Stock market investments offer high liquidity and the potential for rapid gains through trading a diverse portfolio of stocks, enabling investors to capitalize on market fluctuations. Fractional real estate investment provides access to tangible property assets with lower capital requirements, offering steady rental income and long-term appreciation without the need for full property ownership. Evaluating risk tolerance, investment horizon, and income goals is essential when choosing between the volatility of stocks and the relatively stable returns of fractional real estate.
Table of Comparison
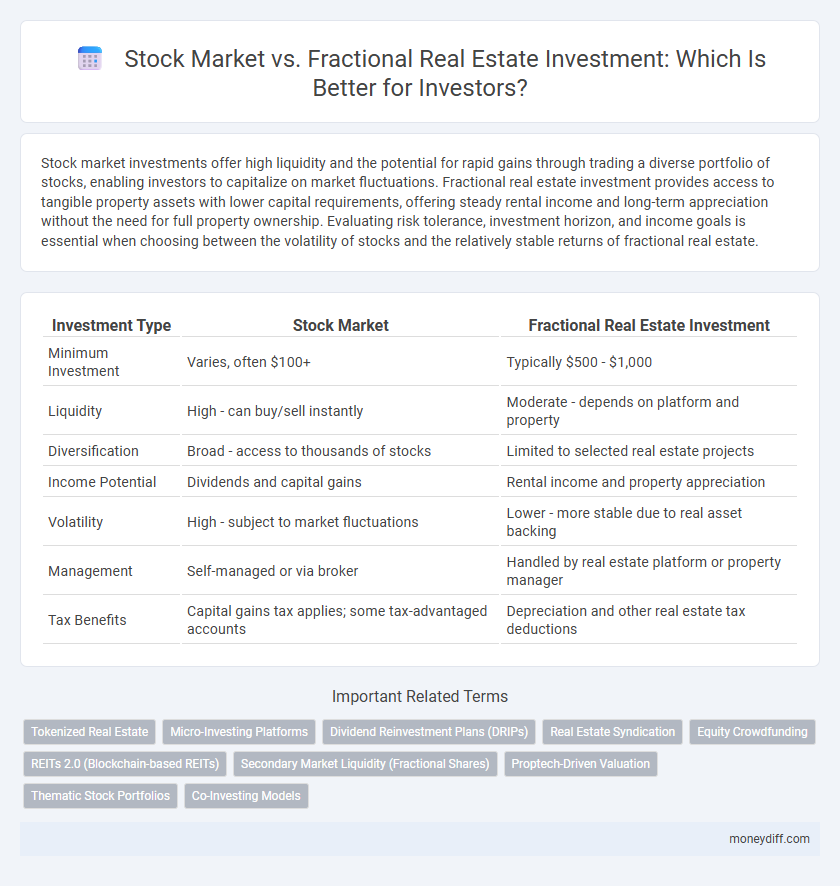
| Investment Type | Stock Market | Fractional Real Estate Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Investment | Varies, often $100+ | Typically $500 - $1,000 |
| Liquidity | High - can buy/sell instantly | Moderate - depends on platform and property |
| Diversification | Broad - access to thousands of stocks | Limited to selected real estate projects |
| Income Potential | Dividends and capital gains | Rental income and property appreciation |
| Volatility | High - subject to market fluctuations | Lower - more stable due to real asset backing |
| Management | Self-managed or via broker | Handled by real estate platform or property manager |
| Tax Benefits | Capital gains tax applies; some tax-advantaged accounts | Depreciation and other real estate tax deductions |
Introduction to Stock Market and Fractional Real Estate Investment
Stock market investment offers liquidity, diverse asset options, and potential for capital gains through buying and selling shares of publicly traded companies. Fractional real estate investment enables investors to own a portion of real estate properties, providing access to real estate markets with lower capital requirements and potential rental income. Both investment types serve different risk profiles and liquidity preferences, with stock markets offering daily trading opportunities and fractional real estate focusing on long-term asset appreciation.
How Stock Market Investments Work
Stock market investments involve purchasing shares of publicly traded companies, allowing investors to gain equity ownership proportional to the number of shares held. These investments fluctuate based on market demand, company performance, and economic indicators, offering liquidity and the potential for dividends and capital gains. Investors execute trades through brokerage accounts, enabling quick entry and exit from market positions compared to fractional real estate investments, which are typically less liquid and involve direct asset management.
Understanding Fractional Real Estate Investment
Fractional real estate investment allows investors to own a percentage of a property, providing access to high-value assets with lower capital outlay compared to traditional stock market investments. This approach offers diversification benefits and potential income through rental yields, while stocks typically provide liquidity and market-driven growth. Understanding fractional real estate requires evaluating factors such as property management, market trends, and investor rights to assess real estate performance relative to equity securities.
Risk Comparison: Stocks vs Fractional Real Estate
Stock market investments exhibit higher volatility due to rapid price fluctuations and market sentiment shifts, increasing risk exposure. Fractional real estate investment tends to offer more stability through tangible asset backing and long-term rental income streams. Unlike stocks, fractional real estate often provides lower liquidity risk but may involve market-specific risks such as property location and management quality.
Potential Returns: Which Investment Performs Better?
Stock market investments often provide higher potential returns through capital gains and dividends, benefiting from market liquidity and growth opportunities in diverse sectors. Fractional real estate investment, while offering steady rental income and asset appreciation, tends to deliver more stable but moderate returns with lower volatility compared to stocks. Analyzing historical data reveals that stocks generally outperform fractional real estate in long-term capital growth, but real estate investments provide valuable diversification and income stability.
