Liability management involves tracking and repaying debts or obligations, ensuring financial stability and risk mitigation. Tokenized debt leverages blockchain technology, allowing debts to be represented as digital tokens, which enhances transparency, liquidity, and ease of transfer. Choosing between traditional liability management and tokenized debt depends on the need for innovation in tracking, efficiency, and accessibility in money management.
Table of Comparison
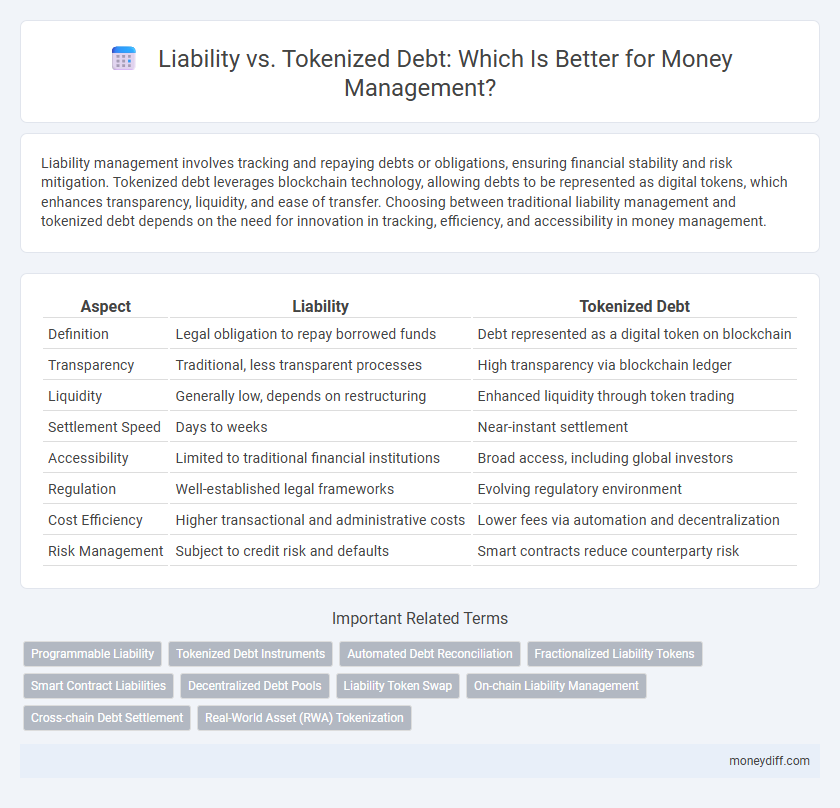
| Aspect | Liability | Tokenized Debt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal obligation to repay borrowed funds | Debt represented as a digital token on blockchain |
| Transparency | Traditional, less transparent processes | High transparency via blockchain ledger |
| Liquidity | Generally low, depends on restructuring | Enhanced liquidity through token trading |
| Settlement Speed | Days to weeks | Near-instant settlement |
| Accessibility | Limited to traditional financial institutions | Broad access, including global investors |
| Regulation | Well-established legal frameworks | Evolving regulatory environment |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher transactional and administrative costs | Lower fees via automation and decentralization |
| Risk Management | Subject to credit risk and defaults | Smart contracts reduce counterparty risk |
Understanding Liability in Traditional Money Management
Liability in traditional money management refers to financial obligations or debts that an individual or business owes to others, such as loans, mortgages, or unpaid bills, which must be repaid over time. These liabilities impact cash flow and net worth by representing claims against assets and requiring scheduled payments that influence budgeting and financial planning. Understanding traditional liability management is crucial for maintaining creditworthiness and ensuring sustainable debt levels within conventional financial systems.
The Rise of Tokenized Debt in Financial Systems
Tokenized debt is revolutionizing financial systems by transforming traditional liabilities into digital assets that offer increased transparency and liquidity. Unlike conventional liabilities, tokenized debt enables fractional ownership and instantaneous settlement on blockchain platforms, significantly reducing transaction costs and counterparty risks. This innovation enhances money management by providing greater flexibility and access to a broader investor base while maintaining the debtor's obligations clearly defined as digital tokens.
Core Differences: Liability vs Tokenized Debt
Liability represents a legal obligation to repay borrowed funds, typically recorded on a company's balance sheet as a debt or payable, while tokenized debt leverages blockchain technology to digitize debt instruments, enabling fractional ownership and enhanced liquidity. Core differences lie in accessibility and transparency: liabilities are traditional, centralized obligations with limited transferability, whereas tokenized debt offers decentralized, programmable contracts allowing seamless trading on digital platforms. This shift from conventional liabilities to tokenized debt improves efficiency in money management by reducing intermediaries and enabling real-time settlement.
Risk Assessment: Traditional Liabilities vs Digital Debt Instruments
Traditional liabilities often involve fixed obligations with clearly defined terms, making risk assessment more straightforward through conventional credit analysis and collateral evaluation methods. Tokenized debt instruments introduce complexities such as liquidity volatility, smart contract dependency, and regulatory uncertainty, requiring enhanced risk models that incorporate blockchain transparency and cyber-security factors. Effective money management demands balancing the predictability of traditional liabilities against the innovative but dynamic risk profile of digital debt instruments.
Regulatory Implications for Liabilities and Tokenized Debt
Regulatory implications for liabilities involve strict adherence to accounting standards, financial reporting, and legal obligations to ensure transparent debt management and creditor protection. Tokenized debt introduces complexities with securities regulations, digital asset custody, and cross-jurisdictional compliance due to its blockchain-based nature and programmable features. Financial institutions must navigate evolving frameworks from entities like the SEC and FINRA to address investor protection, anti-money laundering (AML), and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements in both traditional liabilities and tokenized debt structures.
