Auto loans offer vehicle ownership through financing, requiring monthly payments and interest but building equity over time. Car subscriptions provide flexible access to vehicles with a single monthly fee covering insurance, maintenance, and roadside assistance, eliminating ownership responsibilities. Choosing between an auto loan and a car subscription depends on your preference for long-term ownership versus short-term flexibility.
Table of Comparison
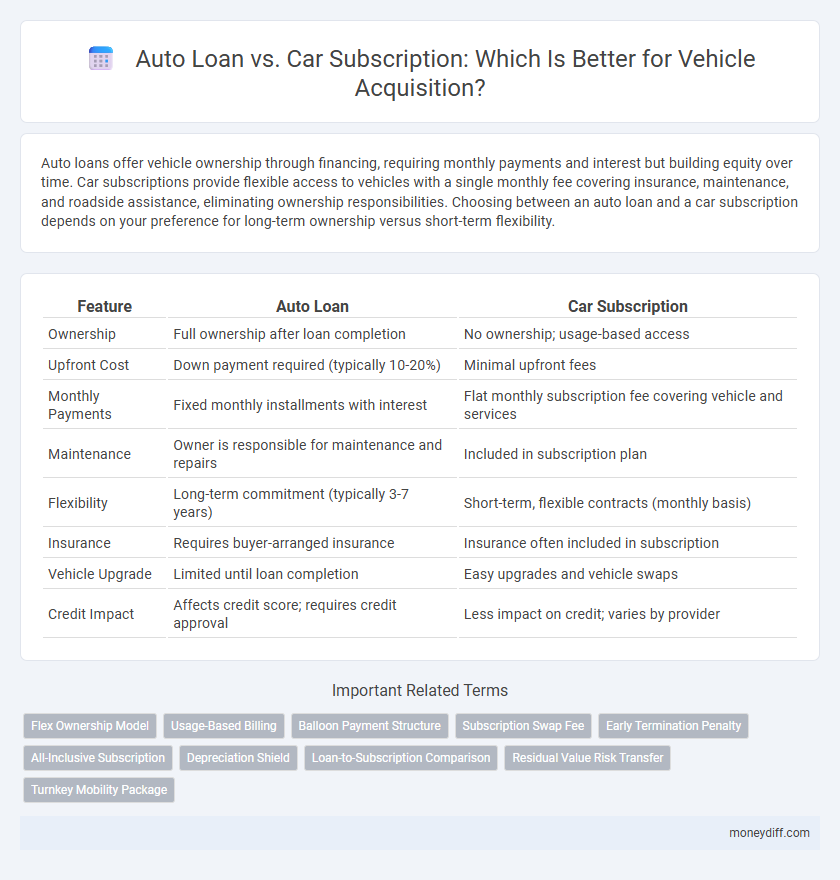
| Feature | Auto Loan | Car Subscription |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Full ownership after loan completion | No ownership; usage-based access |
| Upfront Cost | Down payment required (typically 10-20%) | Minimal upfront fees |
| Monthly Payments | Fixed monthly installments with interest | Flat monthly subscription fee covering vehicle and services |
| Maintenance | Owner is responsible for maintenance and repairs | Included in subscription plan |
| Flexibility | Long-term commitment (typically 3-7 years) | Short-term, flexible contracts (monthly basis) |
| Insurance | Requires buyer-arranged insurance | Insurance often included in subscription |
| Vehicle Upgrade | Limited until loan completion | Easy upgrades and vehicle swaps |
| Credit Impact | Affects credit score; requires credit approval | Less impact on credit; varies by provider |
Understanding Auto Loans: Traditional Vehicle Financing
Auto loans provide structured financing with fixed interest rates and repayment terms, allowing borrowers to own the vehicle after completing payments. These loans often require a down payment and credit evaluation, influencing eligibility and loan conditions. Understanding factors like loan duration, interest rates, and total repayment cost is essential for comparing auto loans to alternative options like car subscriptions.
What is a Car Subscription? An Overview
A car subscription is a flexible vehicle acquisition model allowing users to pay a monthly fee that covers insurance, maintenance, and sometimes taxes, offering access to a range of vehicles without long-term commitment. Unlike auto loans, which involve financing a vehicle purchase with monthly payments plus interest, subscriptions prioritize convenience and vehicle turnover without ownership. This model appeals to consumers seeking hassle-free access and the ability to switch cars frequently without depreciation concerns.
Upfront Costs: Auto Loan vs Car Subscription
Auto loans typically require a substantial upfront payment, including down payments, taxes, and registration fees, which can significantly increase initial expenses. Car subscriptions often minimize or eliminate large upfront costs by bundling fees like insurance, maintenance, and taxes into a fixed monthly rate. This difference in upfront costs makes subscriptions more accessible for consumers seeking flexibility without heavy initial financial commitments.
Monthly Payments Compared: Loan Installments vs Subscription Fees
Monthly payments for auto loans typically involve fixed installments based on the principal amount, interest rate, and loan term, resulting in predictable budgeting over several years. Car subscription fees often encompass not just the vehicle cost but also insurance, maintenance, and roadside assistance, reflecting a higher but all-inclusive monthly expense. Choosing between loan installments and subscription fees depends on the preference for ownership equity versus flexible, hassle-free access to different vehicles.
Ownership vs Usership: Long-term Implications
Auto loans grant full ownership, allowing vehicle customization and eventual asset equity, while car subscriptions provide flexible usership with no ownership responsibilities or resale concerns. Loan repayment terms often extend several years, impacting credit and long-term financial planning, whereas subscriptions operate on shorter, fixed periods with predictable monthly fees. Ownership builds long-term value but includes maintenance costs, versus subscriptions focusing on convenience and bundled services without asset accumulation.
