Liability management involves understanding and mitigating financial obligations to maintain creditworthiness and avoid defaults. Crypto-backed loans offer a unique way to secure funds by leveraging digital assets as collateral, reducing reliance on traditional credit lines while introducing volatility risks. Comparing these options helps optimize money management strategies by balancing asset liquidity and liability exposure.
Table of Comparison
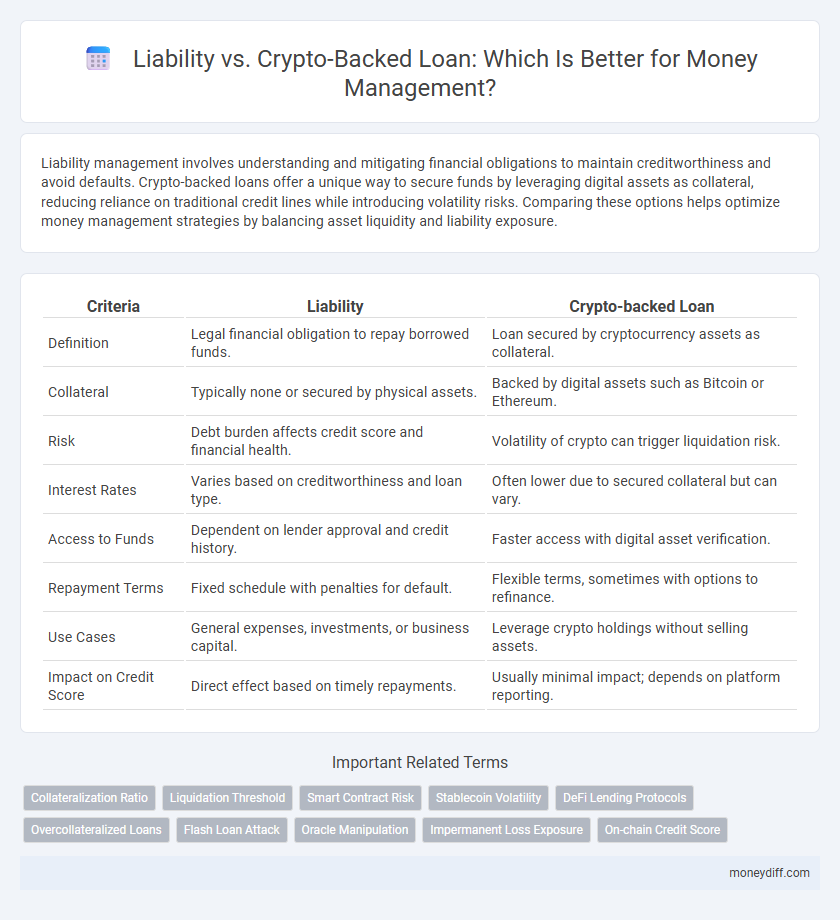
| Criteria | Liability | Crypto-backed Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal financial obligation to repay borrowed funds. | Loan secured by cryptocurrency assets as collateral. |
| Collateral | Typically none or secured by physical assets. | Backed by digital assets such as Bitcoin or Ethereum. |
| Risk | Debt burden affects credit score and financial health. | Volatility of crypto can trigger liquidation risk. |
| Interest Rates | Varies based on creditworthiness and loan type. | Often lower due to secured collateral but can vary. |
| Access to Funds | Dependent on lender approval and credit history. | Faster access with digital asset verification. |
| Repayment Terms | Fixed schedule with penalties for default. | Flexible terms, sometimes with options to refinance. |
| Use Cases | General expenses, investments, or business capital. | Leverage crypto holdings without selling assets. |
| Impact on Credit Score | Direct effect based on timely repayments. | Usually minimal impact; depends on platform reporting. |
Understanding Liability in Traditional Money Management
Liability in traditional money management refers to financial obligations or debts that an individual or business must repay, such as mortgages, credit card debt, and personal loans. These liabilities impact credit scores and liquidity, influencing borrowing capacity and overall financial stability. Understanding the nature, terms, and repayment schedules of traditional liabilities is crucial for effective debt management and maintaining healthy cash flow.
What Are Crypto-Backed Loans?
Crypto-backed loans use digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum as collateral, enabling borrowers to access liquidity without selling their cryptocurrency. These loans reduce the risk of traditional liability by leveraging the value of volatile crypto holdings, often allowing lower interest rates and flexible repayment terms. Managing liability through crypto-backed loans can provide a strategic alternative for money management, balancing asset retention with cash flow needs.
Key Differences: Liability vs. Crypto-Backed Loans
Liability refers to a legal obligation to repay borrowed funds, typically with fixed terms and potential impact on credit scores, whereas crypto-backed loans use digital assets as collateral, offering more flexible borrowing terms and often lower interest rates. Unlike traditional liabilities, crypto-backed loans carry the risk of collateral liquidation due to market volatility but enable borrowers to access liquidity without selling their crypto holdings. Understanding these key differences is essential for effective money management and risk assessment in financial planning.
Risk Assessment: Liability vs. Crypto-Backed Loans
Risk assessment between traditional liabilities and crypto-backed loans reveals distinct financial exposure profiles; liabilities typically involve fixed repayment obligations with clearer credit risk, while crypto-backed loans carry volatility risk tied to cryptocurrency market fluctuations. The collateralization in crypto loans mitigates some default risk; however, sudden drops in crypto asset value can trigger margin calls or forced liquidations. Effective money management requires analyzing the predictable nature of liability schedules versus the dynamic, high-risk environment of crypto-backed loan collateral.
Interest Rates Comparison: Traditional Liability and Crypto Loans
Interest rates for traditional liabilities typically range from 5% to 20%, influenced by credit scores and market conditions. Crypto-backed loans often offer lower rates between 3% and 12%, leveraging collateralized digital assets to reduce lender risk. Borrowers using crypto collateral benefit from faster approval and flexible terms but face volatility risk impacting loan value.
