Liabilities represent financial obligations that reduce your net worth, while social borrowing involves borrowing money from friends or family with potentially less formal terms. Managing liabilities requires careful tracking and repayment to avoid interest and penalties, whereas social borrowing can offer flexible repayment options but may strain personal relationships. Effective money management balances these two by prioritizing the reduction of high-cost liabilities and maintaining clear communication in social borrowing situations.
Table of Comparison
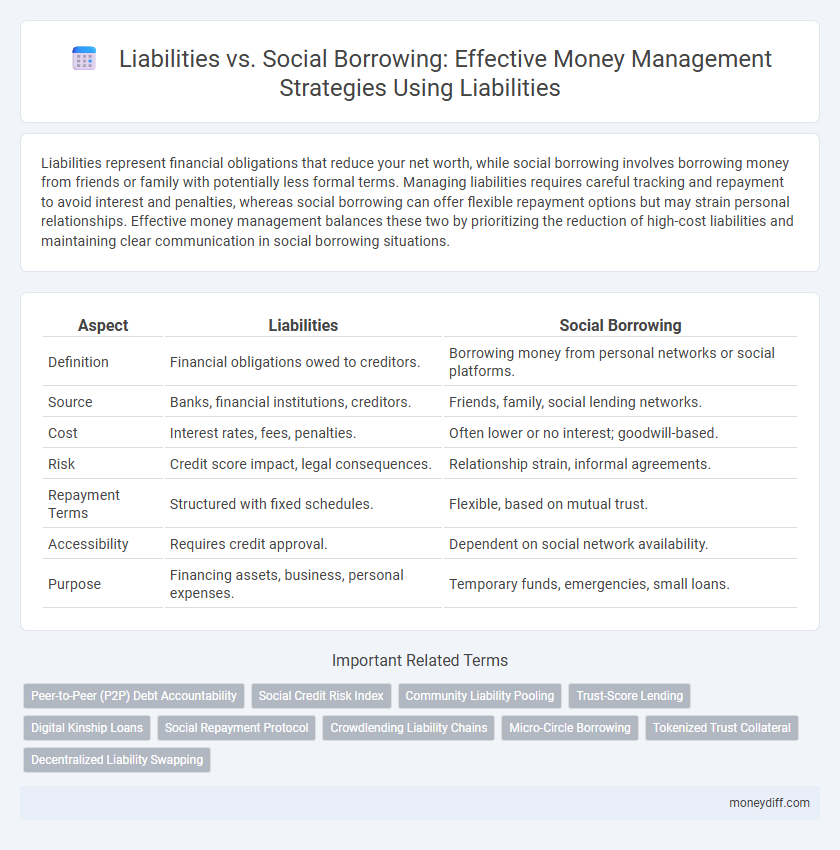
| Aspect | Liabilities | Social Borrowing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial obligations owed to creditors. | Borrowing money from personal networks or social platforms. |
| Source | Banks, financial institutions, creditors. | Friends, family, social lending networks. |
| Cost | Interest rates, fees, penalties. | Often lower or no interest; goodwill-based. |
| Risk | Credit score impact, legal consequences. | Relationship strain, informal agreements. |
| Repayment Terms | Structured with fixed schedules. | Flexible, based on mutual trust. |
| Accessibility | Requires credit approval. | Dependent on social network availability. |
| Purpose | Financing assets, business, personal expenses. | Temporary funds, emergencies, small loans. |
Understanding Liabilities in Personal Finance
Liabilities in personal finance represent financial obligations or debts owed to others, such as loans, credit card balances, and mortgages, which reduce net worth until fully repaid. Understanding liabilities is crucial for effective money management because they directly impact cash flow, creditworthiness, and financial stability. Social borrowing, often informal loans from friends or family, may lack formal terms but still constitutes liabilities that influence personal financial health and planning.
Social Borrowing: Definition and Key Characteristics
Social borrowing refers to obtaining funds through interpersonal networks rather than formal financial institutions, often involving loans from family, friends, or community groups. It is characterized by flexible repayment terms, lower or no interest rates, and a foundation of trust and social relationships. This informal lending approach contrasts with traditional liabilities, which typically involve formal agreements, fixed interest rates, and regulatory oversight.
Traditional Liabilities vs. Social Borrowing: Core Differences
Traditional liabilities involve formal financial obligations like loans or credit card debt with fixed repayment terms, interest rates, and legal enforcement. Social borrowing relies on informal agreements within personal networks, often based on trust rather than strict contractual terms, resulting in flexible repayment conditions. Core differences lie in the formality, regulatory oversight, and the source of funds, where traditional liabilities are institutionally driven and social borrowing is person-to-person based.
Financial Implications of Taking on Liabilities
Taking on liabilities impacts financial stability by increasing debt obligations, which can lead to higher interest expenses and reduced cash flow flexibility. Unlike social borrowing, liabilities often require formal repayment schedules and carry legal consequences for default. Proper assessment of liabilities ensures sustainable money management by balancing debt costs against potential asset growth or income generation.
The Pros and Cons of Social Borrowing
Social borrowing offers accessibility and often lower interest rates compared to traditional liabilities, making it a cost-effective method for managing finances. However, it carries risks such as potential damage to personal relationships and the absence of formal legal protections, which can complicate repayment terms. Careful consideration of these factors is essential to balance the financial benefits against the social and emotional costs involved in social borrowing.
