Microfinance loans offer small-scale borrowers structured repayment plans and often include financial education, making them ideal for individuals seeking stability and support. Peer-to-peer lending provides a more flexible borrowing option with potentially lower interest rates by connecting borrowers directly with investors. Choosing between microfinance loans and peer-to-peer lending depends on the borrower's need for personalized assistance versus access to a wider pool of lenders.
Table of Comparison
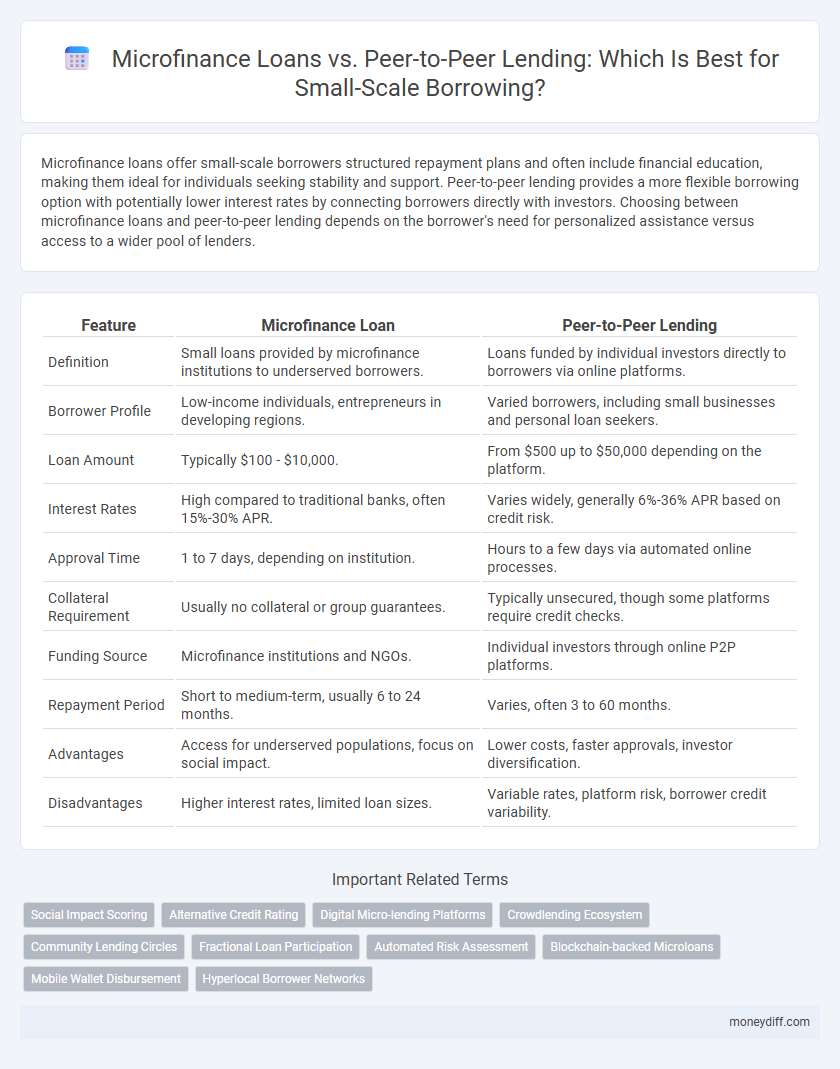
| Feature | Microfinance Loan | Peer-to-Peer Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small loans provided by microfinance institutions to underserved borrowers. | Loans funded by individual investors directly to borrowers via online platforms. |
| Borrower Profile | Low-income individuals, entrepreneurs in developing regions. | Varied borrowers, including small businesses and personal loan seekers. |
| Loan Amount | Typically $100 - $10,000. | From $500 up to $50,000 depending on the platform. |
| Interest Rates | High compared to traditional banks, often 15%-30% APR. | Varies widely, generally 6%-36% APR based on credit risk. |
| Approval Time | 1 to 7 days, depending on institution. | Hours to a few days via automated online processes. |
| Collateral Requirement | Usually no collateral or group guarantees. | Typically unsecured, though some platforms require credit checks. |
| Funding Source | Microfinance institutions and NGOs. | Individual investors through online P2P platforms. |
| Repayment Period | Short to medium-term, usually 6 to 24 months. | Varies, often 3 to 60 months. |
| Advantages | Access for underserved populations, focus on social impact. | Lower costs, faster approvals, investor diversification. |
| Disadvantages | Higher interest rates, limited loan sizes. | Variable rates, platform risk, borrower credit variability. |
Understanding Microfinance Loans: A Quick Overview
Microfinance loans provide small-scale borrowers with accessible credit through institutions specializing in underserved communities, often accompanied by financial literacy support and lower interest rates compared to traditional loans. These loans focus on empowering entrepreneurs in developing regions by offering flexible repayment terms and group-based lending models that reduce default risk. Key players include organizations like Grameen Bank and Kiva, which prioritize social impact alongside financial returns.
