Liabilities represent external financial obligations that must be settled, often involving contracts or legal agreements, whereas on-chain debt exists within blockchain ecosystems, encoded as smart contracts that automatically enforce repayment terms. On-chain debt offers transparency and immutability, reducing the risk of default and enabling real-time tracking of obligations in decentralized finance (DeFi). Effective money management requires balancing traditional liabilities with on-chain debt to optimize liquidity and minimize risks across both conventional and digital financial platforms.
Table of Comparison
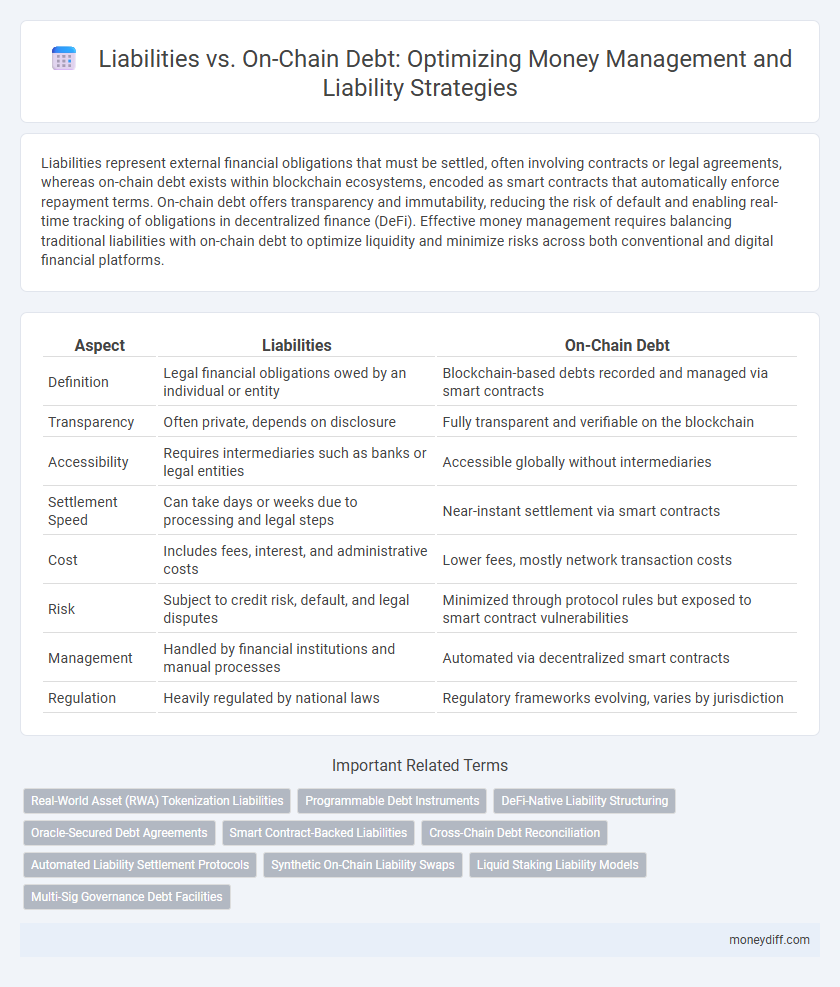
| Aspect | Liabilities | On-Chain Debt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal financial obligations owed by an individual or entity | Blockchain-based debts recorded and managed via smart contracts |
| Transparency | Often private, depends on disclosure | Fully transparent and verifiable on the blockchain |
| Accessibility | Requires intermediaries such as banks or legal entities | Accessible globally without intermediaries |
| Settlement Speed | Can take days or weeks due to processing and legal steps | Near-instant settlement via smart contracts |
| Cost | Includes fees, interest, and administrative costs | Lower fees, mostly network transaction costs |
| Risk | Subject to credit risk, default, and legal disputes | Minimized through protocol rules but exposed to smart contract vulnerabilities |
| Management | Handled by financial institutions and manual processes | Automated via decentralized smart contracts |
| Regulation | Heavily regulated by national laws | Regulatory frameworks evolving, varies by jurisdiction |
Understanding Traditional Liabilities in Money Management
Traditional liabilities encompass financial obligations such as loans, mortgages, credit card debt, and accounts payable, which represent a company's or individual's legal responsibility to repay borrowed funds. Effective money management requires accurately tracking these liabilities to assess overall financial health and cash flow needs. Understanding the distinction between traditional liabilities and on-chain debt is crucial, as the former involves centralized agreements while the latter operates within decentralized blockchain ecosystems.