Collateral Requirements: Fiat vs. Crypto Assets
Collateral requirements for liability management differ significantly between fiat and crypto-backed loans, impacting risk assessment and approval processes. Fiat-based loans typically demand stable, government-backed assets with predictable valuation, ensuring lower volatility and clearer liquidation paths. In contrast, crypto-backed loans accept digital assets that fluctuate rapidly in value, requiring higher collateral ratios and frequent revaluations to mitigate lender exposure to market instability.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Money Management
Liability in traditional loans often involves fixed repayment schedules and less flexibility, limiting accessibility for borrowers with fluctuating incomes. Crypto-backed loans offer enhanced flexibility by allowing users to leverage digital assets as collateral, enabling quicker access to funds without stringent credit checks. This increased accessibility facilitates more adaptable money management strategies tailored to individual financial circumstances.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Liability in traditional loans is clearly defined with regulatory frameworks ensuring borrower protections, whereas crypto-backed loans often operate in a complex legal environment with evolving regulations that vary significantly by jurisdiction. Crypto-backed loans introduce unique risks such as asset volatility and unclear recourse in default situations, requiring borrowers to understand both local financial laws and cryptocurrency-specific compliance standards. Legal considerations include the enforceability of smart contracts, anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, and the regulatory status of digital assets under securities or commodity laws.
Security and Transparency in Liability and Crypto Loans
Liability management offers established security measures through regulatory frameworks, ensuring clear accountability and risk mitigation for borrowers and lenders. Crypto-backed loans leverage blockchain technology, providing enhanced transparency via immutable transaction records but pose higher volatility risks due to cryptocurrency price fluctuations. Both financial instruments require careful assessment of security protocols and transparency standards to optimize money management strategies.
Choosing the Best Option: Liability or Crypto-Backed Loan?
Evaluating liability versus a crypto-backed loan requires considering risk tolerance, repayment terms, and asset volatility. Liability often entails fixed obligations that impact credit and cash flow, while crypto-backed loans leverage digital assets as collateral, offering potentially lower interest but exposing borrowers to market fluctuations. Optimal money management hinges on balancing predictable liabilities with the flexible, yet volatile nature of crypto-backed financing.
Related Important Terms
Collateralization Ratio
Liability management in crypto-backed loans hinges on maintaining an optimal collateralization ratio, which directly impacts risk exposure and liquidation thresholds. Higher collateralization ratios reduce the likelihood of forced asset sales, ensuring more stable debt management compared to unsecured liabilities.
Liquidation Threshold
Liability in traditional finance often involves fixed repayment terms, whereas crypto-backed loans hinge on volatile asset values, making the liquidation threshold a critical risk factor for borrowers. The liquidation threshold sets the asset price at which lenders automatically liquidate collateral to cover outstanding debt, significantly impacting money management strategies in crypto lending.
Smart Contract Risk
Liability in traditional loans typically involves fixed obligations, whereas crypto-backed loans carry inherent Smart Contract risks due to the automated and immutable nature of blockchain protocols, which can lead to potential vulnerabilities or exploits. Managing money with crypto-backed loans requires careful evaluation of the Smart Contract's code integrity and the security measures in place to mitigate systemic risks.
Stablecoin Volatility
Liability in traditional finance offers predictable repayment plans, whereas crypto-backed loans expose borrowers to stablecoin volatility, risking repayment amounts fluctuating with market changes. Managing money with stablecoins requires careful monitoring of their price stability to avoid unexpected increases in liability.
DeFi Lending Protocols
Liability in traditional finance refers to the legal financial obligations a borrower must repay, while crypto-backed loans within DeFi lending protocols offer overcollateralized borrowing using digital assets, reducing counterparty risk through smart contracts and decentralized collateral management. DeFi platforms enable transparent, programmable liability terms and instant loan liquidation to maintain solvency, contrasting with the fixed liabilities and centralized enforcement of conventional loans.
Overcollateralized Loans
Overcollateralized loans in crypto-backed lending mitigate liability risks by requiring borrowers to secure loans with assets exceeding the loan value, reducing the lender's exposure to default. This structure enhances money management by ensuring loan security through collateral surplus, minimizing financial losses compared to traditional unsecured liabilities.
Flash Loan Attack
Liability in money management involves obligations that can expose individuals or institutions to financial risk, whereas crypto-backed loans use digital assets as collateral to secure borrowing, potentially increasing vulnerability. Flash loan attacks exploit this by instantly borrowing large amounts of cryptocurrency without collateral, manipulating systems and causing significant liability risks for decentralized finance platforms.
Oracle Manipulation
Liability in traditional loans poses predictable risks, whereas crypto-backed loans introduce unique vulnerabilities such as oracle manipulation, where tampered price feeds can trigger incorrect collateral valuations and abrupt liquidations. Effective money management requires understanding these oracle risks to mitigate unexpected losses inherent in decentralized finance platforms.
Impermanent Loss Exposure
Liability in traditional finance involves fixed obligations often leading to predictable risk profiles, whereas crypto-backed loans expose borrowers to impermanent loss due to asset volatility and price fluctuations in collateral value. Managing impermanent loss requires continuous monitoring of crypto market dynamics to avoid unexpected liability increases impacting overall money management strategies.
On-chain Credit Score
On-chain credit scores enhance transparency and reduce default risk by utilizing blockchain data to assess borrower reliability in crypto-backed loans, improving liability management. These scores enable lenders to make data-driven decisions, optimizing money management by aligning loan terms with the borrower's verified creditworthiness on-chain.
Liability vs Crypto-backed Loan for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com