International funds offer diverse exposure to established economies with relatively stable returns and lower risk, making them suitable for investors seeking steady growth. Frontier market funds target emerging economies with higher growth potential but greater volatility and political risk, appealing to investors willing to accept uncertainty for potential high rewards. Understanding the risk tolerance and investment horizon is crucial when choosing between these two fund types for portfolio diversification.
Table of Comparison
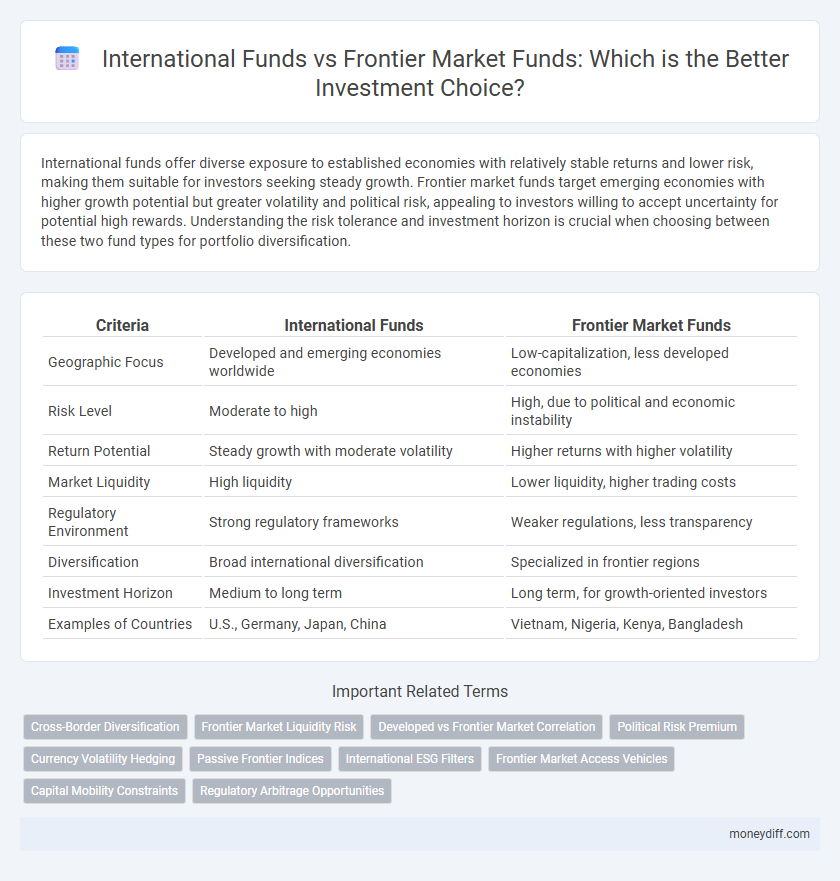
| Criteria | International Funds | Frontier Market Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Geographic Focus | Developed and emerging economies worldwide | Low-capitalization, less developed economies |
| Risk Level | Moderate to high | High, due to political and economic instability |
| Return Potential | Steady growth with moderate volatility | Higher returns with higher volatility |
| Market Liquidity | High liquidity | Lower liquidity, higher trading costs |
| Regulatory Environment | Strong regulatory frameworks | Weaker regulations, less transparency |
| Diversification | Broad international diversification | Specialized in frontier regions |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long term | Long term, for growth-oriented investors |
| Examples of Countries | U.S., Germany, Japan, China | Vietnam, Nigeria, Kenya, Bangladesh |
Overview: International Funds vs Frontier Market Funds
International funds invest in established global markets, offering diversified exposure to developed and emerging economies with relatively lower risk and steady returns. Frontier market funds target smaller, less mature economies characterized by higher growth potential but increased volatility and political risk. Investors seeking balance often choose international funds for stability, while those aiming for aggressive growth may prefer frontier market funds despite their higher risk profiles.
Geographic Diversification: Key Differences
International funds offer broad geographic diversification by investing across established and emerging markets worldwide, reducing country-specific risk. Frontier market funds focus on smaller, less accessible economies with higher growth potential but increased volatility and political risk. The choice between these funds depends on an investor's risk tolerance and desire for exposure to stable versus high-growth regions.
Risk Profiles and Volatility Comparison
International funds typically offer diversified exposure across established and emerging economies, presenting moderate risk profiles with relatively stable volatility due to broader market access and regulatory frameworks. Frontier market funds concentrate on less developed, smaller economies, exhibiting higher risk profiles and elevated volatility driven by political instability, lower liquidity, and nascent market infrastructure. Investors balancing growth potential against risk tolerance often consider international funds for stability and frontier funds for aggressive, high-risk diversification.
Return Potential: Growth Opportunities Analyzed
International funds offer diversified exposure to established economies with moderate return potential driven by stable growth and steady market performance. Frontier market funds target emerging economies with higher growth volatility but greater return potential due to untapped resources and rapid economic development. Investors seeking aggressive capital appreciation may favor frontier markets, while those preferring risk-adjusted returns often opt for international funds.
Currency Exposure and Impact on Returns
International funds often provide diversified currency exposure by investing in developed and emerging markets with relatively stable currencies, mitigating exchange rate volatility and potentially enhancing risk-adjusted returns. Frontier market funds, however, involve higher currency risk due to less liquid and more volatile currencies, which can amplify both gains and losses and lead to greater unpredictability in returns. Investors should assess their risk tolerance and return expectations when considering the distinct currency exposure impact on investment performance between international and frontier market funds.