What is Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending?
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending is a financial technology platform that connects individual borrowers directly with investors, bypassing traditional banks. This method enables small-scale borrowing through online marketplaces where loans are funded by multiple lenders, often resulting in lower interest rates and faster approval compared to microfinance loans. P2P lending platforms use credit scoring algorithms to assess borrower risk, enhancing transparency and accessibility for underbanked populations.
Key Differences Between Microfinance Loans and P2P Lending
Microfinance loans are typically provided by specialized financial institutions focused on offering small loans to underserved populations, often including support and financial education alongside lending. Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms connect individual borrowers directly with investors through an online marketplace, enabling faster access to funds but usually with higher interest rates and less regulatory oversight. Key differences include the source of funds, borrower eligibility criteria, loan terms, and risk management practices, with microfinance institutions emphasizing social impact and P2P lenders prioritizing efficiency and scalability.
Eligibility Criteria for Small-Scale Borrowers
Microfinance loans typically require borrowers to have a proven small business or income source and often emphasize group guarantees or community-based eligibility criteria, making them accessible to low-income entrepreneurs. Peer-to-peer lending platforms usually assess individual credit scores, digital identity verification, and repayment history, catering to small-scale borrowers with decent creditworthiness. Both options prioritize financial inclusion but differ in their approach to assessing risk and borrower eligibility.
Application Process: Microfinance vs P2P Lending
Microfinance loan applications typically require detailed financial documentation and in-person verification, catering to borrowers with limited credit history. Peer-to-peer lending platforms streamline the process through online applications, automated credit assessments, and faster approval times. Small-scale borrowers often find P2P lending more accessible due to its digital approach and lower barriers to entry.
Interest Rates and Repayment Terms Compared
Microfinance loans typically offer lower interest rates compared to peer-to-peer lending platforms, making them more affordable for small-scale borrowers seeking manageable monthly payments. Repayment terms for microfinance loans tend to be more flexible with longer durations, often ranging from six months to two years, allowing borrowers to spread out their repayments comfortably. Peer-to-peer lending usually involves shorter repayment periods and slightly higher interest rates due to individual lender risk, but it provides quicker access to funds for urgent financial needs.
Risks and Benefits of Microfinance Loans
Microfinance loans provide small-scale borrowers with accessible credit through regulated institutions, offering benefits such as lower interest rates and tailored financial education aimed at reducing default risks. Risks include limited loan amounts, potential over-indebtedness, and the stringent eligibility criteria that may exclude the most vulnerable borrowers. Unlike peer-to-peer lending, microfinance loans emphasize social impact and community development, often supported by government or NGO backing to enhance borrower support and repayment stability.
Risks and Benefits of P2P Lending
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending offers small-scale borrowers lower interest rates and faster access to funds compared to traditional microfinance loans, enhancing financial inclusion. However, risks include limited regulatory oversight, potential for higher default rates, and less protection for both lenders and borrowers. The decentralized structure of P2P platforms facilitates direct transactions but requires diligent credit assessment and platform reliability to mitigate financial losses.
Which Option Suits Small-Scale Entrepreneurs Best?
Microfinance loans offer small-scale entrepreneurs access to capital through regulated institutions with structured repayment plans and financial literacy support, making them ideal for those seeking stable, long-term funding. Peer-to-peer lending provides faster access to funds via online platforms by connecting borrowers directly with individual investors, appealing to entrepreneurs needing quick and flexible financing without extensive collateral. Small-scale entrepreneurs prioritizing reliability and support often benefit more from microfinance loans, while those valuing speed and ease might prefer peer-to-peer lending.
