ETFs offer broad market exposure with lower fees and transparency, making them ideal for cost-conscious investors seeking passive growth. Actively managed ETFs provide the potential for higher returns through professional portfolio management and flexibility to adapt to market conditions. Choosing between the two depends on an investor's risk tolerance, investment goals, and preference for control versus cost efficiency.
Table of Comparison
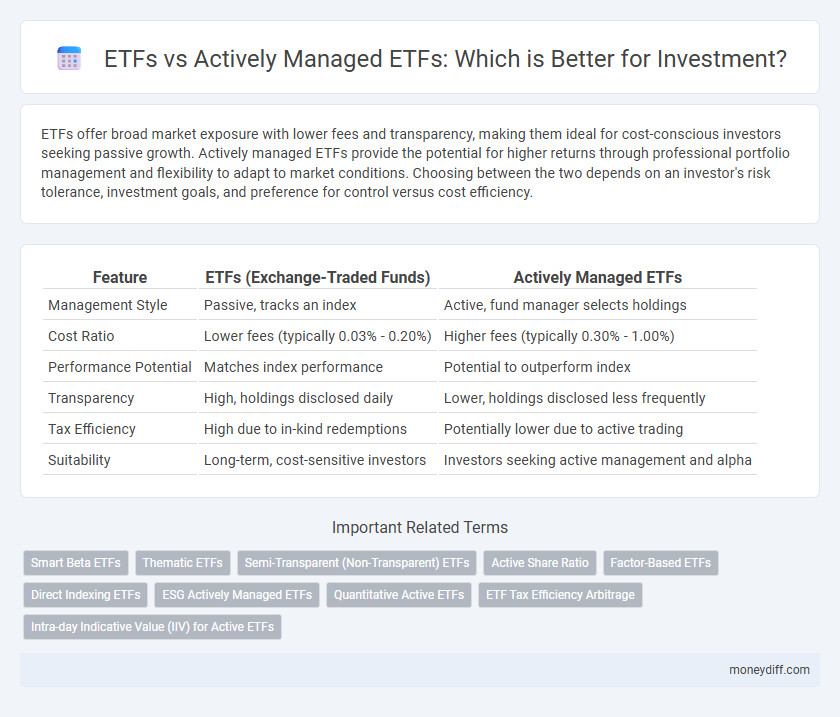
| Feature | ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) | Actively Managed ETFs |
|---|---|---|
| Management Style | Passive, tracks an index | Active, fund manager selects holdings |
| Cost Ratio | Lower fees (typically 0.03% - 0.20%) | Higher fees (typically 0.30% - 1.00%) |
| Performance Potential | Matches index performance | Potential to outperform index |
| Transparency | High, holdings disclosed daily | Lower, holdings disclosed less frequently |
| Tax Efficiency | High due to in-kind redemptions | Potentially lower due to active trading |
| Suitability | Long-term, cost-sensitive investors | Investors seeking active management and alpha |
Understanding ETFs and Actively Managed ETFs
ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) offer diversified, low-cost investment exposure by tracking indexes, allowing investors to buy and sell shares throughout the trading day. Actively managed ETFs differ by employing portfolio managers who make strategic decisions to outperform benchmarks, resulting in potentially higher returns but increased management fees. Understanding the cost structure, risk tolerance, and investment goals is crucial when choosing between passively managed ETFs and actively managed ETFs for portfolio optimization.
Key Differences Between ETFs and Actively Managed ETFs
ETFs typically track a specific index, offering low-cost, passive investment with broad market exposure, while actively managed ETFs involve portfolio managers making strategic decisions to outperform benchmarks, resulting in higher fees and potentially higher returns. The transparency level differs as standard ETFs disclose holdings daily, whereas actively managed ETFs may provide less frequent updates to protect proprietary strategies. Liquidity and trading flexibility are generally similar, but investors should consider the trade-off between cost efficiency and active oversight when choosing between these investment vehicles.
