A fixed-rate loan offers stable monthly payments with a consistent interest rate throughout the loan term, providing predictability and ease of budgeting. Flexible-rate loans have variable interest rates that may fluctuate based on market conditions, potentially lowering initial payments but increasing financial risk over time. Choosing between fixed-rate and flexible-rate loans depends on your risk tolerance and preference for payment stability versus potential cost savings.
Table of Comparison
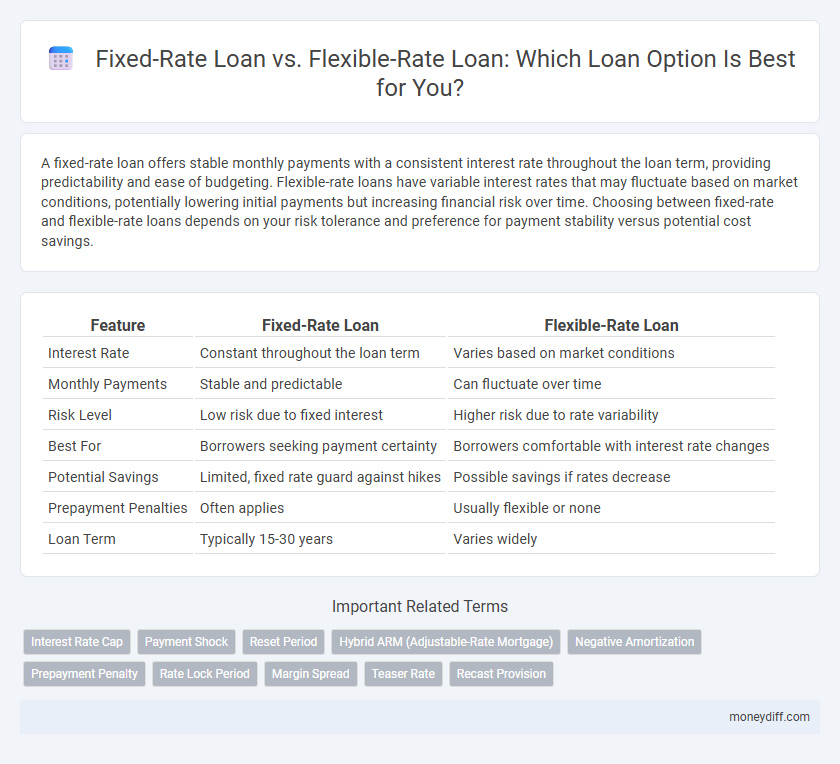
| Feature | Fixed-Rate Loan | Flexible-Rate Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Constant throughout the loan term | Varies based on market conditions |
| Monthly Payments | Stable and predictable | Can fluctuate over time |
| Risk Level | Low risk due to fixed interest | Higher risk due to rate variability |
| Best For | Borrowers seeking payment certainty | Borrowers comfortable with interest rate changes |
| Potential Savings | Limited, fixed rate guard against hikes | Possible savings if rates decrease |
| Prepayment Penalties | Often applies | Usually flexible or none |
| Loan Term | Typically 15-30 years | Varies widely |
Understanding Fixed-Rate Loans
Fixed-rate loans offer a consistent interest rate throughout the loan term, providing predictable monthly payments and protection against market fluctuations. Borrowers benefit from budgeting stability and long-term financial planning without concerns about rising interest rates. This loan type is ideal for individuals seeking certainty and fixed repayment amounts over the life of the loan.
Exploring Flexible-Rate Loans
Flexible-rate loans offer interest rates that adjust periodically based on market conditions, providing borrowers potential savings when rates decrease. These loans typically start with lower initial rates compared to fixed-rate loans, making them attractive for those anticipating short-term borrowing or fluctuating income. Understanding the terms of rate adjustments, caps, and index benchmarks is essential to managing the risks associated with flexible-rate loans.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Flexible Rates
Fixed-rate loans maintain a constant interest rate throughout the loan term, providing predictable monthly payments and shielding borrowers from market fluctuations. Flexible-rate loans, also known as variable or adjustable-rate loans, feature interest rates that can change periodically based on benchmark indices, potentially lowering initial payments but increasing financial uncertainty over time. Key differences include payment stability, interest rate risk, and adaptability to market conditions, influencing borrower choice based on financial goals and risk tolerance.
Pros and Cons of Fixed-Rate Loans
Fixed-rate loans offer the advantage of consistent monthly payments, providing predictability and protection against interest rate fluctuations, making budgeting easier for borrowers. However, their interest rates are typically higher than flexible-rate loans, potentially resulting in higher overall costs if market rates decrease. Borrowers seeking stability may prefer fixed-rate loans despite less flexibility and possible missed savings when rates drop.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Flexible-Rate Loans
Flexible-rate loans offer the advantage of potentially lower initial interest rates compared to fixed-rate loans, allowing borrowers to benefit from market rate decreases over time. However, the downside includes the risk of rising interest rates, which can increase monthly payments unpredictably, affecting budgeting and financial stability. Flexibility in repayment terms can also be a benefit, but it requires borrowers to stay vigilant about rate fluctuations and market conditions.
