Liability in traditional lending often places the borrower directly responsible for repayment, increasing personal financial risk. Peer-to-peer lending distributes risk among multiple individual investors, potentially lowering liability exposure for borrowers. Choosing between liability and peer-to-peer lending depends on balancing risk tolerance and control over money management strategies.
Table of Comparison
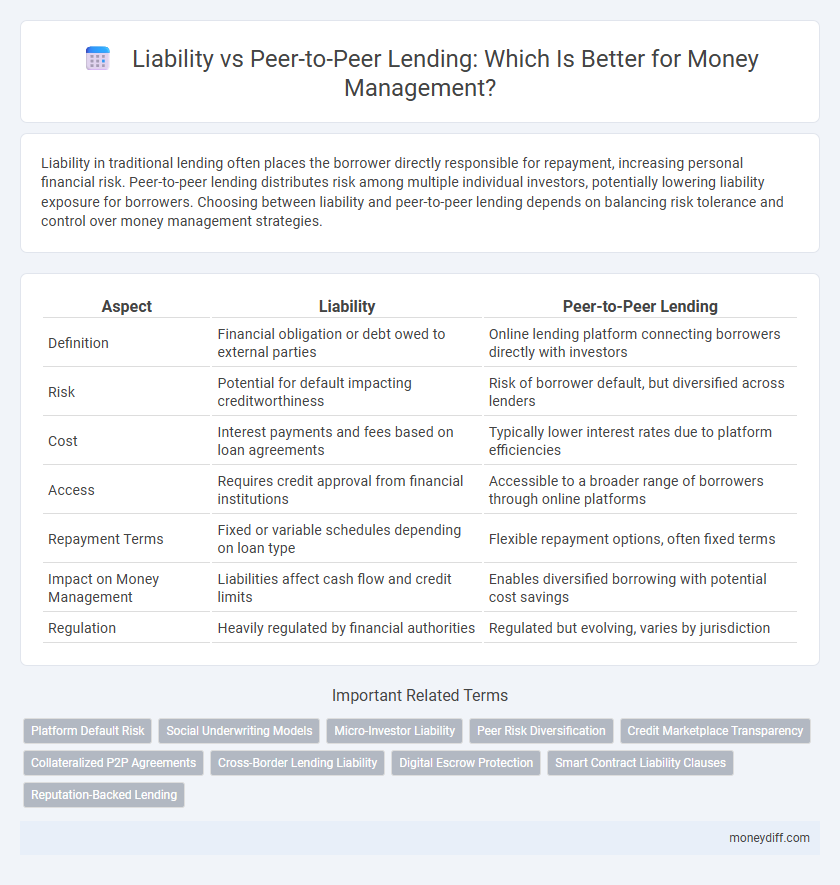
| Aspect | Liability | Peer-to-Peer Lending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial obligation or debt owed to external parties | Online lending platform connecting borrowers directly with investors |
| Risk | Potential for default impacting creditworthiness | Risk of borrower default, but diversified across lenders |
| Cost | Interest payments and fees based on loan agreements | Typically lower interest rates due to platform efficiencies |
| Access | Requires credit approval from financial institutions | Accessible to a broader range of borrowers through online platforms |
| Repayment Terms | Fixed or variable schedules depending on loan type | Flexible repayment options, often fixed terms |
| Impact on Money Management | Liabilities affect cash flow and credit limits | Enables diversified borrowing with potential cost savings |
| Regulation | Heavily regulated by financial authorities | Regulated but evolving, varies by jurisdiction |
Understanding Liability in Money Management
Liability in money management refers to financial obligations or debts that an individual or organization is responsible for repaying, impacting overall financial health and creditworthiness. In contrast to peer-to-peer lending, where borrowers obtain funds directly from investors often with flexible terms, liabilities represent formal commitments like loans, mortgages, or credit card balances that require careful tracking and repayment. Understanding and managing liabilities effectively is crucial for maintaining cash flow, avoiding default risks, and optimizing financial planning strategies.
What is Peer-to-Peer Lending?
Peer-to-peer lending is a financial arrangement where individuals lend money directly to other individuals without involving traditional financial institutions, reducing intermediary liabilities. This method allows borrowers to access funds at potentially lower interest rates while lenders can earn returns by assuming credit risk. Unlike conventional loans, peer-to-peer lending platforms manage borrower-lender matching and risk assessment, shifting certain liabilities away from banks to the platform and participants.
Key Differences: Liability vs Peer-to-Peer Lending
Liability represents a financial obligation or debt that an individual or entity must repay, often incurring interest and impacting creditworthiness. Peer-to-peer lending involves individuals lending money directly to borrowers through online platforms, reducing reliance on traditional financial institutions and often offering lower interest rates. The key difference lies in liability being the borrower's debt responsibility, while peer-to-peer lending is a decentralized method of funding that connects lenders and borrowers without intermediary banks.
Risk Assessment in Liability and P2P Lending
Risk assessment in liability involves evaluating potential financial obligations and the likelihood of legal claims that could affect an individual or organization's assets. In peer-to-peer lending, risk assessment centers on the creditworthiness of borrowers and the probability of default, impacting both lenders' returns and the stability of the lending platform. Effective risk management strategies in both domains rely on thorough analysis of historical data, borrower profiles, and market conditions to mitigate potential losses.
