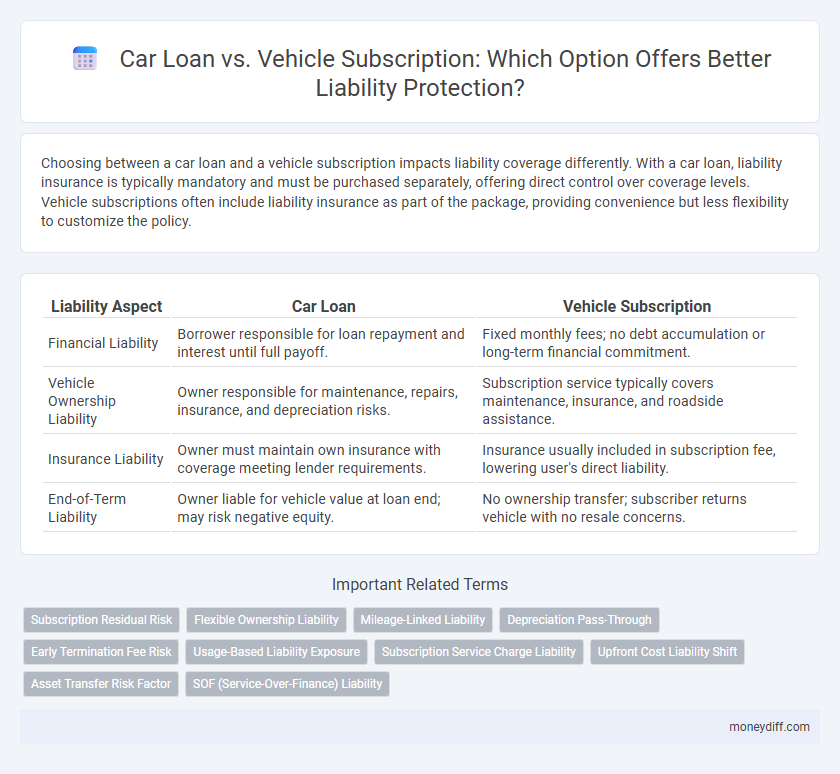
Choosing between a car loan and a vehicle subscription impacts liability coverage differently. With a car loan, liability insurance is typically mandatory and must be purchased separately, offering direct control over coverage levels. Vehicle subscriptions often include liability insurance as part of the package, providing convenience but less flexibility to customize the policy.
Table of Comparison
| Liability Aspect | Car Loan | Vehicle Subscription |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Liability | Borrower responsible for loan repayment and interest until full payoff. | Fixed monthly fees; no debt accumulation or long-term financial commitment. |
| Vehicle Ownership Liability | Owner responsible for maintenance, repairs, insurance, and depreciation risks. | Subscription service typically covers maintenance, insurance, and roadside assistance. |
| Insurance Liability | Owner must maintain own insurance with coverage meeting lender requirements. | Insurance usually included in subscription fee, lowering user's direct liability. |
| End-of-Term Liability | Owner liable for vehicle value at loan end; may risk negative equity. | No ownership transfer; subscriber returns vehicle with no resale concerns. |
Understanding Car Loans as Financial Liabilities
Car loans represent a fixed financial liability where borrowers are responsible for monthly payments that include principal and interest over a set term, directly impacting credit profiles and debt-to-income ratios. Unlike vehicle subscriptions that function as operational expenses with less long-term liability and flexibility, car loans require ownership responsibility and potential depreciation risks. Understanding the detailed loan agreement terms, including interest rates and penalties, is crucial for managing financial liability effectively.
Vehicle Subscription: A New Liability Model
Vehicle subscription introduces a new liability model by shifting responsibility from the user to the service provider, reducing the subscriber's financial and legal risks compared to traditional car loans. Unlike car loans, where owners bear full liability for damages, maintenance, and depreciation, subscriptions often include comprehensive insurance and maintenance within the monthly fee. This model minimizes liability exposure and offers predictable costs, making it a strategic alternative for individuals seeking reduced ownership risks.
Upfront Costs: Car Loan vs Vehicle Subscription
Car loans typically require a substantial upfront down payment, contributing to higher initial liability for borrowers compared to vehicle subscriptions. Vehicle subscriptions often involve lower or no upfront costs, reducing immediate financial liability while providing flexibility through monthly fees that cover insurance and maintenance. This distinction significantly impacts the overall liability exposure and cash flow management for consumers choosing between financing options.
Monthly Payments and Financial Commitment
Car loans typically require monthly payments that include principal, interest, and fees, resulting in a long-term financial commitment that affects your liability over several years. Vehicle subscriptions offer a more flexible monthly fee that often covers insurance, maintenance, and taxes, reducing the risk of unexpected expenses and simplifying liability management. Choosing between the two depends on your preference for predictable costs and the duration of your financial obligation.
Ownership vs Usage: Asset and Liability Implications
Car loans transfer vehicle ownership to the borrower, making the car an asset on the balance sheet but also a liability due to monthly loan payments and interest obligations. Vehicle subscriptions provide usage rights without transferring ownership, eliminating the asset from the subscriber's balance sheet and reducing long-term liabilities. This distinction impacts financial statements, with loans increasing debt ratios while subscriptions streamline liability exposure and enhance cash flow flexibility.