Maintenance and Insurance: Who Pays What?
Auto loans typically require the borrower to handle both maintenance and insurance costs independently, ensuring full responsibility for vehicle upkeep and coverage. Car subscriptions often include maintenance and insurance costs within the monthly fee, providing a hassle-free ownership experience with predictable expenses. This distinction makes subscriptions appealing for those seeking convenience, while auto loans offer more control over individual service choices.
Flexibility and Commitment Levels
Auto loans require a fixed repayment schedule and longer commitment, typically spanning several years, which limits flexibility but builds vehicle ownership equity. Car subscriptions offer month-to-month contracts with inclusive maintenance and insurance, granting higher flexibility and lower long-term commitment without ownership. Consumers prioritizing adaptable usage and minimal obligation often prefer subscriptions, while those seeking asset accumulation usually opt for auto loans.
Total Cost of Ownership: Which Option Saves More?
Auto loans typically involve fixed monthly payments over a set term, often resulting in lower overall costs due to vehicle ownership and the ability to sell or trade in the car. Car subscriptions offer flexibility and include maintenance, insurance, and roadside assistance, but higher monthly fees and limited ownership benefits can increase total expenses over time. Evaluating depreciation, interest rates, insurance premiums, and service fees is crucial to determine which option saves more in the long run.
Credit Requirements and Financial Impact
Auto loans typically require a good credit score, steady income, and a low debt-to-income ratio to qualify, impacting long-term financial commitments with fixed monthly payments and interest rates. Car subscriptions often have less stringent credit requirements but involve higher monthly fees that cover maintenance and insurance, offering more flexibility without the burden of loan interest. Choosing between an auto loan and a car subscription depends on credit availability and preference for financial predictability or flexibility.
Which is Best for You? Decision Factors in Vehicle Acquisition
Choosing between an auto loan and a car subscription depends on your financial goals, usage patterns, and flexibility needs. Auto loans offer ownership with fixed monthly payments and potential equity build-up, ideal for long-term vehicle use and customizing your car. Car subscriptions provide convenience, maintenance, and insurance bundled into one fee, suiting those who prefer short-term access and minimal responsibilities.
Related Important Terms
Flex Ownership Model
Auto loans provide traditional vehicle ownership through financing with fixed monthly payments and eventual full ownership, while car subscriptions offer a flexible ownership model that includes maintenance, insurance, and the ability to switch vehicles without long-term commitment. The Flex Ownership Model enhances consumer convenience by combining access to multiple vehicles with simplified costs, reducing the risks and responsibilities associated with standard auto loans.
Usage-Based Billing
Auto loans provide fixed monthly payments based on the vehicle's purchase price and interest rate, whereas car subscriptions offer usage-based billing that adjusts costs according to mileage, wear, and subscription duration. This usage-based model in car subscriptions delivers flexibility and cost efficiency for drivers with variable driving patterns compared to the static repayment structure of auto loans.
Balloon Payment Structure
Auto loans with balloon payment structures require a large lump sum at the end of the term, reducing monthly payments but increasing the final payoff amount significantly, which can impact long-term budgeting. Car subscriptions typically avoid balloon payments by spreading costs evenly into a monthly fee that includes maintenance and insurance, offering predictable expenses without a large end-of-term financial burden.
Subscription Swap Fee
Auto loans typically involve fixed monthly payments with no swap fees, allowing vehicle ownership upon loan completion. Car subscriptions often include a swap fee for changing vehicles within the contract, offering flexibility but adding extra costs to the subscription model.
Early Termination Penalty
Auto loans typically impose early termination penalties that can include prepayment fees or loss of rebate incentives, increasing the overall cost if the loan is paid off ahead of schedule. Car subscriptions offer more flexibility with fewer or no early termination penalties, allowing users to switch or cancel vehicles quickly without significant financial penalties.
All-Inclusive Subscription
An all-inclusive car subscription offers flexible vehicle acquisition with bundled insurance, maintenance, and roadside assistance, providing convenience and hassle-free budgeting compared to traditional auto loans that require upfront down payments and separate management of expenses. Subscriptions deliver ongoing vehicle upgrades and lower commitment risks, making them ideal for consumers seeking seamless access to multiple vehicles without long-term financial liabilities.
Depreciation Shield
Auto loans transfer vehicle ownership immediately, exposing buyers to full depreciation risk, while car subscriptions offer a depreciation shield by including maintenance and insurance costs, mitigating financial loss from value decline. Car subscriptions provide flexibility without long-term commitment, protecting users from rapid depreciation typically associated with traditional auto loans.
Loan-to-Subscription Comparison
Auto loans offer long-term ownership with fixed interest rates and monthly payments, allowing borrowers to build equity in the vehicle over time. Car subscriptions provide flexible, all-inclusive monthly fees covering insurance, maintenance, and roadside assistance, eliminating ownership responsibilities but typically resulting in higher overall costs.
Residual Value Risk Transfer
Auto loans transfer residual value risk to the borrower, who assumes depreciation costs and potential resale value losses, while car subscriptions shift residual value risk to the service provider, offering fixed monthly payments and eliminating concerns about vehicle depreciation. This risk transfer impacts overall cost predictability and financial planning, with subscriptions generally providing greater flexibility and reduced exposure to asset devaluation.
Turnkey Mobility Package
Auto loans provide ownership through financing with fixed interest rates and monthly payments, often requiring credit approval and a down payment; car subscriptions offer a Turnkey Mobility Package including insurance, maintenance, and flexibility without long-term commitment. The subscription model appeals to drivers seeking hassle-free access and frequent vehicle upgrades, while auto loans favor buyers aiming for eventual ownership and asset accumulation.
Auto loan vs Car subscription for vehicle acquisition. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com