Liabilities in traditional money management represent fixed financial obligations owed to institutions, often involving strict repayment terms and potential penalties for default. Peer-to-peer lending obligations differ by facilitating direct borrowing between individuals, reducing intermediaries and potentially offering more flexible repayment options. Effective management of these liabilities requires understanding the risks and commitments unique to each, ensuring informed decision-making in personal finance.
Table of Comparison
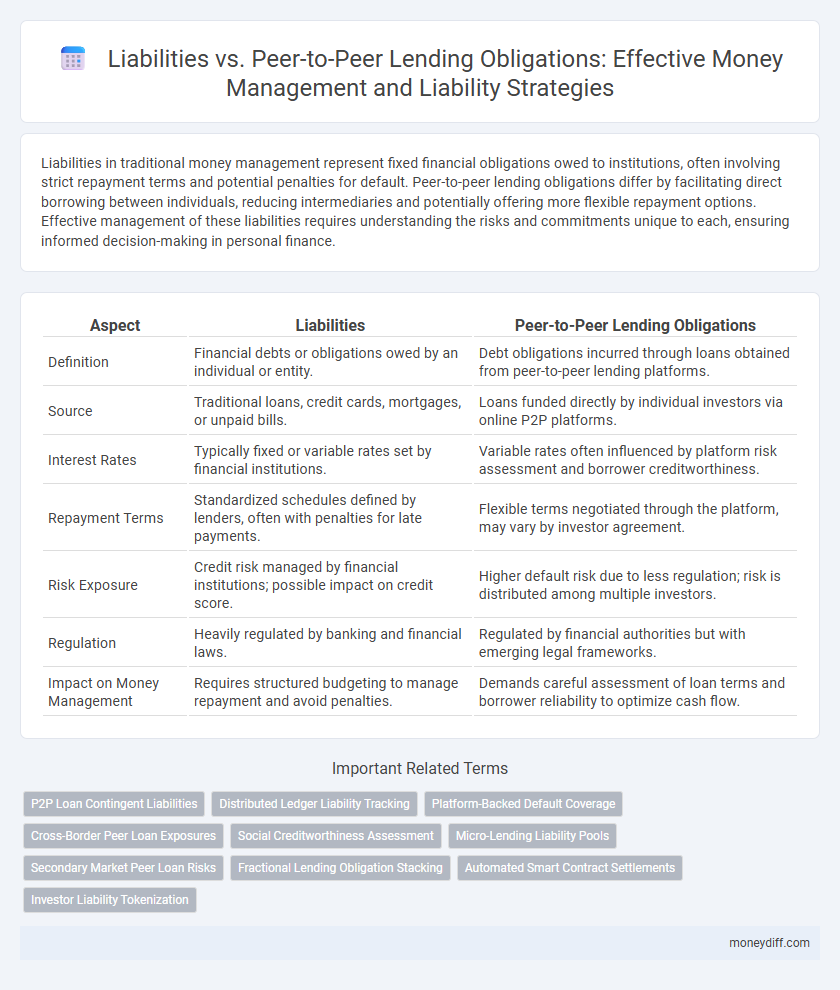
| Aspect | Liabilities | Peer-to-Peer Lending Obligations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial debts or obligations owed by an individual or entity. | Debt obligations incurred through loans obtained from peer-to-peer lending platforms. |
| Source | Traditional loans, credit cards, mortgages, or unpaid bills. | Loans funded directly by individual investors via online P2P platforms. |
| Interest Rates | Typically fixed or variable rates set by financial institutions. | Variable rates often influenced by platform risk assessment and borrower creditworthiness. |
| Repayment Terms | Standardized schedules defined by lenders, often with penalties for late payments. | Flexible terms negotiated through the platform, may vary by investor agreement. |
| Risk Exposure | Credit risk managed by financial institutions; possible impact on credit score. | Higher default risk due to less regulation; risk is distributed among multiple investors. |
| Regulation | Heavily regulated by banking and financial laws. | Regulated by financial authorities but with emerging legal frameworks. |
| Impact on Money Management | Requires structured budgeting to manage repayment and avoid penalties. | Demands careful assessment of loan terms and borrower reliability to optimize cash flow. |
Understanding Financial Liabilities: A Clear Definition
Financial liabilities represent monetary obligations that require repayment to creditors or lenders, forming a critical component of a balance sheet. Unlike peer-to-peer lending obligations, which are specific debts arising from direct borrower-to-lender agreements through online platforms, broader financial liabilities encompass loans, accounts payable, and other forms of debt. Understanding these distinctions aids in accurate financial analysis and effective money management strategies.