Depreciation Impact on Personal Finances
Car loans increase liability through depreciation, as vehicle value declines faster than the loan balance may reduce, leading to potential negative equity and financial strain. Vehicle subscriptions mitigate this risk by spreading depreciation costs into monthly fees, preventing ownership of a rapidly losing asset. Managing liability with a subscription model offers predictable expenses and shields personal finances from unexpected depreciation losses.
Liability Exposure: Maintenance and Repairs
Car loans typically place full liability for maintenance and repairs on the borrower, increasing exposure to unexpected costs and potential insurance claims. Vehicle subscriptions often include maintenance and repair services as part of the monthly fee, significantly reducing financial liability and out-of-pocket expenses. This bundled approach shifts risk away from the consumer, minimizing liability exposure related to vehicle upkeep.
Insurance Considerations: Loan vs Subscription
Car loans often require borrowers to secure comprehensive insurance coverage to protect both the lender's and the owner's interests, typically leading to higher premiums. Vehicle subscriptions generally include insurance within the monthly fee, shifting liability and coverage responsibilities to the subscription provider, which simplifies the process for the user. This bundled insurance model often reduces out-of-pocket expenses and the complexities associated with maintaining separate policies.
Early Termination Fees and Financial Flexibility
Car loans typically incur early termination fees if the borrower pays off the loan ahead of schedule, reducing financial flexibility and potentially increasing overall costs. Vehicle subscription services offer greater financial adaptability with no long-term commitments and minimal early termination penalties, allowing users to switch or cancel without substantial fees. Evaluating early termination fees and financial flexibility is crucial when choosing between a car loan and a vehicle subscription for managing liability effectively.
Long-Term Liability: Which Option Minimizes Risk?
Car loans typically involve long-term liability through fixed monthly payments and ownership responsibilities, which can increase financial risk if the vehicle depreciates or if unexpected repair costs arise. Vehicle subscriptions minimize long-term liability by bundling maintenance, insurance, and depreciation risks into one predictable monthly fee, reducing exposure to unforeseen expenses. Choosing a vehicle subscription limits financial commitment and potential asset loss, making it a lower-risk option for minimizing long-term liability.
Related Important Terms
Subscription Residual Risk
Car loan borrowers retain full liability for the vehicle's residual value risk, facing potential depreciation losses upon sale or trade-in. In contrast, vehicle subscriptions shift residual risk to the service provider, minimizing financial exposure for subscribers but often at a higher recurring cost.
Flexible Ownership Liability
Flexible ownership liability in vehicle subscriptions limits personal financial responsibility to the subscription period, contrasting with car loans where owners assume full liability for damage, depreciation, and loan obligations. Subscription models often include comprehensive insurance and maintenance, reducing unexpected out-of-pocket costs and legal risks compared to traditional car ownership liabilities.
Mileage-Linked Liability
Car loans typically assign full financial liability to the borrower regardless of vehicle usage, while vehicle subscriptions offer mileage-linked liability models that adjust costs based on actual driven miles. This usage-based approach in vehicle subscriptions minimizes overpayment risks and provides more flexible financial responsibility aligned with the driver's mileage patterns.
Depreciation Pass-Through
Car loans transfer depreciation liability to the borrower, who bears the vehicle's value loss over time, impacting resale or trade-in value. Vehicle subscriptions mitigate depreciation risk by including it in monthly fees, shifting liability for value decline to the provider.
Early Termination Fee Risk
Car loans typically involve a fixed liability with potential early termination fees calculated on outstanding principal balances, increasing financial risk if the loan is paid off prematurely. Vehicle subscription services usually include termination fees within the contract, but these are often more predictable and may be lower than car loan penalties, reducing unexpected liability exposure.
Usage-Based Liability Exposure
Car loans involve direct ownership, making the borrower liable for all damages, repairs, and insurance claims related to the vehicle, with liability exposure increasing based on usage and risk factors. Vehicle subscriptions typically include insurance and maintenance, transferring some liability to the provider and reducing the subscriber's direct financial responsibility for usage-based incidents.
Subscription Service Charge Liability
Vehicle subscription service charge liability is typically limited to the monthly fee agreed upon in the contract, reducing unexpected financial exposure compared to car loans that require ongoing loan repayments and potential liabilities for depreciation, insurance, and maintenance costs. Subscription models often include insurance and maintenance in the fee, shifting liability for these costs away from the subscriber.
Upfront Cost Liability Shift
Car loans typically require a significant upfront down payment, increasing immediate financial liability for the borrower, whereas vehicle subscriptions often shift this liability by incorporating costs into a fixed monthly fee with minimal initial outlay. This structure reduces the upfront cost liability, providing more predictable expenses and less risk of large initial financial commitments.
Asset Transfer Risk Factor
Car loans involve direct ownership transfer, increasing asset transfer risk due to title and lien complexities, while vehicle subscriptions minimize this risk by retaining ownership with the provider, reducing liability exposure. Understanding the differences in asset transfer risk factors is crucial for managing potential financial liabilities associated with vehicle usage.
SOF (Service-Over-Finance) Liability
Car loans typically involve higher liability risks due to long-term financial obligations and depreciation impacting balance sheets, while vehicle subscriptions shift liability toward service providers by bundling maintenance and insurance, reducing direct consumer financial exposure. Service-over-finance (SOF) liability models prioritize flexible, usage-based payments which limit consumer liability and transfer asset depreciation risk to subscription companies, optimizing financial predictability.
Car Loan vs Vehicle Subscription for liability. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com