What Is On-Chain Debt?
On-chain debt refers to financial obligations recorded and managed directly on a blockchain, enabling transparent and immutable tracking of borrowed assets. Unlike traditional liabilities, on-chain debt is governed by smart contracts that automatically enforce loan terms, repayment schedules, and collateral management. This decentralized approach reduces reliance on intermediaries and enhances security in digital money management.
Key Differences: Liabilities vs On-Chain Debt
Liabilities encompass all financial obligations a business or individual owes, including loans, accounts payable, and accrued expenses, while on-chain debt specifically refers to debt recorded and managed on blockchain networks through smart contracts. Unlike traditional liabilities that rely on centralized legal frameworks, on-chain debt offers transparency, immutability, and automated execution governed by decentralized protocols. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective money management, as on-chain debt provides real-time visibility and reduced counterparty risks compared to conventional liabilities.
Risk Profiles: Traditional vs Blockchain-Based Debt
Traditional liabilities often carry credit risk tied to centralized institutions, whereas on-chain debt leverages decentralized protocols that offer transparency and immutable records, reducing counterparty risk. Blockchain-based debt introduces smart contract risks and volatility in collateral value, which traditional liabilities typically do not face. Risk profiles differ as traditional debt is subject to regulatory frameworks and credit assessments, while on-chain debt exposes borrowers to network-specific risks and potential rapid liquidation events.
Transparency and Accountability in Debt Management
On-chain debt offers unparalleled transparency by leveraging blockchain's immutable ledger, enabling real-time tracking and verification of liabilities. Traditional liabilities often lack this level of visibility, making accountability in debt management more challenging for stakeholders. Implementing on-chain mechanisms ensures accurate, auditable records that enhance trust and streamline fiduciary responsibility.
Security Concerns: Protecting Assets and Repayments
Liabilities in traditional finance are subject to regulatory oversight, offering established protections for assets and repayments, whereas on-chain debt involves smart contracts that require robust cybersecurity measures to prevent exploits and unauthorized access. Securing on-chain debt relies heavily on encryption protocols and decentralized validation, which can mitigate but not eliminate risks of hacking or code vulnerabilities. Effective money management demands continuous monitoring of both liability structures to safeguard assets and ensure reliable repayment mechanisms.
Efficiency and Speed: Settling Liabilities On-Chain
Settling liabilities on-chain significantly enhances efficiency and speed by automating transactions through smart contracts, reducing the need for intermediaries and manual reconciliations. This on-chain debt management allows for real-time updates and transparent audit trails, minimizing delays and errors inherent in traditional liability settlements. Leveraging blockchain technology ensures swift execution and settlement finality, optimizing cash flow and financial operations for businesses.
Regulatory Implications for Liabilities and On-Chain Debt
Regulatory implications for liabilities and on-chain debt center on compliance with financial laws and anti-money laundering (AML) standards, with traditional liabilities subject to established banking regulations while on-chain debt faces evolving crypto-specific frameworks. On-chain debt introduces transparency challenges and jurisdictional complexities that demand tailored regulatory approaches to ensure consumer protection and systemic stability. Effective money management requires navigating these regulatory landscapes to mitigate legal risks and align with compliance mandates across diverse financial ecosystems.
Integrating On-Chain Solutions in Financial Strategies
Integrating on-chain solutions into financial strategies transforms traditional liability management by enabling transparent, automated, and immutable tracking of debts on blockchain networks such as Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain. On-chain debt platforms like Aave and Compound offer real-time collateral monitoring and programmable smart contracts that reduce counterparty risk and streamline repayment processes. Leveraging these decentralized finance (DeFi) tools enhances efficiency, security, and liquidity management in corporate and personal money management frameworks.