Liquidity and Accessibility: Ease of Buying and Selling
Stock market investments offer high liquidity with shares easily bought and sold on major exchanges within seconds, appealing to investors seeking quick access to their funds. Fractional real estate investment provides increased accessibility by lowering entry barriers, allowing investors to purchase partial ownership in properties without substantial capital. However, fractional real estate tends to have reduced liquidity compared to stocks, as selling shares in properties may involve longer transaction times and limited secondary markets.
Diversification Opportunities in Both Investments
Stock market investing offers diversification through access to thousands of companies across various sectors and geographies, enabling portfolio spread and risk mitigation. Fractional real estate investment provides diversification by allowing investors to own portions of multiple properties in different locations and asset types without large capital commitments. Combining both strategies enhances risk management and potential returns by balancing market volatility with tangible asset stability.
Entry Barriers: Minimum Investment and Accessibility
Stock market investments typically require lower minimum capital, often allowing purchases of individual shares or ETFs with amounts as low as $50 to $100, making entry highly accessible for most investors. Fractional real estate investments, while offering lower capital requirements than traditional property purchases, generally start around $500 to $1,000, which remains higher compared to stock market options. The stock market's greater liquidity and multiple trading platforms enhance accessibility, whereas fractional real estate investments may involve longer holding periods and less secondary market availability.
Tax Implications for Stock and Fractional Real Estate Investors
Stock market investments often benefit from preferential tax rates on long-term capital gains and qualified dividends, while fractional real estate investors may leverage depreciation deductions and mortgage interest deductions to reduce taxable income. However, fractional real estate gains are typically subject to ordinary income tax rates upon sale unless 1031 exchange provisions are utilized. Understanding specific tax treatments, such as the impact of state taxes on stock dividends versus property taxes in real estate, is crucial for maximizing after-tax returns.
Which Investment Suits Your Financial Goals?
Stock market investments offer high liquidity, potential for rapid growth, and ease of diversification through ETFs and mutual funds, ideal for investors seeking short to medium-term gains and active trading opportunities. Fractional real estate investment provides stable cash flow, long-term appreciation, and lower volatility, making it suitable for risk-averse investors aiming for steady income and portfolio diversification. Assess your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon to determine whether the dynamic nature of stocks or the tangible asset approach of fractional real estate better aligns with your wealth-building strategy.
Related Important Terms
Tokenized Real Estate
Tokenized real estate offers fractional ownership in property assets via blockchain technology, providing increased liquidity and transparency compared to traditional stock market investments. Unlike stocks, tokenized real estate enables investors to diversify portfolios with tangible assets while benefiting from lower entry barriers and potentially stable income streams through rental yields.
Micro-Investing Platforms
Micro-investing platforms democratize access to both stock markets and fractional real estate, allowing investors to purchase small shares with minimal capital. These platforms provide diversified portfolios, liquidity in stock investments, and potential for steady income through fractional real estate dividends, catering to varied risk appetites and long-term wealth growth.
Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs)
Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs) in the stock market allow investors to automatically reinvest dividends to purchase additional shares, compounding growth over time with low fees and increased share accumulation. Fractional real estate investment offers dividend-like distributions but typically lacks automated reinvestment options, making DRIPs a more efficient choice for passive, long-term capital growth through stock ownership.
Real Estate Syndication
Stock market investments offer liquidity and diversified exposure through publicly traded shares, while fractional real estate investment via syndication provides access to income-generating commercial properties with potential tax benefits and capital appreciation. Real estate syndication pools capital from multiple investors to acquire high-value assets, enabling smaller investors to participate in institutional-grade real estate without direct management responsibilities.
Equity Crowdfunding
Equity crowdfunding platforms enable investors to access fractional real estate ownership, offering diversification and tangible asset exposure often absent in traditional stock market investments. Unlike volatile stock market equities, fractional real estate investments through crowdfunding combine steady income potential with long-term capital appreciation, appealing to those seeking a balanced investment portfolio.
REITs 2.0 (Blockchain-based REITs)
Blockchain-based REITs, also known as REITs 2.0, combine the liquidity and accessibility of the stock market with the tangible asset value of real estate, offering fractional ownership backed by secure, transparent smart contracts. These tokenized REITs enable investors to diversify portfolios with lower entry costs, faster transactions, and enhanced transparency compared to traditional stock market investments and conventional real estate funds.
Secondary Market Liquidity (Fractional Shares)
Secondary market liquidity in fractional real estate investment often lags behind the stock market, where fractional shares enable immediate buying and selling with high volume and transparency. Stock market fractional shares benefit from established exchanges, providing investors with greater flexibility and quicker access to funds compared to the relatively nascent and less liquid secondary markets for fractional real estate.
Proptech-Driven Valuation
Proptech-driven valuation enhances transparency and accuracy in fractional real estate investment by leveraging AI analytics and blockchain for real-time asset pricing, outperforming the traditional stock market's reliance on market sentiment and quarterly earnings reports. This innovative approach enables investors to access granular property data and dynamic valuation models, optimizing portfolio diversification and risk management in a rapidly evolving investment landscape.
Thematic Stock Portfolios
Thematic stock portfolios offer targeted exposure to emerging industries like clean energy, technology, and healthcare, enabling investors to capitalize on specific market trends with diversified stock holdings. Fractional real estate investment provides direct property ownership benefits with lower capital requirements but lacks the liquidity and sector-specific focus that thematic stock portfolios deliver in the dynamic stock market.
Co-Investing Models
Co-investing models in stock markets offer diversified portfolios through pooled funds and enable access to high-value assets with liquidity and transparency. Fractional real estate investment co-investing models provide direct ownership in property assets, potentially higher returns from rental income and appreciation, with benefits of tangible asset backing but lower liquidity compared to stocks.
Stock Market vs Fractional Real Estate Investment for investment. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com