Risk Factors: Liabilities Compared to Social Borrowing
Liabilities carry higher financial risk due to fixed repayment schedules and potential interest rate fluctuations, which can strain cash flow and increase default probability. Social borrowing often involves informal agreements with flexible terms, reducing immediate financial stress but potentially affecting personal relationships if obligations are unmet. Understanding these risk factors helps individuals and businesses make informed decisions about leveraging debt versus social credit for money management.
Credit Impact: Liabilities Versus Social Lending
Liabilities such as traditional loans and credit card debts directly affect credit scores by increasing debt-to-income ratios and payment obligations, often leading to higher interest rates and reduced borrowing capacity. Social borrowing through peer-to-peer lending platforms can offer alternative credit sources with potentially lower impact on traditional credit metrics, as some platforms report only after full repayment or utilize alternative credit assessments. Understanding the differential credit impact helps individuals manage their financial profiles effectively, balancing liabilities and social borrowing to optimize creditworthiness.
Strategies for Managing Financial Liabilities
Effective strategies for managing financial liabilities include prioritizing high-interest debts and consolidating loans to reduce overall interest costs. Implementing a structured repayment plan and regularly reviewing liabilities against income helps maintain a balanced cash flow. Leveraging social borrowing through trusted networks can offer flexible repayment terms but requires careful assessment to avoid strained relationships.
Social Borrowing: Best Practices and Potential Pitfalls
Social borrowing involves obtaining funds from personal connections such as friends or family, offering flexible repayment terms and often lower or no-interest rates compared to traditional liabilities like loans or credit cards. Best practices include clear communication, setting formal agreements, and maintaining transparency to prevent misunderstandings and preserve relationships. Potential pitfalls include strained relationships due to missed payments, lack of legal protections, and informal arrangements that may lead to financial complications.
Choosing Between Liabilities and Social Borrowing for Smart Money Management
Choosing between liabilities and social borrowing for smart money management requires evaluating interest rates, repayment terms, and credit impact. Liabilities like loans and credit cards often have fixed terms and interest, while social borrowing from friends or family may offer more flexible conditions but can strain relationships if not managed properly. Prioritizing clear communication and realistic repayment plans ensures financial stability and preserves personal connections.
Related Important Terms
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Debt Accountability
Liabilities represent financial obligations owed to external parties, whereas social borrowing through Peer-to-Peer (P2P) lending platforms facilitates direct debt accountability between individuals, reducing reliance on traditional institutions and enhancing transparency. P2P debt accountability leverages smart contracts and real-time tracking to ensure borrowers meet repayment schedules, effectively minimizing default risks and improving money management strategies.
Social Credit Risk Index
The Social Credit Risk Index evaluates individual and corporate liabilities by measuring the likelihood of default in social borrowing, providing a nuanced approach to managing financial obligations beyond traditional liabilities. This index enhances risk assessment accuracy by incorporating social trust metrics and repayment behavior patterns, facilitating more informed money management strategies.
Community Liability Pooling
Community Liability Pooling enhances money management by distributing financial risk across a network of individuals, contrasting with traditional liabilities that burden a single borrower with debt repayment. This collective approach reduces individual financial strain and fosters social borrowing mechanisms, promoting shared responsibility and improved access to credit.
Trust-Score Lending
Trust-Score Lending leverages social borrowing by utilizing individual trust metrics to assess creditworthiness, contrasting traditional liabilities that rely strictly on financial history and collateral. This innovative approach enhances money management by reducing default risk through personalized trust scores, enabling more flexible and equitable lending options.
Digital Kinship Loans
Digital Kinship Loans leverage social borrowing by formalizing financial support within trusted networks, reducing reliance on traditional liabilities like bank loans and credit cards. This method enhances money management by minimizing interest rates and fostering accountability through transparent digital platforms, which optimize both liquidity and relationship equity.
Social Repayment Protocol
The Social Repayment Protocol enhances money management by structuring liabilities through community-based lending and repayment mechanisms, reducing individual risk and fostering trust. This protocol shifts traditional liabilities into collaborative financial commitments, optimizing debt accountability and promoting transparent social borrowing practices.
Crowdlending Liability Chains
Crowdlending liability chains create interconnected financial obligations where each borrower's default risks cascading effects on subsequent lenders, amplifying systemic vulnerability compared to traditional liabilities. Efficient management of these liability chains requires transparent credit assessment and real-time monitoring to mitigate contagion and ensure sustainable social borrowing practices.
Micro-Circle Borrowing
Micro-circle borrowing, a localized form of social borrowing, involves small groups lending money within trusted networks, often minimizing interest rates and default risks compared to traditional liabilities. This method enhances community financial resilience by promoting informal credit access while reducing the need for formal liabilities with stringent repayment terms.
Tokenized Trust Collateral
Tokenized Trust Collateral transforms traditional liabilities into digitally secured assets, enabling transparent and efficient social borrowing frameworks that reduce risk and improve liquidity. By leveraging blockchain technology, tokenized collateral ensures verifiable ownership and facilitates peer-to-peer lending, optimizing money management within decentralized financial ecosystems.
Decentralized Liability Swapping
Decentralized Liability Swapping innovatively mitigates risks by enabling parties to exchange liabilities directly on blockchain platforms, enhancing transparency and reducing reliance on traditional social borrowing methods. This mechanism optimizes money management by leveraging smart contracts to automate liability transfers, minimize counterparty risks, and foster a more efficient decentralized financial ecosystem.
Liabilities vs Social Borrowing for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com