Auto loans and electric vehicle loans both provide financing options tailored to purchasing vehicles, but electric vehicle loans often come with lower interest rates or special incentives to promote eco-friendly transportation. While traditional auto loans cover a wide range of gasoline and diesel vehicles, electric vehicle loans focus specifically on EVs, sometimes including costs for charging equipment and installation. Considering the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance, electric vehicle loans may offer more cost-effective financing despite similar loan terms.
Table of Comparison
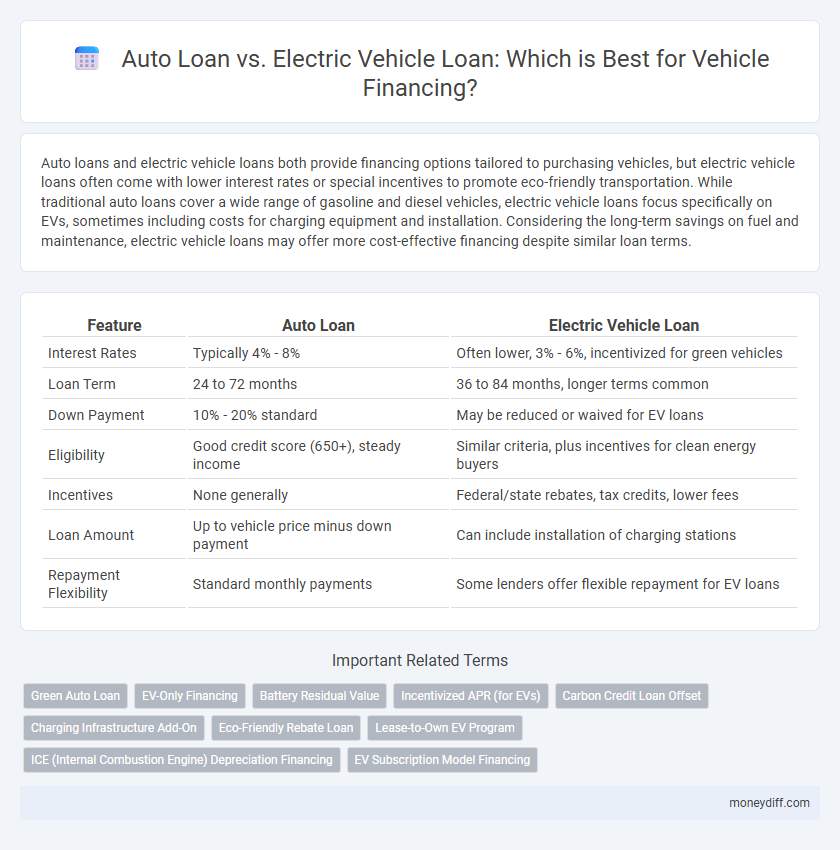
| Feature | Auto Loan | Electric Vehicle Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Typically 4% - 8% | Often lower, 3% - 6%, incentivized for green vehicles |
| Loan Term | 24 to 72 months | 36 to 84 months, longer terms common |
| Down Payment | 10% - 20% standard | May be reduced or waived for EV loans |
| Eligibility | Good credit score (650+), steady income | Similar criteria, plus incentives for clean energy buyers |
| Incentives | None generally | Federal/state rebates, tax credits, lower fees |
| Loan Amount | Up to vehicle price minus down payment | Can include installation of charging stations |
| Repayment Flexibility | Standard monthly payments | Some lenders offer flexible repayment for EV loans |
Understanding Auto Loans and Electric Vehicle Loans
Auto loans typically finance traditional gasoline-powered vehicles with standard interest rates and terms, while electric vehicle (EV) loans often feature specialized incentives such as lower interest rates, tax credits, and longer repayment periods to encourage eco-friendly transportation. Understanding the distinct eligibility criteria, approval processes, and potential savings associated with EV loans can significantly impact a borrower's total financing cost. Analyzing current market trends and government policies helps consumers make informed decisions between conventional auto loans and electric vehicle loans for optimal financial benefits.
