Liability pet refers to financial obligations that can impact money management, distinguishing between general liabilities and green debt is crucial for optimizing financial health. Liability encompasses all debts and financial responsibilities, while green debt specifically targets eco-friendly investments or sustainable projects, often carrying unique incentives or benefits. Understanding the differences allows better allocation of funds, balancing risk with opportunities for environmental impact and potential cost savings.
Table of Comparison
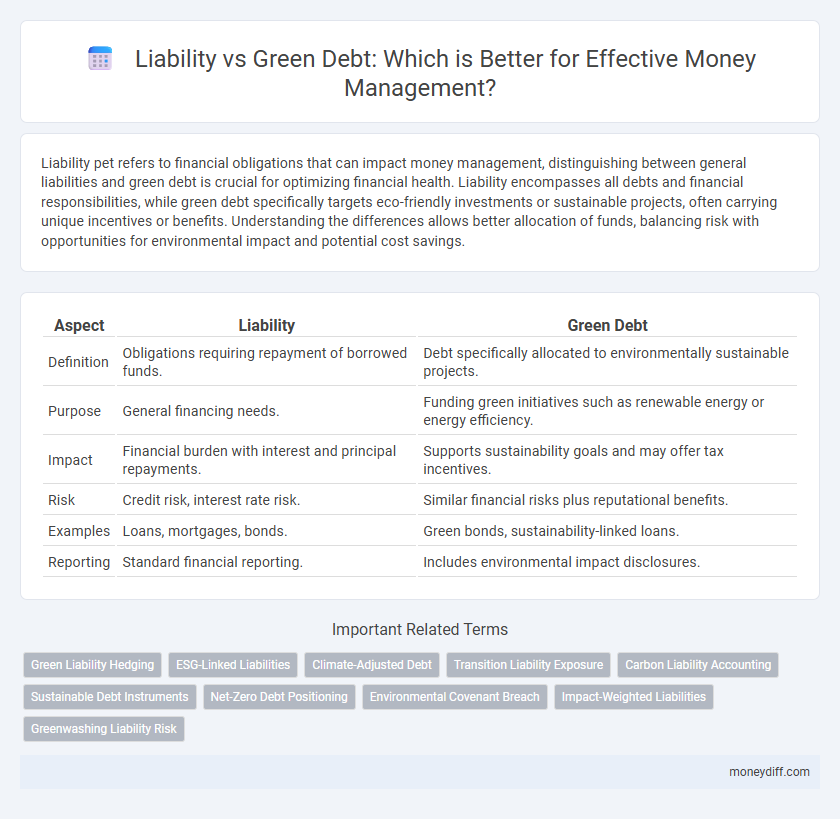
| Aspect | Liability | Green Debt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Obligations requiring repayment of borrowed funds. | Debt specifically allocated to environmentally sustainable projects. |
| Purpose | General financing needs. | Funding green initiatives such as renewable energy or energy efficiency. |
| Impact | Financial burden with interest and principal repayments. | Supports sustainability goals and may offer tax incentives. |
| Risk | Credit risk, interest rate risk. | Similar financial risks plus reputational benefits. |
| Examples | Loans, mortgages, bonds. | Green bonds, sustainability-linked loans. |
| Reporting | Standard financial reporting. | Includes environmental impact disclosures. |
Understanding Liability in Money Management
Liability in money management represents financial obligations or debts a person or business owes to others, crucial for assessing overall financial health and risk exposure. Understanding liability involves distinguishing between secured and unsecured debts, interest rates, repayment terms, and their impact on cash flow and creditworthiness. Comparing liability to green debt highlights how traditional liabilities prioritize cost and risk, whereas green debt integrates environmental impact with financial responsibility.
What is Green Debt?
Green debt refers to financial obligations incurred specifically to fund environmentally sustainable projects, such as renewable energy installations or energy-efficient infrastructure. Unlike traditional liabilities, green debt aligns with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, appealing to investors seeking to support eco-friendly initiatives. Managing green debt involves assessing both financial returns and the positive environmental impact, integrating sustainability goals into overall money management strategies.
Key Differences Between Liability and Green Debt
Liability refers to any financial obligation or debt a company owes, typically encompassing loans, accounts payable, and other forms of borrowed money. Green debt specifically targets funds raised through bonds or loans designated for environmentally sustainable projects, aligning financial practices with ecological goals. The key differences lie in purpose and reporting requirements: liabilities are general obligations without a specific use, while green debt supports sustainable initiatives and often includes transparency on environmental impact.
Financial Impact of Liabilities vs Green Debt
Liabilities represent financial obligations that can reduce net worth and increase risk due to interest payments and repayment schedules, impacting cash flow and creditworthiness. Green debt, a subset of liabilities, often carries favorable terms such as lower interest rates and tax incentives, promoting sustainable investment while potentially enhancing a company's financial stability. Assessing the financial impact involves comparing the cost of capital, risk-adjusted returns, and long-term benefits associated with conventional liabilities versus green debt instruments.
Risk Assessment: Liability vs Green Debt
Risk assessment for liability versus green debt involves evaluating financial obligations with different environmental and regulatory implications. Traditional liabilities often carry generic credit and market risks, while green debt incorporates sustainability criteria that may reduce regulatory risk but introduce project-specific environmental performance uncertainties. Effective money management requires balancing these risks by analyzing potential impacts on cash flow, compliance costs, and reputational factors tied to green debt investments.
