When considering liability coverage, car loans typically require comprehensive insurance with higher premiums due to ownership responsibility. Electric vehicle subscriptions often include liability coverage within the monthly fee, reducing out-of-pocket expenses and simplifying risk management. This subscription model can lower financial exposure while providing flexible access to electric vehicles.
Table of Comparison
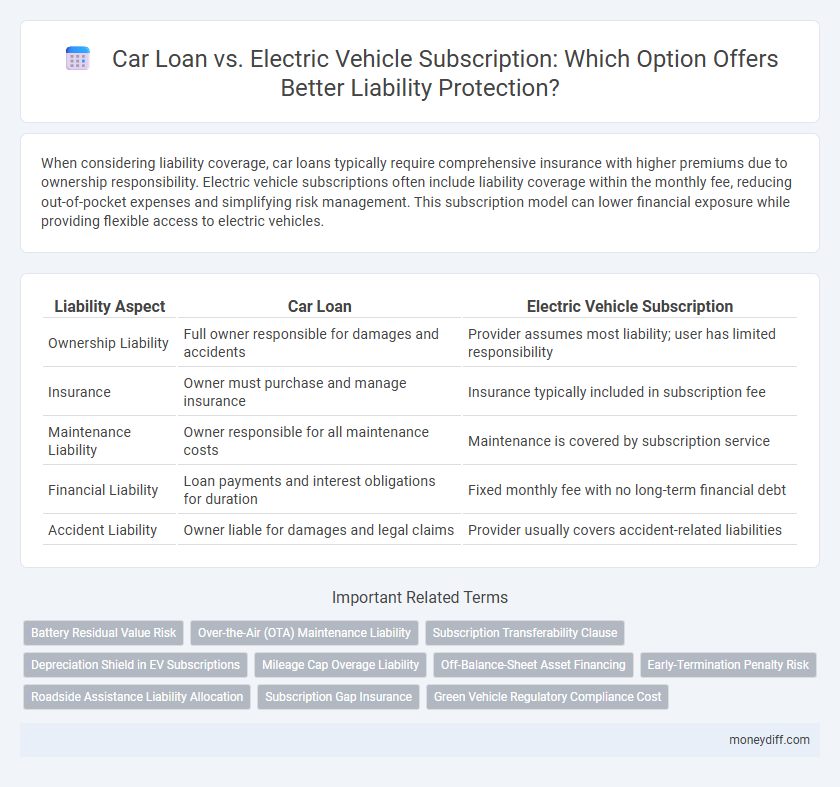
| Liability Aspect | Car Loan | Electric Vehicle Subscription |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership Liability | Full owner responsible for damages and accidents | Provider assumes most liability; user has limited responsibility |
| Insurance | Owner must purchase and manage insurance | Insurance typically included in subscription fee |
| Maintenance Liability | Owner responsible for all maintenance costs | Maintenance is covered by subscription service |
| Financial Liability | Loan payments and interest obligations for duration | Fixed monthly fee with no long-term financial debt |
| Accident Liability | Owner liable for damages and legal claims | Provider usually covers accident-related liabilities |
Understanding Liability in Car Loans vs. EV Subscriptions
Car loans typically assign full liability to the borrower for maintenance, insurance, and damages, while electric vehicle (EV) subscriptions often include comprehensive coverage and shared liability within the subscription fee. With car loans, the owner is responsible for unexpected repair costs and depreciation risks, whereas EV subscriptions offer predictable monthly expenses and built-in liability protections. Understanding these liability differences helps consumers choose financial options aligned with their risk tolerance and budget flexibility.
Financial Responsibility: Ownership vs. Subscription Models
Car loans place full financial responsibility for liability, insurance, and maintenance on the owner, increasing potential out-of-pocket expenses in case of accidents. Electric vehicle subscriptions typically include insurance and maintenance within the monthly fee, limiting the subscriber's direct liability and financial risk. Choosing between ownership and subscription models impacts the degree of personal financial exposure associated with vehicle liability.
Liability Coverage: What’s Included in Car Loans?
Car loans typically include liability coverage that protects against bodily injury and property damage claims resulting from accidents involving the financed vehicle. This coverage often meets state minimum requirements but can be supplemented with additional protection like uninsured motorist and personal injury protection. Electric vehicle subscriptions may offer liability coverage as part of the package, but car loans generally provide clearer and more customizable liability insurance options tailored to the borrower's needs.
Liability Protections under Electric Vehicle Subscriptions
Electric vehicle (EV) subscriptions often include comprehensive liability protections that surpass traditional car loan agreements by bundling insurance coverage within the monthly fee, reducing the risk and administrative burden on the subscriber. These subscriptions typically cover liability for property damage, bodily injury, and uninsured motorist incidents, offering peace of mind without the need for separate insurance policies. Furthermore, the liability limits in EV subscriptions are frequently set at higher thresholds, providing enhanced financial protection compared to standard car loan liability coverage.
Insurance Implications for Car Loans and Subscriptions
Car loans typically require comprehensive insurance coverage, including liability, collision, and comprehensive policies, to protect both the lender and borrower from financial loss. Electric vehicle subscriptions often include insurance within the monthly fee, simplifying liability coverage by bundling protection and reducing out-of-pocket expenses for subscribers. Understanding the differences in insurance obligations between car loans and subscriptions is crucial for managing liability risk effectively.
Debt Liability: Car Loan Repayments Compared to Subscription Fees
Debt liability from car loan repayments typically involves fixed monthly obligations with interest accrual, increasing the total repayment amount over time. Electric vehicle subscription fees, on the other hand, are often all-inclusive, covering maintenance and insurance without long-term debt commitment. Comparing these liabilities reveals that subscription models reduce financial risk by avoiding principal debt, whereas car loans create ongoing liabilities until full repayment.