Key Differences Between Auto Loans and EV Loans
Auto loans typically offer standard interest rates and loan terms based on conventional internal combustion engine vehicles, while electric vehicle (EV) loans may include incentives such as lower interest rates, tax credits, or specialized financing options tailored for EVs. EV loans often consider the vehicle's battery life and technology depreciation differently, affecting loan-to-value ratios and repayment plans. Regulatory benefits and government subsidies uniquely impact EV loan structures, distinguishing them significantly from traditional auto loans.
Interest Rates: Auto Loan vs Electric Vehicle Loan
Auto loans typically offer interest rates ranging from 4% to 10%, depending on credit score and loan term, while electric vehicle loans often feature lower rates due to government incentives and manufacturer promotions, sometimes as low as 0% APR. Interest rates for electric vehicle loans can decrease total financing costs significantly over the loan period, making them more affordable despite potentially higher upfront prices. Comparing lender offers and factoring in these rates is crucial for optimal financing decisions between traditional auto loans and specialized electric vehicle loans.
Eligibility Criteria for Auto and EV Loans
Auto loan eligibility typically requires a stable income, good credit score above 650, and proof of residency, while electric vehicle (EV) loans often include additional criteria such as eligibility for green incentives and lower debt-to-income ratios. Lenders for EV loans might require documentation of the vehicle's electric specifications and may prioritize applicants demonstrating environmental commitments. Both loan types demand verifiable employment history and acceptable credit risk, but EV loan programs may offer more flexible terms to support sustainable transportation goals.
Down Payment Requirements: Auto vs EV Financing
Down payment requirements for traditional auto loans typically range from 10% to 20% of the vehicle's purchase price, reflecting the vehicle's depreciation and lender risk assessment. Electric vehicle (EV) loans often demand similar or slightly higher down payments due to the higher initial vehicle costs and limited resale market, which influences lender risk calculations. Some financial institutions offer specialized EV financing programs with reduced down payment options to promote clean energy adoption and make EV ownership more accessible.
Government Incentives for Electric Vehicle Loans
Government incentives for electric vehicle loans include tax credits, rebates, and reduced interest rates that significantly lower the overall cost of financing compared to traditional auto loans. Many states offer additional incentives such as registration fee reductions and access to HOV lanes, making electric vehicle loans more financially attractive. These benefits enhance affordability and encourage the adoption of eco-friendly transportation options.
Loan Terms and Repayment Options
Auto loans typically offer flexible loan terms ranging from 24 to 72 months with varied interest rates based on credit score and lender policies. Electric vehicle (EV) loans often feature incentives such as lower interest rates or longer repayment periods to accommodate higher upfront costs and potential tax credits. Repayment options for both include fixed monthly payments, with some lenders offering deferred payment plans or customized schedules to align with borrower cash flow.
Total Cost of Ownership: Gas vs Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicle loans often offer lower total cost of ownership compared to auto loans for gasoline vehicles due to reduced fuel expenses and lower maintenance costs. While the upfront price for electric vehicles may be higher, incentives and tax credits can significantly offset initial costs, improving loan affordability. Over the loan term, savings on electricity versus gasoline and fewer mechanical repairs contribute to a more cost-effective financing option for electric vehicles.
Impact on Credit Score: Choosing the Right Loan
Auto loans and electric vehicle (EV) loans both influence credit scores by reporting payment history and credit utilization, but EV loans may offer specialized incentives affecting credit terms. Timely payments on either loan type positively impact credit scores, while missed payments can cause significant credit damage. Evaluating interest rates, loan terms, and lender policies specific to EV financing is crucial for minimizing credit risk and maximizing financial benefits.