Peer-to-Peer Lending Obligations: What You Need to Know
Peer-to-peer lending obligations represent financial commitments where individuals borrow directly from other individuals through online platforms, bypassing traditional financial institutions. These obligations often carry specific terms regarding repayment schedules, interest rates, and risk factors distinct from conventional liabilities. Understanding the legal and financial implications of peer-to-peer lending obligations is essential for effective money management and minimizing potential defaults.
Key Differences Between Traditional Liabilities and P2P Lending
Traditional liabilities typically represent obligations to banks or financial institutions with fixed terms, interest rates, and regulatory oversight; peer-to-peer (P2P) lending obligations involve decentralized loans directly between individuals, often characterized by variable interest rates and less stringent regulation. P2P lending platforms use technology to match borrowers and lenders, reducing intermediaries and sometimes offering more flexible repayment options compared to conventional liabilities. Risk profiles differ as traditional liabilities generally have established credit assessments, whereas P2P lending carries higher default risk but allows for diversification across multiple peer loans.
Risk Assessment: Liabilities vs P2P Lending Commitments
Risk assessment of liabilities involves evaluating fixed financial obligations and potential default impacts on overall creditworthiness. Peer-to-peer lending commitments require analyzing borrower credit profiles and platform-specific risks, including liquidity and platform solvency. Understanding the differences between traditional liabilities and P2P obligations helps optimize risk management strategies in money management portfolios.
Interest Rates: Traditional Loans vs Peer-to-Peer Lending
Interest rates for traditional loans typically range from 5% to 15%, influenced by credit scores and banking regulations, while peer-to-peer lending platforms often offer rates between 6% and 12%, depending on borrower risk profiles. Peer-to-peer lending can provide competitive interest rates due to reduced overhead costs and direct investor-borrower connections. Effective money management requires evaluating these interest rate differences to minimize liabilities and optimize borrowing costs.
Legal Implications of Liabilities and P2P Lending Obligations
Liabilities encompass legally binding financial obligations owed to creditors, including loans, accounts payable, and other debts, while Peer-to-Peer (P2P) lending obligations arise from contracts between individual lenders and borrowers facilitated through online platforms. Legal implications of liabilities demand strict adherence to regulatory frameworks such as the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) and local commercial laws, ensuring enforceability and creditor protection. In contrast, P2P lending obligations involve compliance with securities regulations, consumer protection laws, and data privacy statutes, with platform operators often acting as intermediaries to mitigate risks and ensure transparent transaction processes.
Impact on Credit Score: Liability vs Peer-to-Peer Loans
Liabilities such as credit card debt, mortgages, and personal loans directly affect credit scores by influencing credit utilization, payment history, and debt-to-income ratios. Peer-to-peer lending obligations impact credit scores based on timely repayments reported to credit bureaus, with missed payments potentially causing significant score drops similar to traditional liabilities. Understanding these differences helps in managing creditworthiness effectively and optimizing financial health.
Debt Management Strategies for Liabilities and P2P Lending
Effective debt management strategies differentiate between traditional liabilities and peer-to-peer (P2P) lending obligations by prioritizing structured repayment plans and monitoring interest rates. Managing liabilities involves consolidating high-interest debts and maintaining a healthy credit score to reduce borrowing costs, while P2P lending requires careful assessment of borrower risk profiles and diversification to minimize default risks. Leveraging automated payment systems and negotiating loan terms enhances overall financial stability and optimizes cash flow management in both scenarios.
How to Prioritize Payments: Traditional Debts vs P2P Loans
Prioritizing payments between traditional liabilities and peer-to-peer (P2P) lending obligations depends on interest rates, penalties, and credit impact; conventional debts like credit cards or mortgages usually demand higher priority due to established legal consequences and credit score effects. P2P loans often offer flexible terms but should be managed to avoid default risk and preserve peer relationships. Strategic prioritization involves assessing payment schedules, negotiating terms with lenders, and targeting high-interest liabilities first to optimize overall money management.