How Interest Rate Changes Impact Your Loan
Fixed-rate loans maintain a consistent interest rate throughout the loan term, providing predictable monthly payments and protection from market fluctuations. Flexible-rate loans, often tied to benchmark rates like the prime rate or LIBOR, can fluctuate over time, potentially lowering initial payments but increasing financial risk if interest rates rise. Understanding how interest rate changes impact your loan helps choose between stability with fixed rates or potential savings with flexible rates.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Loan Type
Choosing between a fixed-rate loan and a flexible-rate loan depends on interest rate stability, financial predictability, and risk tolerance. Fixed-rate loans offer consistent monthly payments, shielding borrowers from interest rate fluctuations, making them ideal for long-term budgeting. Flexible-rate loans can provide lower initial rates but carry the risk of future increases, requiring consideration of market trends and individual financial flexibility.
Budgeting with Fixed vs Flexible-Rate Loans
Fixed-rate loans provide predictable monthly payments, making it easier for borrowers to budget and plan long-term financial commitments without worrying about interest rate fluctuations. Flexible-rate loans, often linked to market interest rates like the LIBOR or prime rate, can result in varying monthly payments, potentially complicating budget stability but offering lower initial rates. Borrowers seeking consistent expenses typically prefer fixed-rate loans, while those comfortable with some risk may opt for flexible-rate loans to take advantage of possible rate decreases.
Long-Term Financial Impact of Loan Rate Types
Fixed-rate loans offer predictable monthly payments, protecting borrowers from interest rate fluctuations and facilitating long-term financial planning. Flexible-rate loans, often starting with lower initial rates, can lead to increased payments if market rates rise, potentially straining budgets over time. Evaluating the long-term impact of these loan types helps borrowers balance initial affordability with future financial stability.
Which Loan Type Suits Your Financial Goals?
Fixed-rate loans offer consistent monthly payments and protection against interest rate fluctuations, making them ideal for borrowers seeking budgeting stability and long-term financial predictability. Flexible-rate loans, often tied to benchmark interest rates, provide lower initial rates and potential savings if rates decrease, suiting those with variable incomes or short-term borrowing plans. Assess your risk tolerance, income stability, and loan duration to determine whether the security of fixed rates or the potential cost savings of flexible rates align better with your financial goals.
Related Important Terms
Interest Rate Cap
Fixed-rate loans offer a consistent interest rate throughout the loan term, providing predictable monthly payments and budgeting stability. Flexible-rate loans may have lower initial rates but include an interest rate cap that limits how much the rate can increase, protecting borrowers from significant payment spikes over time.
Payment Shock
Fixed-rate loans provide predictable monthly payments, reducing the risk of payment shock even if interest rates rise, while flexible-rate loans may start with lower payments but can cause significant payment shock when rates adjust upward. Borrowers seeking financial stability often prefer fixed-rate loans to avoid sudden increases in loan repayments.
Reset Period
Fixed-rate loans feature a consistent interest rate throughout the loan term, eliminating reset periods and ensuring predictable monthly payments. Flexible-rate loans include periodic reset periods where the interest rate adjusts based on market indices, potentially altering payment amounts and loan affordability.
Hybrid ARM (Adjustable-Rate Mortgage)
Hybrid ARMs combine the stability of fixed-rate loans with the adaptability of flexible-rate loans by offering a fixed interest rate for an initial period followed by adjustable rates. This structure allows borrowers to benefit from lower initial payments like fixed-rate loans while potentially saving money if interest rates decline during the adjustable period.
Negative Amortization
Fixed-rate loans maintain consistent monthly payments, preventing negative amortization by ensuring each payment covers both interest and principal. Flexible-rate loans can trigger negative amortization if payments fall below the interest accrued, causing the loan balance to increase over time.
Prepayment Penalty
Fixed-rate loans often include prepayment penalties to compensate lenders for lost interest revenue, limiting borrowers' ability to repay early without additional fees. Flexible-rate loans typically offer lower or no prepayment penalties, providing borrowers greater freedom to make early repayments and reduce overall interest costs.
Rate Lock Period
Fixed-rate loans offer a guaranteed interest rate throughout the entire loan term, providing stability and predictability in monthly payments. Flexible-rate loans feature a rate lock period that secures the interest rate for an initial timeframe before adjusting based on market fluctuations, potentially resulting in variable payment amounts.
Margin Spread
Fixed-rate loans maintain a consistent margin spread over the life of the loan, providing predictable monthly payments and shielding borrowers from market interest rate fluctuations. Flexible-rate loans feature a variable margin spread tied to benchmark rates, allowing adjustments that can lower or increase repayment amounts based on prevailing market conditions.
Teaser Rate
Fixed-rate loans maintain a consistent interest rate throughout the loan term, providing predictable monthly payments, whereas flexible-rate loans often start with a low teaser rate that can increase after an initial period, potentially raising monthly costs. Borrowers should carefully evaluate the initial teaser rate and subsequent adjustment terms to understand long-term affordability and interest rate risk.
Recast Provision
Fixed-rate loans offer stable monthly payments while flexible-rate loans often include a recast provision, allowing borrowers to reduce their monthly payments by making a lump-sum principal payment without refinancing. This recast feature provides a cost-effective way to lower payments during financial changes without incurring new loan origination fees.
Fixed-Rate Loan vs Flexible-Rate Loan for loan. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com