Choosing between a personal loan and a microloan for liability management depends on the amount needed and repayment terms. Personal loans typically offer larger sums with longer repayment periods, making them suitable for significant liabilities. Microloans provide smaller amounts with quicker repayment schedules, ideal for urgent or minor liability coverage.
Table of Comparison
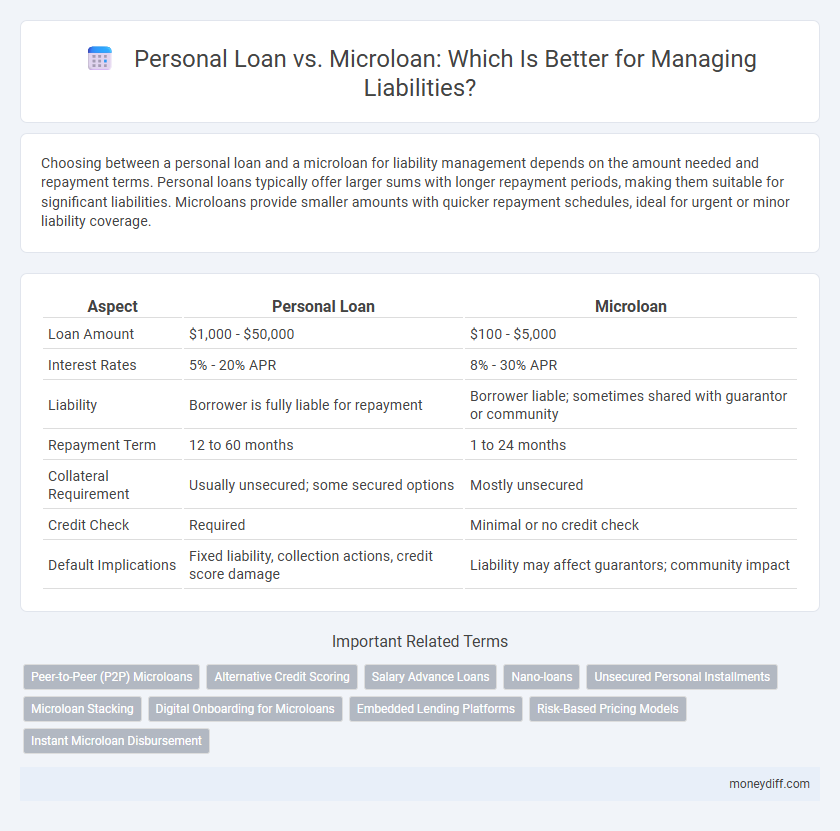
| Aspect | Personal Loan | Microloan |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Amount | $1,000 - $50,000 | $100 - $5,000 |
| Interest Rates | 5% - 20% APR | 8% - 30% APR |
| Liability | Borrower is fully liable for repayment | Borrower liable; sometimes shared with guarantor or community |
| Repayment Term | 12 to 60 months | 1 to 24 months |
| Collateral Requirement | Usually unsecured; some secured options | Mostly unsecured |
| Credit Check | Required | Minimal or no credit check |
| Default Implications | Fixed liability, collection actions, credit score damage | Liability may affect guarantors; community impact |
Understanding Personal Loans vs Microloans: An Overview
Personal loans typically offer larger borrowing amounts with fixed interest rates and longer repayment terms, making them suitable for substantial liabilities such as home improvements or debt consolidation. Microloans, often provided by non-profit organizations or online lenders, usually involve smaller sums with shorter repayment periods and higher interest rates, targeting entrepreneurs or individuals with limited credit history. Understanding the distinctions in loan size, interest rates, and repayment flexibility is essential for managing personal liability effectively.
Key Differences in Terms and Interest Rates
Personal loans generally offer larger borrowing limits with fixed interest rates ranging from 6% to 36%, suitable for moderate to substantial liabilities. Microloans typically provide smaller amounts, often up to $50,000, with higher interest rates between 7% and 45%, reflecting increased risk and shorter repayment periods. The key distinction lies in microloans' faster approval process and stricter terms, making them ideal for urgent, low-value liabilities compared to the more flexible but lengthier personal loan terms.
Eligibility Requirements for Personal Loans and Microloans
Personal loans typically require a higher credit score, steady income, and proof of employment, reflecting their larger loan amounts and longer repayment terms. Microloans often have more lenient eligibility criteria, targeting borrowers with limited credit history or lower income, making them accessible for small business owners and individuals in need of quick, low-value funding. Understanding these distinct eligibility requirements helps borrowers assess their liability risk and choose the most suitable loan type.
Loan Amounts: How Much Can You Borrow?
Personal loans typically offer higher loan amounts ranging from $1,000 to $50,000, making them suitable for larger financial liabilities. Microloans generally provide smaller sums, usually between $100 and $5,000, designed for minor expenses or business startups. Understanding these loan amount limits is crucial for managing liability effectively based on your borrowing needs.
Application Process: What to Expect
Personal loan applications typically require a comprehensive evaluation including credit checks, income verification, and extensive documentation, which can extend the approval timeline. Microloan applications are generally faster and more accessible, often designed for individuals or small businesses with less stringent credit and documentation requirements. Understanding these differences helps borrowers anticipate the complexity and speed of liability commitments associated with each loan type.