Efficiency and Transparency in Tokenized Debt Management
Tokenized debt enhances efficiency in money management by automating repayment schedules and reducing intermediaries through blockchain technology. This transparency allows real-time tracking of debt ownership and transaction history, minimizing disputes and improving auditability. Compared to traditional liabilities, tokenized debt promotes faster settlements and lowers operational costs, fostering trust among stakeholders.
How Tokenized Debt Reshapes Financial Reporting
Tokenized debt transforms financial reporting by enabling real-time tracking and enhanced transparency of liabilities on distributed ledgers, reducing reconciliation errors and improving auditability. This technology provides precise documentation of debt ownership and payment history, facilitating automated compliance and streamlined accounting processes. By digitizing debt instruments, organizations gain clearer visibility into obligations, enhancing risk management and decision-making accuracy in money management.
Security Concerns: Liability Systems vs Blockchain-Based Debt
Liability systems often face security vulnerabilities due to centralized data storage and potential single points of failure, increasing risks of fraud and unauthorized access. Blockchain-based tokenized debt utilizes decentralized ledgers and cryptographic protections, offering enhanced transparency and reduced susceptibility to hacking. The immutable nature of blockchain records provides stronger audit trails and mitigates common liability concerns in traditional financial management frameworks.
Adoption Challenges: From Liabilities to Tokenized Debt
Adoption challenges in transitioning from traditional liabilities to tokenized debt include regulatory uncertainty, technological integration, and market acceptance. Financial institutions face hurdles in aligning blockchain-based debt instruments with existing compliance frameworks and risk management practices. Overcoming these barriers requires standardized protocols, enhanced transparency, and collaboration between regulators, technology providers, and market participants.
Future Outlook: The Evolution of Money Management Through Tokenization
Tokenized debt represents a transformative shift in money management by converting traditional liabilities into programmable digital assets on blockchain platforms, enhancing transparency and liquidity. This evolution enables real-time tracking, fractional ownership, and automated compliance, significantly reducing administrative costs and counterparty risks associated with conventional liabilities. As tokenization gains regulatory clarity and adoption, future financial ecosystems will likely prioritize decentralized and efficient debt instruments, reshaping liability management toward greater accessibility and innovation.
Related Important Terms
Programmable Liability
Programmable liability enhances traditional debt management by enabling automated, transparent, and conditional repayments through smart contracts on blockchain networks, reducing default risks and administrative costs. Tokenized debt transforms liabilities into digital assets that can be traded or split, improving liquidity and enabling more efficient money management strategies.
Tokenized Debt Instruments
Tokenized debt instruments leverage blockchain technology to enhance transparency and liquidity in financial portfolios, offering fractional ownership and streamlined settlement processes unlike traditional liabilities that rely on conventional debt frameworks. This innovation in money management allows for efficient tracking, reduced counterparty risk, and improved access to diverse investors through digitized asset representation.
Automated Debt Reconciliation
Automated debt reconciliation streamlines liability tracking by integrating tokenized debt on blockchain platforms, ensuring real-time accuracy and transparency in financial records. This technology reduces manual errors and accelerates cash flow management, enhancing overall efficiency in money management systems.
Fractionalized Liability Tokens
Fractionalized Liability Tokens enable precise risk distribution by converting traditional liabilities into divisible digital assets, enhancing transparency and liquidity in debt management. This tokenized approach streamlines obligations tracking, reduces counterparty risk, and facilitates flexible financial strategies compared to conventional liability frameworks.
Smart Contract Liabilities
Smart contract liabilities streamline money management by automating debt obligations through blockchain technology, ensuring transparency and reducing counterparty risk compared to traditional tokenized debt instruments. These liabilities enable programmable, self-executing financial contracts that enforce repayment terms without intermediaries, enhancing security and efficiency in digital asset management.
Decentralized Debt Pools
Decentralized Debt Pools offer enhanced transparency and security compared to traditional liabilities by leveraging blockchain technology to tokenize debt instruments, enabling fractional ownership and automated smart contract enforcement. Tokenized debt increases liquidity and reduces counterparty risk, transforming conventional liability management into a more efficient, decentralized financial ecosystem.
Liability Token Swap
Liability token swaps enable efficient restructuring of debt obligations by converting traditional liabilities into digital tokens, enhancing transparency and liquidity for money management. This innovative approach streamlines repayment processes and reduces counterparty risk by facilitating seamless trading and settlement on blockchain platforms.
On-chain Liability Management
On-chain liability management leverages blockchain technology to enhance transparency and automation in distinguishing traditional liabilities from tokenized debt instruments, enabling real-time tracking and efficient repayment processes. Tokenized debt offers programmable conditions and fractional ownership, reducing counterparty risk compared to conventional liability frameworks while streamlining financial operations through smart contracts.
Cross-chain Debt Settlement
Cross-chain debt settlement enables seamless liability management by allowing tokenized debt instruments to be settled across multiple blockchain networks, reducing counterparty risk and enhancing liquidity. This approach leverages decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to optimize debt repayment processes and improve transparency in cross-chain financial transactions.
Real-World Asset (RWA) Tokenization
Tokenized debt transforms traditional liabilities by converting real-world assets (RWA) into digital tokens, enabling fractional ownership, enhanced liquidity, and transparent transaction records on blockchain platforms. This innovation streamlines money management by reducing counterparty risk and improving asset traceability compared to conventional liability structures.
Liability vs Tokenized Debt for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com