Resale and Depreciation: Who Bears the Financial Risk?
Car loans place the financial risk of resale value and depreciation squarely on the borrower, who must manage the vehicle's declining worth over time and potential resale challenges. Electric vehicle subscriptions transfer this liability to the provider, as monthly fees typically cover depreciation costs and eliminate concerns about residual value. Subscribers avoid unexpected losses from rapid depreciation, whereas loan holders face direct exposure to market fluctuations affecting the vehicle's resale price.
Maintenance and Repair Liabilities: Loan Holders vs. Subscribers
Car loan holders bear full responsibility for maintenance and repair liabilities, including unexpected costs and vehicle depreciation that affect the total loan repayment. Electric vehicle subscription subscribers typically encounter lower maintenance liabilities, as service, repairs, and insurance are often included in the subscription fee, reducing financial risks. This fundamental difference makes subscriptions a more predictable option for managing ongoing vehicle-related liabilities compared to traditional car loans.
Early Termination Liability: Car Loans vs. EV Subscriptions
Car loans typically impose significant early termination fees and outstanding balance payments, increasing financial liability if the borrower ends the contract prematurely. Electric vehicle subscription services often offer more flexible early termination terms with lower or no penalties, reducing early termination liability for subscribers. Understanding these differences is crucial for managing potential financial risks associated with ending a vehicle financing agreement prematurely.
Choosing the Right Option: Minimizing Liability for Money Management
Car loans typically involve higher financial liability due to long-term debt and interest payments, increasing overall risk exposure. Electric vehicle subscriptions offer a flexible alternative with predictable monthly costs and reduced responsibility for depreciation and maintenance liabilities. Selecting an electric vehicle subscription can effectively minimize financial liability and enhance money management by limiting unexpected expenses and debt obligations.
Related Important Terms
Battery Residual Value Risk
Car loans transfer the battery residual value risk to the borrower, who may face high depreciation costs if battery performance declines or technology advances rapidly. Electric vehicle subscriptions typically include battery maintenance and upgrades, minimizing the subscriber's liability for battery depreciation and residual value fluctuations.
Over-the-Air (OTA) Maintenance Liability
Car loans typically place full maintenance liability on the vehicle owner, including costs arising from Over-the-Air (OTA) updates, while electric vehicle subscriptions often shift OTA maintenance liability to the provider, ensuring seamless software updates and reducing unexpected repair expenses for subscribers. This transfer of OTA maintenance responsibility minimizes user risk related to software faults, enhancing overall liability protection in electric vehicle subscriptions compared to traditional car loan agreements.
Subscription Transferability Clause
Car loan agreements typically have limited or no transferability clauses, binding the original borrower to the liability until the loan is fully paid, whereas electric vehicle subscription contracts often include transferability clauses allowing subscribers to transfer the liability and service agreement to another user, reducing long-term financial risk. This transferability feature in subscription models enhances flexibility and limits direct liability exposure compared to traditional car loans.
Depreciation Shield in EV Subscriptions
Electric vehicle subscriptions provide a depreciation shield by transferring the risk of rapid value loss from the consumer to the service provider, unlike traditional car loans where the owner bears full depreciation costs. This model reduces financial liability and unexpected expenses associated with asset depreciation during the contract period.
Mileage Cap Overage Liability
Car loan agreements typically impose mileage caps that, when exceeded, result in significant overage liability fees calculated per mile, increasing overall costs. Electric vehicle subscription plans often include higher or flexible mileage limits with reduced or no overage penalties, minimizing financial risk related to excessive mileage usage.
Off-Balance-Sheet Asset Financing
Car loan financing for vehicles results in on-balance-sheet liabilities, increasing reported debt and impacting credit ratios, while electric vehicle subscriptions typically operate as off-balance-sheet asset financing, reducing direct liability recognition and enhancing financial flexibility. This off-balance-sheet treatment minimizes the borrowing company's debt exposure and can improve key financial metrics such as debt-to-equity ratio and return on assets.
Early-Termination Penalty Risk
Car loans typically involve high early-termination penalties that increase financial liability if the loan is paid off or the vehicle is surrendered ahead of schedule. Electric vehicle subscriptions often offer lower or no early-termination fees, reducing the risk of significant liability exposure for subscribers wanting to exit the agreement prematurely.
Roadside Assistance Liability Allocation
Car loans typically place roadside assistance liability on the vehicle owner, requiring them to manage and cover any associated risks or costs. Electric vehicle subscriptions often include roadside assistance within the service package, shifting liability to the provider and reducing the subscriber's financial exposure.
Subscription Gap Insurance
Car loan borrowers assume direct liability for vehicle damage and theft, often requiring traditional comprehensive and collision insurance, whereas electric vehicle subscriptions commonly include Subscription Gap Insurance that covers the difference between the vehicle's depreciated value and the outstanding balance, reducing financial exposure during total loss or theft. Subscription Gap Insurance specifically mitigates liability risks by preventing borrowers or subscribers from owing more than the vehicle's market value, enhancing financial protection in the event of an accident or write-off.
Green Vehicle Regulatory Compliance Cost
Electric vehicle subscriptions typically include regulatory compliance costs for green vehicle standards, reducing the liability burden on consumers compared to traditional car loans. In contrast, car loans often require owners to independently manage emission-related compliance expenses, increasing potential financial liability.
Car Loan vs Electric Vehicle Subscription for Liability Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com