Tips for Selecting the Best Vehicle Financing Option
Compare interest rates and loan terms carefully between auto loans and electric vehicle loans to find the most cost-effective option. Evaluate incentives such as tax credits and rebates specific to electric vehicles that can lower overall financing costs. Consider loan duration, monthly payment affordability, and eligibility criteria to select the best vehicle financing option tailored to your budget and vehicle choice.
Related Important Terms
Green Auto Loan
Green Auto Loans offer lower interest rates and tax incentives compared to traditional auto loans, specifically designed to finance electric vehicles (EVs) with benefits like reduced emissions and energy savings. These loans promote environmentally friendly transportation by supporting the purchase of EVs and hybrid cars, often including government rebates that reduce the overall loan amount.
EV-Only Financing
Electric vehicle (EV)-only financing offers tailored auto loans with lower interest rates, extended repayment terms, and incentives such as federal tax credits and rebates that are unavailable with traditional auto loans. Specialized EV loans often include benefits like charging station installation support and flexible options aligned with the higher upfront costs and unique depreciation rates of electric vehicles.
Battery Residual Value
Electric vehicle loans often include considerations for the battery residual value, which can significantly impact the overall financing terms due to battery degradation and replacement costs. Auto loans for traditional vehicles usually do not factor in battery depreciation, resulting in differing loan structures and repayment strategies between the two financing options.
Incentivized APR (for EVs)
Electric vehicle (EV) loans often feature incentivized APR rates as low as 0%, significantly lower than traditional auto loans, aiming to boost EV adoption through government and manufacturer rebates. These reduced APRs can substantially decrease overall financing costs, making EVs more affordable compared to conventional gasoline vehicles financed with standard auto loan rates.
Carbon Credit Loan Offset
Electric vehicle loans often qualify for carbon credit loan offsets, reducing the overall financing cost by incentivizing eco-friendly purchases, unlike traditional auto loans that lack such environmental benefits. Borrowers financing electric vehicles can leverage carbon credit programs to lower interest rates and enhance savings, promoting sustainable transportation choices.
Charging Infrastructure Add-On
Auto loans typically cover traditional vehicles without specialized add-ons, while electric vehicle loans often include options for charging infrastructure add-ons such as home chargers or public charging memberships, enhancing overall financing value. Financing with charging infrastructure add-ons supports EV adoption by offsetting upfront installation costs and ensuring convenient access to charging networks.
Eco-Friendly Rebate Loan
Electric Vehicle Loans often qualify for eco-friendly rebate programs that reduce overall financing costs, making them a financially attractive alternative to traditional Auto Loans. Leveraging government incentives and lower interest rates through specialized Electric Vehicle Loan options maximizes savings while promoting sustainable transportation choices.
Lease-to-Own EV Program
The Lease-to-Own EV Program offers a flexible alternative to traditional auto loans by allowing consumers to lease electric vehicles with the option to purchase at the end of the term, often with lower monthly payments and reduced upfront costs. This financing model supports access to electric vehicles for a broader market, promoting sustainability while providing predictable expenses and potential tax incentives linked to electric vehicle ownership.
ICE (Internal Combustion Engine) Depreciation Financing
Auto loans for internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles typically factor in faster depreciation rates due to higher maintenance costs and fuel expenses compared to electric vehicle (EV) loans, which often offer lower interest rates and incentives reflecting the growing market demand for EVs. Financing an ICE vehicle involves managing accelerated value loss over time, making electric vehicle loans more attractive through potential tax credits and lower total cost of ownership.
EV Subscription Model Financing
Electric Vehicle Loan financing often supports the EV subscription model by offering flexible terms tailored to lower depreciation rates and government incentives, contrasting with traditional auto loans that generally have fixed rates and shorter durations. EV subscription financing maximizes benefits such as reduced upfront costs, maintenance coverage, and easy vehicle upgrades, making it a more adaptive option for electric vehicle ownership.
Auto Loan vs Electric Vehicle Loan for vehicle financing. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com