Choosing the Right Loan: Practical Tips for Borrowers
Microfinance loans offer small-scale borrowers access to credit through regulated institutions with structured repayment plans, fostering financial inclusion and steady credit building. Peer-to-peer lending provides a platform for direct borrowing from individual investors, often featuring flexible terms and competitive interest rates tailored to unique borrower profiles. Assess interest rates, repayment flexibility, approval speed, and eligibility criteria to select the optimal loan type that aligns with your financial needs and repayment capacity.
Related Important Terms
Social Impact Scoring
Microfinance loans utilize social impact scoring to assess borrowers' community involvement and repayment reliability, fostering financial inclusion for underserved populations. Peer-to-peer lending platforms incorporate social impact metrics to connect socially responsible investors with small-scale borrowers, enhancing transparency and promoting sustainable economic development.
Alternative Credit Rating
Microfinance loans leverage alternative credit rating methods by using qualitative data such as community reputation and cash flow history to assess creditworthiness, making them accessible for borrowers with limited formal credit records. Peer-to-peer lending platforms enhance credit evaluation through algorithm-driven alternative credit scoring models using social media data, transaction patterns, and behavioral analytics to offer personalized risk assessments for small-scale borrowers.
Digital Micro-lending Platforms
Digital micro-lending platforms revolutionize small-scale borrowing by providing rapid access to microfinance loans with flexible terms tailored to low-income borrowers, emphasizing financial inclusion and credit building. Peer-to-peer lending on these platforms connects individual investors directly with borrowers, often offering competitive interest rates and decentralized credit evaluation, enhancing transparency and reducing reliance on traditional banking institutions.
Crowdlending Ecosystem
Microfinance loans provide underbanked small-scale borrowers with access to capital through specialized institutions that emphasize social impact and financial inclusion. Peer-to-peer lending within the crowdlending ecosystem connects individual lenders directly to borrowers via online platforms, offering competitive interest rates and streamlined approval processes for microloans.
Community Lending Circles
Microfinance loans provide small-scale borrowers with access to capital through regulated institutions that often include financial education and support, while peer-to-peer lending connects individuals directly via online platforms, offering flexible terms but less community engagement. Community Lending Circles combine the strengths of both by fostering trust and mutual accountability among members, enabling collective borrowing and repayment without relying on traditional credit checks.
Fractional Loan Participation
Microfinance loans provide small-scale borrowers with access to credit through institutions targeting low-income individuals, whereas peer-to-peer lending enables fractional loan participation by allowing multiple investors to fund portions of a single loan, thereby diversifying risk. Fractional loan participation in peer-to-peer lending enhances liquidity and borrower access to capital by pooling resources from a distributed network of lenders.
Automated Risk Assessment
Microfinance loans utilize automated risk assessment algorithms that analyze borrower credit history and income data to determine eligibility and interest rates, enabling faster and more precise lending decisions for small-scale borrowers. Peer-to-peer lending platforms also employ automated risk scoring systems but combine social data and peer evaluations to assess borrower reliability, enhancing risk prediction accuracy in decentralized lending environments.
Blockchain-backed Microloans
Blockchain-backed microfinance loans offer enhanced transparency and security through decentralized ledgers, reducing fraud and lowering transaction costs for small-scale borrowers. Peer-to-peer lending, while providing direct access to funds, often lacks the robust verification and immutable record-keeping inherent in blockchain technology, making blockchain microloans a more reliable option for micro-entrepreneurs.
Mobile Wallet Disbursement
Microfinance loans provide small-scale borrowers access to credit through structured institutions utilizing mobile wallet disbursement for secure and efficient fund transfers. Peer-to-peer lending leverages digital platforms to connect borrowers directly with individual lenders, enabling rapid loan disbursement via mobile wallets and enhancing financial inclusion.
Hyperlocal Borrower Networks
Microfinance loans leverage established hyperlocal borrower networks to provide tailored financial support, enhancing trust and lower default risks within small-scale communities. Peer-to-peer lending platforms utilize digital networks to connect local borrowers with individual lenders, offering competitive rates and increased access to capital while maintaining community-level engagement.
Microfinance Loan vs Peer-to-Peer Lending for small-scale borrowing Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com