Returns: Liability Strategies vs P2P Lending Yields
Liability strategies typically involve predictable, lower-risk returns such as fixed interest payments on loans or bonds, providing stability in money management. Peer-to-peer lending yields often offer higher returns by directly matching borrowers with lenders, but these come with increased credit risk and less liquidity. Evaluating returns requires balancing the consistent cash flow of liability instruments against the potentially higher but variable yields from P2P lending platforms.
Regulatory Considerations for Liability and P2P Lending
Regulatory considerations for liability in traditional finance involve stringent compliance with federal and state laws designed to protect consumers and manage risk exposure. Peer-to-peer lending platforms operate under evolving regulatory frameworks that focus on transparency, borrower protection, and anti-fraud measures, often requiring registration with financial authorities like the SEC or FCA. Understanding the differing liabilities in these domains is crucial for both investors and borrowers to navigate legal responsibilities and minimize financial risks.
Diversification Opportunities in P2P Lending and Liability
Diversification opportunities in peer-to-peer lending allow investors to spread risk across multiple borrowers, reducing exposure to individual defaults compared to traditional liabilities tied to singular debt obligations. P2P lending platforms provide access to varied credit profiles and loan terms, enhancing portfolio resilience and potential returns through broader market participation. Managing liabilities through diversified P2P investments can optimize cash flow balance and mitigate concentrated risk inherent in conventional lending liabilities.
Impact on Personal Credit and Financial Health
Liability in peer-to-peer lending directly affects personal credit as borrowers are fully responsible for timely repayments, which, if missed, can significantly lower credit scores and damage financial health. Unlike traditional loans, peer-to-peer lending often lacks formal guarantees, increasing personal risk and potential liabilities for borrowers. Proper management of these liabilities is crucial to maintaining strong creditworthiness and overall financial stability.
Suitability for Different Investor Profiles
Liability considerations differ significantly between traditional lending and peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, impacting investor suitability based on risk tolerance and financial goals. Traditional lending often involves institutions with established credit risk assessments, making it suitable for conservative investors prioritizing stable returns and lower default risk. In contrast, P2P lending exposes investors to higher default probabilities and less regulatory oversight, aligning better with risk-tolerant investors seeking diversified portfolios and potentially higher yields.
Choosing Between Liability and Peer-to-Peer Lending
Choosing between liability and peer-to-peer lending for money management depends on assessing risk exposure and financial obligations. Liability involves fixed repayment terms and potential legal consequences for defaults, whereas peer-to-peer lending offers more flexible borrowing options but may involve higher interest rates and variable risk profiles. Prioritizing creditworthiness, repayment capacity, and interest cost helps in making an informed decision aligned with personal financial goals.
Related Important Terms
Platform Default Risk
Platform default risk in peer-to-peer lending directly impacts investor liability by increasing the potential for complete loss of funds, unlike traditional liabilities backed by regulated financial institutions. The absence of federal insurance or guarantees elevates the risk profile, requiring stringent due diligence and risk assessment before investment.
Social Underwriting Models
Social underwriting models reduce liability risks in peer-to-peer lending by leveraging personal data and social networks to assess borrower creditworthiness beyond traditional financial metrics. These models enhance money management by enabling more accurate risk prediction and fostering trust among lenders, minimizing default rates and potential financial losses.
Micro-Investor Liability
Micro-investor liability in peer-to-peer lending is typically limited to the amount invested, reducing personal financial risk compared to traditional liability models. This limited liability framework encourages smaller investors to participate without the fear of losing beyond their principal investment.
Peer Risk Diversification
Peer-to-peer lending mitigates liability risk through peer risk diversification by spreading investments across multiple borrowers, reducing exposure to any single default. In contrast, traditional liability-based lending concentrates risk, potentially amplifying losses without the benefit of diversified credit profiles.
Credit Marketplace Transparency
Liability in traditional lending often involves opaque credit terms and centralized risk allocation, whereas peer-to-peer lending platforms enhance credit marketplace transparency by providing clear borrower profiles, interest rates, and risk assessments directly to investors. This increased visibility in peer-to-peer lending reduces information asymmetry, enabling more informed decision-making and effective money management.
Collateralized P2P Agreements
Collateralized peer-to-peer lending agreements mitigate liability risks by securing loans with tangible assets, ensuring lender protection in case of default. This structure contrasts traditional liability frameworks by directly linking borrower obligations to collateral value, enhancing financial accountability and risk management.
Cross-Border Lending Liability
Cross-border lending liability involves complex legal and regulatory risks due to differing jurisdictional requirements and enforcement mechanisms, which can significantly impact peer-to-peer lending platforms. Unlike traditional liability frameworks, peer-to-peer lending exposes lenders and borrowers to increased uncertainty and potential disputes arising from international loan agreements and currency fluctuations.
Digital Escrow Protection
Digital escrow protection in peer-to-peer lending significantly reduces liability risks by securely holding funds until all contractual conditions are met, ensuring transparent transaction management. This technology minimizes fraud exposure and enforces accountability, setting it apart from traditional liability frameworks in conventional lending.
Smart Contract Liability Clauses
Smart contract liability clauses in peer-to-peer lending automate dispute resolution and enforce repayment terms, significantly reducing traditional liability risks for both lenders and borrowers. These clauses provide transparent and immutable contractual obligations, minimizing ambiguities and potential legal disputes in money management agreements.
Reputation-Backed Lending
Reputation-backed lending leverages borrower credibility to reduce liability risks, contrasting traditional peer-to-peer lending where default risk primarily impacts investors directly. This model enhances trust and accountability, minimizing financial exposure and fostering sustainable money management.
Liability vs Peer-to-Peer Lending for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com