Hedge funds offer professional management and sophisticated strategies designed to maximize returns while managing risk, often requiring high minimum investments and accreditation. Social trading funds provide a more accessible platform by allowing investors to mirror the trades of experienced peer traders, promoting transparency and community engagement. Choosing between these depends on an investor's risk tolerance, budget, and preference for active management versus social insights.
Table of Comparison
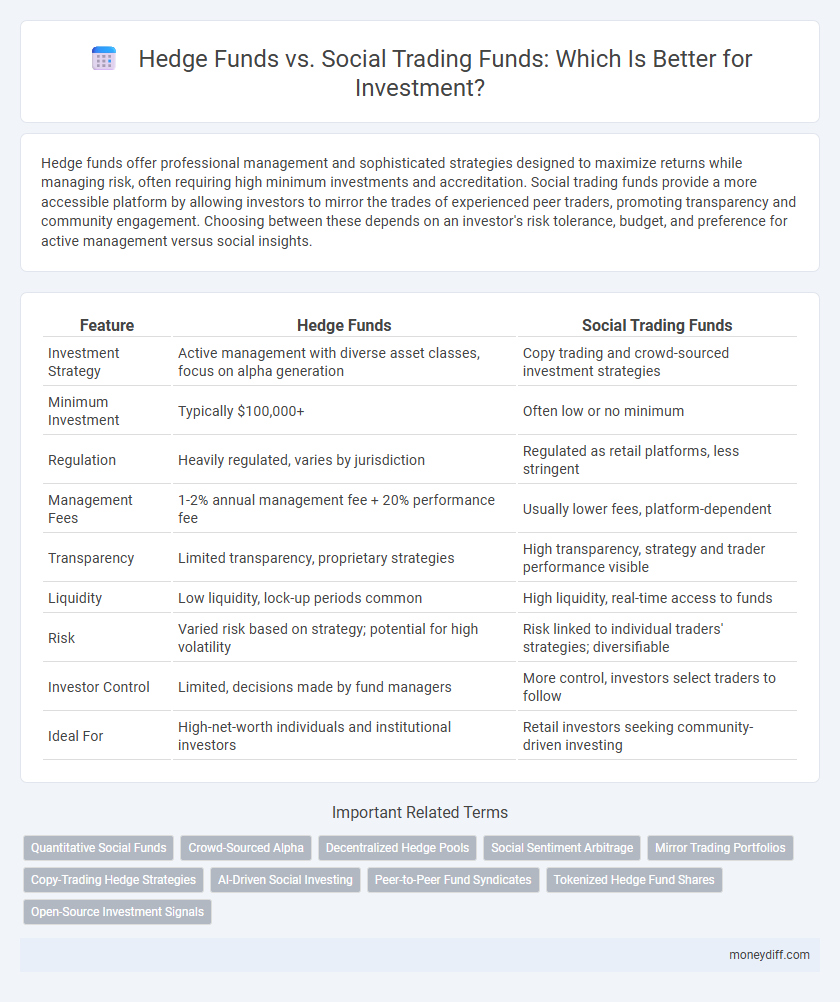
| Feature | Hedge Funds | Social Trading Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Strategy | Active management with diverse asset classes, focus on alpha generation | Copy trading and crowd-sourced investment strategies |
| Minimum Investment | Typically $100,000+ | Often low or no minimum |
| Regulation | Heavily regulated, varies by jurisdiction | Regulated as retail platforms, less stringent |
| Management Fees | 1-2% annual management fee + 20% performance fee | Usually lower fees, platform-dependent |
| Transparency | Limited transparency, proprietary strategies | High transparency, strategy and trader performance visible |
| Liquidity | Low liquidity, lock-up periods common | High liquidity, real-time access to funds |
| Risk | Varied risk based on strategy; potential for high volatility | Risk linked to individual traders' strategies; diversifiable |
| Investor Control | Limited, decisions made by fund managers | More control, investors select traders to follow |
| Ideal For | High-net-worth individuals and institutional investors | Retail investors seeking community-driven investing |
Understanding Hedge Funds and Social Trading Funds
Hedge funds employ advanced strategies like leverage, derivatives, and short selling to achieve high returns, often requiring significant capital and offering limited liquidity. Social trading funds enable investors to replicate the trades of experienced traders through online platforms, promoting transparency and accessibility with lower entry barriers. Understanding the distinct risk profiles, fee structures, and regulatory frameworks is crucial when choosing between hedge funds and social trading funds for investment diversification.
