tailored to the immediate needs of micro-entrepreneurs.
Alternative Data Lending
Microfinance loans leverage alternative data such as transaction history and social behavior to assess creditworthiness for small-scale borrowers without traditional credit scores. Peer-to-peer microloans also utilize alternative data but emphasize real-time social network analysis and digital footprints to connect individual lenders directly with micro-entrepreneurs.
Digital Group Lending Circles
Digital Group Lending Circles leverage technology to facilitate peer-to-peer microloans, enabling small-scale borrowers to access funds collaboratively without conventional credit checks. This model enhances financial inclusion by promoting trust-based lending within digital communities, often offering lower interest rates and increased repayment flexibility compared to traditional microfinance loans.
Crowdlending for Unbanked
Crowdlending for unbanked individuals provides an alternative to traditional microfinance loans by connecting small-scale borrowers directly with peer investors through online platforms, bypassing conventional banking infrastructure. This model enhances financial inclusion by offering more flexible terms, quicker access to funds, and fostering community-driven support for underserved populations.
API-driven Loan Origination
API-driven loan origination streamlines both microfinance loans and peer-to-peer microloans by enabling real-time credit assessments, automated underwriting, and seamless integration with financial platforms. This technology enhances efficiency, reduces loan processing time, and improves borrower experience for small-scale borrowing.
Embedded Microcredit Platforms
Embedded microcredit platforms integrate microfinance loans directly into digital ecosystems, enabling small-scale borrowing with streamlined access to funds through trusted service providers. Peer-to-peer microloans on these platforms leverage community lending networks, reducing reliance on traditional intermediaries and fostering quicker, more flexible microcredit solutions.
Microfinance Loan vs Peer-to-Peer Microloan for small-scale borrowing. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com