Liability pet management requires careful distinction between personal liabilities and social lending arrangements to ensure clear accountability. Social lending often involves informal financial exchanges without legal protections, increasing the risk of disputes or unpaid debts. Proper liability management incorporates formal agreements and transparent tracking to mitigate financial risks linked to borrowing or lending money within social contexts.
Table of Comparison
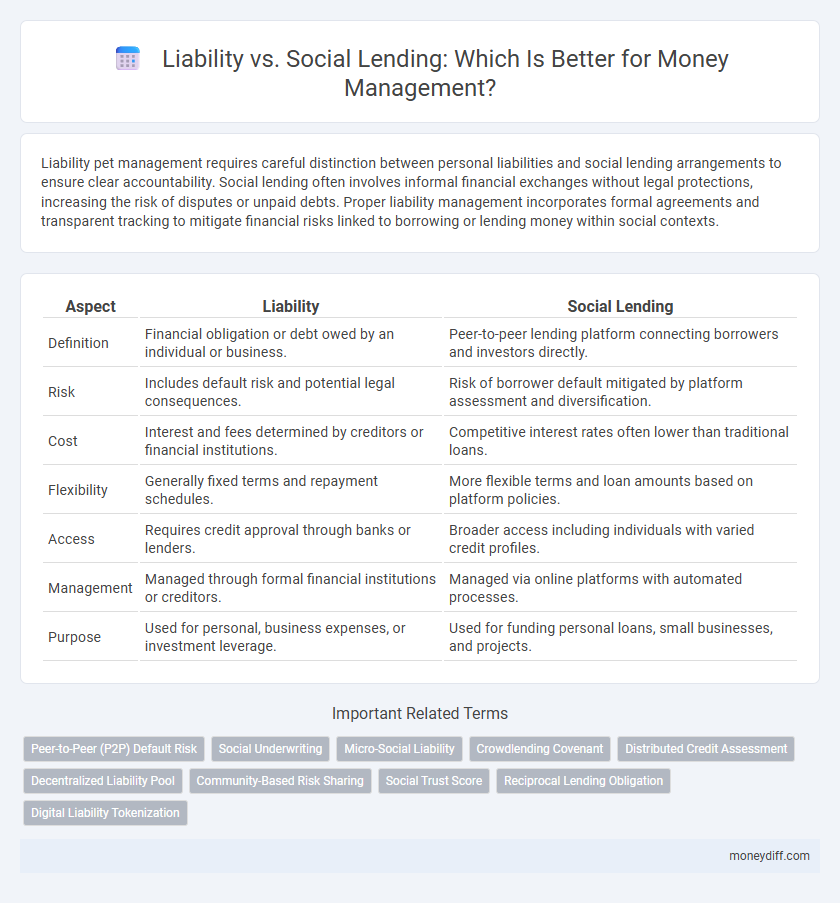
| Aspect | Liability | Social Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial obligation or debt owed by an individual or business. | Peer-to-peer lending platform connecting borrowers and investors directly. |
| Risk | Includes default risk and potential legal consequences. | Risk of borrower default mitigated by platform assessment and diversification. |
| Cost | Interest and fees determined by creditors or financial institutions. | Competitive interest rates often lower than traditional loans. |
| Flexibility | Generally fixed terms and repayment schedules. | More flexible terms and loan amounts based on platform policies. |
| Access | Requires credit approval through banks or lenders. | Broader access including individuals with varied credit profiles. |
| Management | Managed through formal financial institutions or creditors. | Managed via online platforms with automated processes. |
| Purpose | Used for personal, business expenses, or investment leverage. | Used for funding personal loans, small businesses, and projects. |
Understanding Liability in Money Management
Liability in money management refers to the legal financial obligations that an individual or entity must repay, including loans, mortgages, and credit card debts. Unlike social lending, which involves peer-to-peer borrowing often characterized by flexible terms and community trust, liabilities typically involve formal agreements and fixed repayment schedules. Understanding the impact of liabilities is crucial for effective money management, as it affects credit score, cash flow, and the ability to invest or save.
Defining Social Lending in Personal Finance
Social lending in personal finance refers to the peer-to-peer borrowing and lending platforms that connect individual borrowers directly with lenders, bypassing traditional financial institutions. This form of lending reduces reliance on formal liabilities by creating flexible, transparent loan agreements based on personal creditworthiness and trust within the lending community. Social lending diversifies risk exposure and often offers lower interest rates compared to conventional liabilities, making it an innovative approach to managing personal debt and cash flow.
Key Differences Between Liability and Social Lending
Liability refers to a legal obligation to repay borrowed money, often with fixed terms and interest rates, while social lending involves peer-to-peer lending platforms connecting borrowers directly with individual lenders, often with more flexible terms. Key differences include the source of funds--traditional financial institutions for liabilities versus individual lenders for social lending--and the risk distribution, as social lending spreads risk across multiple peers rather than relying on a single creditor. Furthermore, liabilities typically impose a formal legal framework, whereas social lending relies on platform agreements and community trust mechanisms.
Liability Implications in Social Lending Platforms
Liability implications in social lending platforms revolve around the responsibility for loan defaults and borrower solvency, which often shifts from traditional financial institutions to individual lenders within the platform. Social lending exposes lenders to higher credit risk due to limited regulatory oversight and the peer-to-peer nature of transactions, increasing potential personal financial liability. Effective risk assessment tools and clear contractual agreements are essential to mitigate liabilities arising from non-repayment or fraud in social lending environments.