Key Differences Between Hedge Funds and Social Trading Funds
Hedge funds typically involve high-net-worth investors seeking advanced portfolio strategies managed by professional fund managers, utilizing leverage and derivatives for potentially higher returns. Social trading funds allow individual investors to mimic trades of experienced traders through online platforms, promoting transparency and community engagement but often with lower barriers to entry and regulatory oversight. Key differences include management style, risk exposure, fee structures, and accessibility to retail investors.
Investment Strategies: Hedge Funds vs Social Trading Funds
Hedge funds employ complex investment strategies including long-short equity, market neutral, and global macro tactics, leveraging derivatives and high leverage to capitalize on market inefficiencies. Social trading funds rely on collective intelligence by mirroring successful traders' portfolios, utilizing crowd-sourced insights and real-time data for diversified, transparent investment decisions. Hedge funds prioritize alpha generation through active management, whereas social trading funds emphasize community-driven strategies and ease of access for retail investors.
Risk Profiles and Diversification Approaches
Hedge funds typically employ complex strategies with high-risk profiles aiming for absolute returns, often investing in diverse asset classes including derivatives and leverage to manage risk and enhance diversification. Social trading funds leverage collective intelligence by replicating trades of experienced investors, offering diversified exposure through multiple strategies with varying risk levels depending on the traders followed. Understanding these risk profiles and diversification approaches helps investors align fund selection with their risk tolerance and portfolio goals.
Accessibility for Retail and Institutional Investors
Hedge funds typically require high minimum investments and are primarily accessible to institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals, limiting retail participation due to regulatory and capital constraints. Social trading funds, on the other hand, offer greater accessibility by enabling retail investors to replicate the trades of experienced traders with lower entry thresholds and user-friendly platforms. This democratization fosters broader market participation and diversification opportunities for individuals with varying investment capital.
Performance Metrics and Historical Returns
Hedge funds typically exhibit higher risk-adjusted returns with strategies emphasizing alpha generation and diversification, often showcasing a multi-year annualized return between 7% and 12%. Social trading funds leverage collective intelligence by replicating top traders' portfolios, demonstrating variable performance that can range widely based on trader expertise and market conditions, with historical returns often lagging hedge funds in volatility management. Performance metrics such as the Sharpe ratio and Sortino ratio generally favor hedge funds due to their robust risk controls and experienced asset management teams.
Fee Structures: Costs and Transparency Compared
Hedge funds typically charge a 2% management fee plus 20% performance fees, leading to higher costs that may reduce net returns, whereas social trading funds often have lower fees, focusing on subscription or small commission models that enhance cost-efficiency. Transparency in hedge funds is limited due to private structures and restricted reporting, while social trading platforms provide greater fee transparency and accessible real-time data for investors. Investors seeking lower expenses and clearer fee disclosure may prefer social trading funds, whereas those willing to pay premium fees for active management might lean toward hedge funds.
Regulatory Frameworks for Hedge Funds and Social Trading Funds
Hedge funds operate under stringent regulatory frameworks such as the Investment Company Act of 1940 and are typically subject to strict disclosure and reporting requirements enforced by the SEC, ensuring investor protection and market stability. Social trading funds, while growing in popularity, often face less rigorous regulation, primarily governed by financial authorities overseeing online platforms, which may result in varied investor protections depending on jurisdiction. Understanding these regulatory differences is crucial for investors assessing risk and compliance standards associated with each fund type.
Investor Protection and Due Diligence
Hedge funds employ rigorous due diligence processes and stringent regulatory compliance to ensure robust investor protection, often requiring accredited investor status and offering transparent risk disclosures. Social trading funds, while accessible and user-friendly, may present higher risks due to less stringent regulatory oversight and potential lack of comprehensive due diligence on individual traders' strategies. Investors should weigh the level of professional management and regulatory safeguards in hedge funds against the collaborative but variable nature of social trading platforms to optimize protection and return potential.