Financial Planning Tips: Balancing Liabilities and P2P Obligations
Effective financial planning requires distinguishing traditional liabilities such as loans and credit card debts from peer-to-peer (P2P) lending obligations, as the latter often involve flexible terms and variable risk profiles. Prioritize assessing interest rates and repayment schedules to balance high-interest liabilities against potentially lower-cost P2P loans, optimizing overall debt management strategies. Maintaining a diversified approach by monitoring cash flow impact and adjusting payment prioritization enhances financial stability and reduces default risk.
Related Important Terms
P2P Loan Contingent Liabilities
Peer-to-peer (P2P) loan contingent liabilities arise when lenders are exposed to potential defaults, creating off-balance-sheet risks that traditional liabilities do not typically encompass. Effective money management requires monitoring these contingent obligations closely to mitigate financial exposure and maintain liquidity amidst unpredictable borrower repayment behaviors.
Distributed Ledger Liability Tracking
Distributed ledger technology enhances liability tracking by providing transparent, immutable records of peer-to-peer lending obligations, reducing discrepancies compared to traditional liability management systems. This real-time synchronization allows more accurate assessment of financial liabilities, improving risk management and accountability in decentralized money management.
Platform-Backed Default Coverage
Platform-backed default coverage in peer-to-peer lending mitigates investor risk by absorbing loan defaults, differentiating these obligations from traditional liabilities that represent direct repayment commitments. This coverage enhances money management strategies by reducing potential losses and improving cash flow predictability for lenders operating within the platform.
Cross-Border Peer Loan Exposures
Cross-border peer loan exposures present distinct liability risks compared to traditional liabilities due to varying international regulations and currency fluctuations impacting repayment obligations. Effective money management requires rigorous assessment of credit risk, jurisdiction enforcement, and liquidity considerations to mitigate potential defaults in peer-to-peer lending frameworks.
Social Creditworthiness Assessment
Liabilities represent traditional debt obligations recorded on a balance sheet, whereas peer-to-peer lending obligations rely heavily on social creditworthiness assessments that evaluate borrowers' reputation and behavior within digital networks. This shift enhances risk management by integrating social data analytics, providing a more dynamic and personalized approach to credit evaluation compared to conventional financial liabilities.
Micro-Lending Liability Pools
Micro-lending liability pools aggregate individual lender obligations, distributing risk across numerous small loans and minimizing exposure compared to traditional liabilities. This decentralized structure enhances money management efficiency by leveraging peer-to-peer lending obligations, reducing default impact through diversified micro-loan portfolios.
Secondary Market Peer Loan Risks
Secondary market peer loan risks include heightened exposure to borrower default and reduced loan liquidity, complicating accurate liability management for investors. These risks contrast with traditional liabilities by introducing variable asset valuation and potential delays in loan repayment, challenging effective portfolio risk mitigation.
Fractional Lending Obligation Stacking
Liabilities in traditional finance represent fixed repayment obligations, whereas peer-to-peer lending obligations, especially with fractional lending obligation stacking, involve multiple fractional claims on a single borrower's debt, increasing complexity in liability tracking and risk assessment. Fractional lending obligation stacking requires sophisticated management systems to allocate repayments among various lenders accurately and mitigate default risks in money management portfolios.
Automated Smart Contract Settlements
Automated smart contract settlements in peer-to-peer lending obligations enhance transparency and reduce the risk of default by enforcing terms without intermediaries, contrasting traditional liabilities that rely on manual oversight and legal enforcement. These smart contracts ensure timely repayment and automatic allocation of funds, optimizing money management and minimizing liability exposure.
Investor Liability Tokenization
Investor liability tokenization transforms traditional liabilities into digital assets, enabling precise tracking and management of peer-to-peer lending obligations. This approach reduces risk exposure by clearly delineating investor responsibilities and enhancing transparency in money management.
Liabilities vs Peer-to-Peer Lending Obligations for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com