Sustainable Finance: The Role of Green Debt
Green debt plays a pivotal role in sustainable finance by providing funds specifically earmarked for environmentally friendly projects, which contrasts with traditional liabilities that often support conventional, non-sustainable investments. These financial instruments enable organizations to align their capital structure with sustainability goals, reducing carbon footprints while maintaining fiscal responsibility. By prioritizing green debt, companies can attract ESG-focused investors and contribute to environmental stewardship, distinguishing their balance sheets in the evolving landscape of responsible money management.
Cost Implications in Liability and Green Debt
Liability in money management often involves fixed interest rates that can lead to predictable but sometimes higher overall costs compared to green debt, which typically benefits from lower interest rates due to environmental incentives and subsidies. Green debt reduces the cost of capital by leveraging government-backed tax credits and grants, decreasing the financial burden on borrowers while promoting sustainable investments. Companies managing liabilities with green debt can optimize their cost structure by aligning financial strategies with sustainability goals, resulting in potential long-term savings and enhanced creditworthiness.
Strategic Money Management Using Green Debt
Strategic money management leverages green debt to align financial liabilities with sustainable development goals, reducing environmental risk exposure while enhancing creditworthiness. Integrating green debt instruments into liability portfolios enables organizations to access favorable borrowing terms and investor interest driven by environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. This approach not only optimizes capital structure but also supports long-term value creation through responsible investment and risk mitigation.
Long-Term Effects of Liability vs Green Debt
Long-term liability impacts financial stability by increasing debt obligations that may limit future borrowing capacity and reduce cash flow flexibility, potentially raising the cost of capital. Green debt, often tied to sustainable projects, can enhance a company's credit profile through favorable interest rates and incentives while promoting environmental responsibility. Over time, green debt may contribute to improved asset valuation and risk mitigation, contrasting with conventional liabilities that typically impose higher financial strain.
Choosing the Right Debt Instrument for Your Portfolio
Evaluating liability versus green debt involves assessing risk profiles, interest rates, and environmental impact to optimize portfolio performance. Green debt offers ESG-aligned benefits and potential tax incentives, enhancing responsible investing strategies while mitigating traditional liability risks. Selecting the appropriate debt instrument depends on balancing financial returns with sustainability goals to achieve long-term portfolio resilience.
Related Important Terms
Green Liability Hedging
Green liability hedging strategically offsets environmental risk exposure by aligning debt instruments with sustainable assets, minimizing climate-related financial volatility. Effective green liability management enhances a company's credit profile and supports compliance with evolving ESG regulations while fostering long-term fiscal resilience.
ESG-Linked Liabilities
ESG-linked liabilities integrate environmental, social, and governance criteria into debt instruments, aligning financial obligations with sustainability targets and reducing long-term risk exposure. Unlike traditional liabilities, green debt specifically finances projects with measurable environmental benefits, offering increased transparency and potentially favorable financing terms for companies committed to ESG principles.
Climate-Adjusted Debt
Climate-adjusted debt incorporates environmental risk factors into traditional liability assessments, providing a more accurate reflection of potential financial losses linked to climate change. This approach enables businesses to manage green debt more effectively by aligning their liabilities with sustainability goals and regulatory frameworks.
Transition Liability Exposure
Transition liability exposure refers to financial risks companies face when shifting from traditional to sustainable practices, impacting both conventional liabilities and green debt portfolios. Effective money management requires balancing transition liabilities with green debt to optimize funding costs and mitigate regulatory or market-related risks during the sustainability transition.
Carbon Liability Accounting
Carbon liability accounting quantifies an entity's financial obligation tied to greenhouse gas emissions, distinguishing it from green debt, which represents funds raised specifically for environmentally sustainable projects. Effective money management requires integrating carbon liabilities into balance sheets to assess true environmental impact and regulatory risks, ensuring accurate financial reporting and strategic carbon reduction investments.
Sustainable Debt Instruments
Sustainable debt instruments, such as green bonds, offer targeted financing for environmentally-friendly projects, distinguishing them from traditional liabilities by aligning financial returns with sustainability goals. These instruments reduce the issuer's carbon footprint while attracting investors prioritizing ESG criteria, enhancing long-term value and risk management in money management strategies.
Net-Zero Debt Positioning
Liability management prioritizes reducing financial obligations, while green debt targets funding specifically for environmentally sustainable projects, both critical for achieving a net-zero debt positioning that balances fiscal responsibility with carbon reduction goals. Effective net-zero debt strategies leverage green bonds and sustainable financing instruments to minimize carbon footprints while maintaining manageable liabilities.
Environmental Covenant Breach
Liability related to environmental covenant breaches often results in significant financial obligations compared to green debt, which is structured to fund sustainable projects with predefined environmental benefits. Managing liabilities from covenant violations involves addressing remediation costs and potential regulatory penalties, whereas green debt supports proactive environmental improvements that mitigate long-term risk exposure.
Impact-Weighted Liabilities
Impact-weighted liabilities integrate environmental and social costs into financial obligations, providing a more comprehensive measure than traditional liability accounting. This approach enables companies to manage green debt more effectively by quantifying the real-world consequences of their borrowing on sustainability goals.
Greenwashing Liability Risk
Liability in money management involves obligations that can expose companies to financial risks, with Green Debt specifically tied to environmentally focused financing that requires stringent compliance to avoid misleading claims. Greenwashing liability risk arises when organizations inaccurately represent the environmental benefits of their green debt, potentially resulting in legal penalties, reputational damage, and loss of investor trust.
Liability vs Green Debt for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com