Choosing the Right Fund for Your Investment Goals
Hedge funds offer active management with strategies including long-short equity, arbitrage, and leverage, suitable for investors seeking higher risk-adjusted returns and willing to accept liquidity constraints. Social trading funds enable investors to replicate the trades of experienced traders via platforms that emphasize transparency, lower minimum investments, and community-driven decision-making. Selecting the right fund depends on your risk tolerance, investment horizon, desired level of engagement, and objectives for diversification and return consistency.
Related Important Terms
Quantitative Social Funds
Quantitative Social Funds leverage advanced algorithms and collective investor sentiment to optimize portfolio performance, blending data-driven strategies with the transparency of social trading platforms. Unlike traditional hedge funds, these funds enable crowd-sourced decision-making while maintaining rigorous quantitative analytics to manage risk and maximize returns.
Crowd-Sourced Alpha
Hedge funds leverage expert-driven strategies with high capital requirements, while social trading funds utilize crowd-sourced alpha by aggregating diverse retail investor insights to enhance performance through collective decision-making. Crowd-sourced alpha captures real-time market sentiment and democratizes access to investment opportunities, creating dynamic risk-adjusted returns distinct from traditional hedge fund models.
Decentralized Hedge Pools
Decentralized hedge pools leverage blockchain technology to offer transparent, low-fee investment alternatives compared to traditional hedge funds, emphasizing collective asset management and reduced intermediaries. Social trading funds enhance this model by integrating real-time trader insights and performance-based strategies, creating a dynamic, community-driven investment ecosystem.
Social Sentiment Arbitrage
Social Sentiment Arbitrage in investment leverages real-time data from social media platforms to identify market sentiment shifts, allowing social trading funds to make agile, crowd-driven decisions that often outperform traditional hedge funds. Hedge funds primarily rely on fundamental analysis and quantitative models, whereas social trading funds exploit collective investor behavior insights, enhancing opportunities for arbitrage based on sentiment trends.
Mirror Trading Portfolios
Mirror trading portfolios in social trading funds enable investors to replicate the strategies of experienced traders automatically, offering transparency and real-time portfolio adjustments often absent in traditional hedge funds. Unlike hedge funds, social trading platforms provide lower entry barriers, increased accessibility, and community-driven insights, making mirror trading portfolios a compelling option for retail investors seeking diversified exposure and active management.
Copy-Trading Hedge Strategies
Copy-trading hedge strategies leverage the expertise of seasoned hedge fund managers by automatically replicating their trades, offering investors diversified exposure with minimized research effort. Social trading funds enhance transparency and community-driven insights, yet typically present higher risks and lower regulatory oversight compared to traditional hedge funds.
AI-Driven Social Investing
Hedge funds utilize complex AI algorithms and proprietary data models to optimize asset allocation and risk management, often requiring high minimum investments and offering limited transparency. In contrast, AI-driven social trading funds leverage collective investor behavior and machine learning to democratize market insights, enabling lower entry barriers and real-time adaptive strategies based on community-driven data.
Peer-to-Peer Fund Syndicates
Hedge funds offer professional management with high minimum investments and complex strategies, while social trading funds enable peer-to-peer fund syndicates, allowing individual investors to pool capital and replicate top traders' moves with lower entry barriers. Peer-to-peer fund syndicates enhance transparency and collective decision-making in social trading, providing diversified exposure and democratizing access to sophisticated trading approaches.
Tokenized Hedge Fund Shares
Tokenized hedge fund shares provide enhanced liquidity and accessibility compared to social trading funds by allowing fractional ownership and seamless blockchain transactions. While hedge funds offer professional management and diversified strategies, tokenization bridges traditional investment with decentralized finance, attracting investors seeking transparency and efficient asset transfer.
Open-Source Investment Signals
Hedge funds leverage proprietary algorithms and confidential data to generate alpha, while social trading funds prioritize transparency by utilizing open-source investment signals from community-driven platforms. Investors seeking collaborative insights and real-time strategy adaptation often prefer social trading funds for their democratized access to collective market intelligence.
Hedge Funds vs Social Trading Funds for investment Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com