Risk Assessment: Liability vs Social Lending
Risk assessment in liability management prioritizes identifying and mitigating obligations that can result in financial losses or legal consequences, emphasizing creditworthiness and contractual terms. In social lending, risk assessment focuses on peer-to-peer trust, borrower credibility verified through social data, and community-based repayment incentives to minimize default rates. Quantitative metrics in liability risk include debt-to-income ratios and collateral value, while social lending relies on social scoring algorithms and network reliability analyses.
How Liability Affects Borrowers and Lenders
Liability impacts borrowers by imposing legal and financial obligations to repay debts, which can influence their creditworthiness and risk profile. For lenders, liability determines the extent of responsibility for losses or defaults, affecting their decision-making and risk exposure in social lending platforms. Understanding liability helps both parties manage risks effectively and promotes transparency in money management practices.
Social Lending Strategies to Minimize Liability
Social lending strategies focus on minimizing liability by diversifying borrower portfolios and implementing rigorous credit assessments to reduce default risks. Leveraging peer-to-peer platforms enhances transparency and distributes financial exposure among multiple investors, limiting individual liability. Employing automated risk management tools aids in proactive monitoring and mitigation of potential loan delinquencies.
Regulatory Perspectives: Liability and Social Lending
Regulatory perspectives on liability emphasize strict compliance with financial laws and risk management protocols to protect creditors and borrowers in traditional lending frameworks. In contrast, social lending operates under evolving regulatory standards that prioritize transparency, investor protection, and peer-to-peer accountability, often requiring specialized licensing and adherence to consumer protection regulations. The juxtaposition highlights how liability frameworks in conventional finance focus on institutional risk, while social lending regulations adapt to decentralized, community-driven financial interactions.
Benefits and Drawbacks: Liability vs Social Lending
Liability management involves fixed repayment obligations with predictable financial responsibilities, ensuring creditworthiness but potentially limiting cash flow flexibility. Social lending offers access to diverse peer-to-peer funding with community-driven terms, enhancing borrowing options but carrying risks of variable interest rates and less regulatory protection. Balancing these approaches requires evaluating cost efficiency, repayment structure, and risk tolerance for optimal money management.
Choosing the Right Approach for Effective Money Management
Liability management focuses on minimizing debts and obligations to maintain financial stability, while social lending leverages peer-to-peer platforms to access funds more flexibly. Choosing the right approach involves assessing risk tolerance, repayment capacity, and interest cost to align with personal financial goals. Effective money management balances reducing liabilities with utilizing social lending opportunities to optimize cash flow and credit standing.
Related Important Terms
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Default Risk
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending carries a higher default risk compared to traditional liability management due to the lack of comprehensive credit guarantees and regulatory oversight. Social lending platforms mitigate this risk using credit scoring algorithms and diversification strategies, but investors must still account for potential borrower defaults impacting overall portfolio stability.
Social Underwriting
Social underwriting leverages collective community insights and trust metrics to assess borrower creditworthiness, reducing traditional liability risks in money management. This method enhances transparency and accountability, enabling more accurate risk evaluation compared to conventional liability frameworks.
Micro-Social Liability
Micro-social liability leverages collective borrowing within communities, reducing individual risk through shared responsibility and promoting financial inclusion. This model contrasts traditional liability by emphasizing trust and social collateral over formal credit checks, enhancing access to capital for underserved populations.
Crowdlending Covenant
Liability in crowdlending covenant frameworks shifts towards shared financial commitment among multiple investors, reducing individual risk compared to traditional social lending models where single lenders bear full liability. Crowdlending covenants enforce stricter repayment terms and transparent risk assessments, enhancing borrower accountability and protecting investor interests in decentralized funding environments.
Distributed Credit Assessment
Distributed Credit Assessment enhances accuracy in Social Lending by leveraging decentralized data sources and blockchain technology, reducing the risks associated with traditional Liability-based credit evaluations. This method enables peer-to-peer platforms to assess borrower trustworthiness more transparently and efficiently, minimizing default rates and improving overall financial inclusion.
Decentralized Liability Pool
A decentralized liability pool enables collective risk-sharing by pooling funds from multiple participants, enhancing capital efficiency and reducing individual borrower risk compared to traditional social lending models. This structure leverages blockchain technology to ensure transparency, automated contract enforcement, and lower operational costs while diversifying liability across a broader spectrum of lenders.
Community-Based Risk Sharing
Community-based risk sharing in social lending reduces individual liability by distributing financial responsibility among members, enhancing collective creditworthiness and minimizing default risks. Unlike traditional liability models that place burden on single entities, social lending leverages group trust and peer accountability to manage and mitigate financial obligations effectively.
Social Trust Score
Social Lending leverages a Social Trust Score to assess borrower credibility, reducing reliance on traditional liability-based credit evaluations. This trust-driven model enhances money management by promoting transparent peer-to-peer transactions and minimizing default risks through community-validated reputation.
Reciprocal Lending Obligation
Reciprocal lending obligation in social lending creates a mutual liability where borrowers and lenders share financial risks and responsibilities, differing from traditional liability models that place full accountability on a single party. This reciprocal framework enhances collective trust and risk mitigation in money management by distributing liabilities among network members.
Digital Liability Tokenization
Digital liability tokenization transforms traditional liability structures by converting debt obligations into blockchain-based tokens, enhancing transparency and liquidity compared to social lending models. This technology enables precise tracking and real-time trading of liabilities, reducing risks and improving efficiency in money management ecosystems.
Liability vs Social Lending for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com