Repayment Schedules and Flexibility
Personal loans typically offer fixed repayment schedules with consistent monthly installments over terms ranging from one to seven years, providing predictability in liability management. Microloans often feature shorter terms of six to twelve months and may offer more flexible repayment options, including weekly or biweekly payments, accommodating borrowers with fluctuating incomes. Understanding these differences helps optimize liability by aligning repayment commitments with cash flow capabilities.
Impact on Credit Score and Financial Liability
Personal loans typically have a larger impact on credit scores due to higher borrowing amounts and longer repayment terms, increasing financial liability risk if payments are missed. Microloans often involve smaller sums and shorter terms, which can minimize negative effects on credit scores and limit financial liability exposure. Understanding the differences in their repayment structures is crucial for managing overall credit risk and maintaining positive credit health.
Use Cases: When to Choose a Personal Loan or Microloan
Personal loans are suitable for borrowers needing larger sums to consolidate high-interest debt, finance significant expenses, or handle emergencies with predictable repayment capacity. Microloans fit small business owners or individuals requiring minimal financing to cover short-term cash flow gaps or startup costs with quicker approval and less stringent credit requirements. Evaluating the loan amount, purpose, interest rates, and repayment terms helps determine whether a personal loan or microloan aligns best with your liability management needs.
Risks and Liabilities Associated with Each Loan Type
Personal loans often come with higher liability risks due to larger loan amounts and longer repayment terms, increasing the potential financial burden if default occurs. Microloans typically present lower liability risks, given their smaller amounts and shorter durations, but they may have higher interest rates that can affect overall repayment costs. Borrowers should carefully assess the risk of default and associated liability for each loan type to make informed financial decisions.
Making the Right Choice: Which Loan Minimizes Your Liability?
Choosing between a personal loan and a microloan depends on the amount of liability you can responsibly manage; personal loans generally offer higher borrowing limits with fixed interest rates, which can minimize liability by providing predictable monthly payments. Microloans, typically smaller and short-term, may carry higher interest rates but reduce total liability exposure due to lower principal amounts. Evaluating repayment terms, interest rates, and your financial capacity ensures the optimal loan type to minimize overall liability risk.
Related Important Terms
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Microloans
Peer-to-peer (P2P) microloans offer a flexible liability option with typically lower principal amounts and shorter repayment terms compared to personal loans, reducing risk exposure for borrowers. These microloans facilitate direct lending between individuals, leveraging online platforms to provide accessible financing while allowing lenders to diversify and limit their liability on smaller loan sizes.
Alternative Credit Scoring
Personal loans typically rely on traditional credit scoring methods that assess borrowers based primarily on credit history and FICO scores, while microloans often utilize alternative credit scoring models incorporating non-traditional data such as mobile payment records, utility bills, and social behavior to evaluate borrower liability. This approach in microloans enhances credit accessibility for individuals with limited credit history by providing a more comprehensive risk assessment beyond conventional metrics.
Salary Advance Loans
Salary advance loans, a subset of personal loans, typically offer higher borrowing limits compared to microloans, impacting overall liability management by increasing repayment obligations tied directly to the borrower's salary cycle. Microloans, often smaller in amount and short-term, present lower liability risk but may include higher interest rates, influencing the total cost of borrowing for individuals seeking quick financial relief.
Nano-loans
Nano-loans, as a subset of microloans, carry lower liability risks due to their smaller principal amounts and shorter repayment terms compared to traditional personal loans. Borrowers can manage their liabilities more effectively with nano-loans, minimizing debt exposure while meeting urgent financial needs.
Unsecured Personal Installments
Unsecured personal installment loans typically offer higher borrowing limits and longer repayment terms compared to microloans, making them more suitable for managing larger liabilities. Microloans, while generally easier to obtain with less stringent credit requirements, provide smaller amounts that may not fully cover significant personal liabilities.
Microloan Stacking
Microloan stacking involves obtaining multiple small loans simultaneously or consecutively to manage liabilities, often leading to higher overall debt and increased financial risk compared to a single personal loan. While personal loans typically offer a fixed repayment schedule and consolidated liability, microloan stacking can complicate liability tracking and increase the cost due to overlapping interest rates and fees.
Digital Onboarding for Microloans
Microloans offer streamlined digital onboarding processes that minimize liability risks by ensuring precise borrower verification and transparent agreement tracking. This digital approach reduces default rates compared to traditional personal loans by enhancing credit assessment accuracy and compliance adherence.
Embedded Lending Platforms
Embedded lending platforms streamline access to personal loans and microloans by integrating borrowing options directly into digital services, reducing liability risks through real-time credit assessment and automated compliance checks. Microloans offered via these platforms carry lower liability due to smaller amounts and shorter terms, whereas personal loans involve higher liability exposure requiring more stringent underwriting and risk management.
Risk-Based Pricing Models
Risk-based pricing models adjust personal loan interest rates according to borrowers' creditworthiness and repayment history, often resulting in lower rates for those with strong credit profiles, whereas microloans typically apply standardized rates due to higher default risks and limited borrower data. Understanding these pricing disparities is crucial for managing liability exposure and optimizing loan affordability in diverse risk environments.
Instant Microloan Disbursement
Instant microloan disbursement reduces liability risk by providing quick access to funds, enabling timely debt repayment and minimizing interest accumulation. Personal loans often involve longer approval times, increasing the chance of delayed payments and higher liability costs.
Personal Loan vs Microloan for Liability. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com