Accessibility and Investment Barriers
International funds offer broader accessibility with established regulatory frameworks and easier currency convertibility, attracting investors seeking diversification and lower entry barriers. Frontier market funds often present higher investment barriers due to limited market infrastructure, lower liquidity, and political risks, making accessibility more challenging for average investors. Understanding these factors helps investors balance potential returns against ease of market entry and operational complexities.
Regulatory Environment and Market Stability
International funds generally benefit from well-established regulatory frameworks and higher market stability, offering investors greater transparency and risk mitigation. Frontier market funds, while potentially providing higher growth opportunities, often face less stringent regulations and increased market volatility, which can elevate investment risk. Understanding the regulatory environment and stability metrics is crucial for aligning investment strategies with risk tolerance and return expectations.
Expense Ratios and Management Fees
International funds typically feature higher expense ratios ranging from 0.75% to 1.5%, reflecting the increased costs of managing diverse global portfolios. Frontier market funds often command even higher management fees, sometimes exceeding 1.5%, due to limited market liquidity and higher operational risks. Investors seeking cost efficiency should carefully compare these fees as they directly impact net returns over time.
Suitable Investor Profiles
International funds cater to investors with moderate risk tolerance seeking diversified exposure to well-established global markets, including developed and emerging economies. Frontier market funds suit aggressive investors aiming for high growth potential in less liquid, smaller economies with higher volatility and unique geopolitical risks. Portfolio diversification strategies often recommend combining both fund types to balance risk and reward according to specific financial goals.
Strategic Allocation in a Diversified Portfolio
Strategic allocation between international funds and frontier market funds enhances portfolio diversification by balancing risk exposure and growth potential. International funds provide access to established economies with stable returns, while frontier market funds target emerging economies offering higher growth prospects amid increased volatility. Integrating both fund types enables investors to optimize long-term performance through diversified geographic and economic risk.
Related Important Terms
Cross-Border Diversification
International funds offer broad exposure to developed markets with established regulatory frameworks, enhancing portfolio stability through diversified geopolitical risk. Frontier market funds provide access to high-growth potential economies with less market saturation, presenting unique cross-border diversification benefits despite higher volatility and liquidity risks.
Frontier Market Liquidity Risk
Frontier market funds typically carry higher liquidity risk compared to international funds due to less developed financial markets and lower trading volumes, which can result in greater price volatility and difficulty in executing large transactions. Investors need to consider this liquidity risk carefully, as it may impact the ability to quickly enter or exit positions without substantial cost or delay.
Developed vs Frontier Market Correlation
International funds primarily target developed markets with established economies and lower volatility, whereas frontier market funds focus on less mature economies with higher growth potential and increased risk. The low correlation between developed and frontier markets offers diversification benefits, reducing overall portfolio risk while providing opportunities for higher returns in frontier investments.
Political Risk Premium
International funds typically offer broader diversification and lower political risk premiums due to investments in established economies, whereas frontier market funds carry higher political risk premiums reflecting less stable regulatory environments and governance structures. Investors seeking higher returns must weigh these elevated premiums against potential volatility and geopolitical uncertainties inherent in frontier markets.
Currency Volatility Hedging
International funds typically offer stronger currency volatility hedging mechanisms by diversifying across stable, developed economies with robust financial infrastructures, reducing exchange rate risks. Frontier market funds often face higher currency volatility due to less developed financial systems and limited hedging options, increasing potential returns but also currency risk exposure.
Passive Frontier Indices
Passive frontier indices offer exposure to high-growth potential economies within the least developed markets, providing diversification beyond traditional international funds that primarily target emerging or developed markets. Investing in frontier market funds through passive strategies often results in lower management fees and enhanced liquidity compared to actively managed international funds, while capturing unique risk-return profiles associated with frontier economies.
International ESG Filters
International ESG filters in investment funds prioritize environmental, social, and governance criteria to enhance sustainability and ethical impact. Comparing International Funds and Frontier Market Funds, ESG integration tends to be more robust and standardized in International Funds, while Frontier Market Funds may face challenges in data availability and regulatory consistency, impacting ESG screening effectiveness.
Frontier Market Access Vehicles
Frontier market access vehicles offer investors exposure to high-growth, underexplored economies with potential for substantial returns compared to traditional international funds that focus on more established markets. These funds typically provide diversification benefits by targeting early-stage markets like Vietnam, Nigeria, and Bangladesh, which remain less correlated with global market movements.
Capital Mobility Constraints
International funds typically face fewer capital mobility constraints due to established regulatory frameworks and higher liquidity in developed markets, enabling more efficient capital flows and portfolio adjustments. Frontier market funds encounter significant capital mobility restrictions stemming from underdeveloped financial infrastructures, strict foreign investment limits, and political risks, often resulting in reduced liquidity and higher transaction costs.
Regulatory Arbitrage Opportunities
International funds typically benefit from more established regulatory frameworks, offering greater transparency and risk mitigation, whereas frontier market funds present significant regulatory arbitrage opportunities due to less stringent regulations and higher market inefficiencies. Investors seeking outsized returns often exploit these disparities by strategically allocating capital to frontier markets, capitalizing on regulatory gaps and rapidly evolving policy landscapes.
International Funds vs Frontier Market Funds for investment. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com