The Future of Liabilities Management: Digital vs Traditional Approaches
Digital liabilities management leverages blockchain technology to provide transparent, immutable records of on-chain debt, enabling real-time tracking and automated repayment through smart contracts. Traditional liabilities management relies on manual reconciliation and centralized financial institutions, often leading to delays and increased risk of errors. The future of liabilities will see a hybrid model combining the efficiency and security of digital solutions with regulatory frameworks and oversight from traditional finance systems.
Related Important Terms
Real-World Asset (RWA) Tokenization Liabilities
Liabilities in traditional finance represent legal obligations, while on-chain debt within Real-World Asset (RWA) tokenization enables transparent and immutable tracking of these obligations on blockchain networks. Tokenizing liabilities transforms real-world financial commitments into programmable assets, enhancing liquidity and risk management through decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols.
Programmable Debt Instruments
Programmable debt instruments leverage blockchain technology to automate repayments, interest calculations, and enforce contractual terms, distinguishing them from traditional liabilities that require manual management and oversight. On-chain debt provides transparency, immutability, and real-time tracking, enhancing efficiency and reducing risks associated with conventional liability management.
DeFi-Native Liability Structuring
DeFi-native liability structuring optimizes money management by distinguishing on-chain debt, which offers programmability and transparency, from traditional liabilities that are off-chain and often less efficient. Utilizing smart contracts and blockchain protocols enhances risk allocation and enables automated repayment schedules, reducing counterparty risk in decentralized finance ecosystems.
Oracle-Secured Debt Agreements
Oracle-Secured Debt Agreements enhance money management by anchoring liabilities to on-chain data, reducing counterparty risk through automated, transparent enforcement of debt terms. This integration ensures real-time verification of collateral and repayment status, streamlining liability tracking compared to traditional off-chain liabilities.
Smart Contract-Backed Liabilities
Smart contract-backed liabilities enable transparent, automated management of obligations recorded on blockchain, reducing counterparty risk and enhancing real-time auditing capabilities. Unlike traditional liabilities, on-chain debt leverages programmable contracts to enforce terms and collateralization without intermediaries, improving efficiency in decentralized finance ecosystems.
Cross-Chain Debt Reconciliation
Cross-chain debt reconciliation enhances money management by synchronizing liabilities across multiple blockchain networks, ensuring accurate consolidation of on-chain debt records and reducing the risk of double-counting liabilities. This approach leverages interoperable protocols to maintain a unified view of financial obligations, improving transparency and optimizing liquidity allocation in decentralized finance ecosystems.
Automated Liability Settlement Protocols
Automated Liability Settlement Protocols streamline money management by integrating real-time tracking of liabilities with on-chain debt positions, ensuring precise reconciliation of obligations without manual intervention. These protocols enhance transparency and reduce settlement risks through smart contracts that automatically execute payments once predefined conditions are met.
Synthetic On-Chain Liability Swaps
Synthetic on-chain liability swaps enable decentralized finance platforms to manage liabilities by tokenizing debt positions, facilitating transparent and efficient risk distribution across participants. Compared to traditional liabilities, these swaps enhance liquidity and mitigate counterparty risks through smart contract automation and blockchain-enforced settlement mechanisms.
Liquid Staking Liability Models
Liquid staking liability models represent obligations arising from staked assets that remain liquid and transferable on-chain, differing from traditional on-chain debt which involves direct borrowing and repayment schedules. Managing these liabilities requires accurately accounting for tokenized staked positions that fluctuate in value and liquidity risk, impacting a protocol's solvency and risk exposure.
Multi-Sig Governance Debt Facilities
Multi-Sig Governance Debt Facilities enhance liability management by distributing on-chain debt control across multiple parties, reducing risks associated with centralized liability exposure. This decentralized approach ensures transparent and secure execution of debt obligations within blockchain ecosystems, optimizing financial governance and risk mitigation.
Liabilities vs On-Chain Debt for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com