Performance Comparison: ETFs vs Actively Managed ETFs
Passively managed ETFs typically track an index, offering lower expense ratios and consistent market-matching returns, while actively managed ETFs aim to outperform benchmarks by leveraging expert portfolio managers and dynamic strategies. Performance comparisons often show that actively managed ETFs can outperform during volatile or bear markets but may underperform in stable, bull markets due to higher fees and management risks. Investors should weigh the trade-offs between the potential for alpha generation in actively managed ETFs and the cost-efficiency and predictability of passive ETFs.
Cost Efficiency: Expense Ratios and Fees
ETFs generally offer lower expense ratios and fees compared to actively managed ETFs, making them more cost-efficient for long-term investors. Actively managed ETFs incur higher management costs due to ongoing research and frequent portfolio adjustments, impacting overall returns. Investors focused on minimizing expenses often prefer passive ETFs to enhance portfolio cost efficiency.
Tax Implications and Efficiency
ETFs typically offer higher tax efficiency due to their in-kind creation and redemption process that limits capital gains distributions, making them cost-effective for taxable accounts. Actively managed ETFs may incur higher capital gains taxes as portfolio managers frequently trade securities to meet investment objectives. Investors should weigh the tax advantages of passive ETFs against the potential for enhanced returns in actively managed ETFs, considering their own tax situations and investment goals.
Transparency and Portfolio Disclosure
ETFs offer superior transparency through daily portfolio disclosures, enabling investors to monitor holdings and assess risk in real time. Actively managed ETFs typically disclose their portfolios less frequently, often on a quarterly basis, which can limit insight into current investment strategies. This reduced transparency may affect investor confidence and complicate performance evaluation compared to the clear, consistent visibility provided by traditional ETFs.
Liquidity and Trading Flexibility
ETFs typically offer higher liquidity and greater trading flexibility due to their structure of continuous market trading and tight bid-ask spreads. Actively managed ETFs may experience lower liquidity and wider spreads because of less frequent portfolio adjustments and potentially limited market maker participation. Investors prioritizing intraday trading opportunities generally prefer traditional ETFs, while those seeking professional management might accept some liquidity trade-offs with actively managed ETFs.
Risk Management Strategies
ETFs typically employ passive risk management by tracking market indexes, which limits portfolio volatility through broad diversification and low expense ratios. Actively managed ETFs utilize dynamic risk management strategies, including sector rotation, tactical asset allocation, and real-time market analysis to mitigate downside risks and adapt to market fluctuations. Investors seeking tailored risk control may prefer actively managed ETFs for their potential to outperform benchmarks during volatile periods.
Suitability for Different Investment Goals
ETFs provide broad market exposure with lower fees, making them suitable for long-term, passive investment goals focused on diversification and cost efficiency. Actively managed ETFs target specific sectors or strategies through professional oversight, appealing to investors seeking potential outperformance and tailored asset allocation. Choosing between these options depends on risk tolerance, investment horizon, and desired involvement in portfolio management.
How to Choose: ETFs or Actively Managed ETFs?
When choosing between ETFs and actively managed ETFs, consider factors like expense ratios, investment objectives, and risk tolerance. ETFs typically offer lower fees and track indexes passively, while actively managed ETFs aim for outperformance through expert stock selection and trading strategies. Assess your preference for cost efficiency versus potential alpha generation to align with your investment goals and time horizon.
Related Important Terms
Smart Beta ETFs
Smart Beta ETFs offer a rules-based investment approach that combines passive index tracking efficiency with strategic factor exposure, often resulting in lower fees and enhanced risk-adjusted returns compared to traditional actively managed ETFs. These ETFs systematically target factors like value, momentum, and quality, leveraging data-driven models to optimize portfolio construction while maintaining greater transparency and cost-effectiveness.
Thematic ETFs
Thematic ETFs offer targeted exposure to specific trends or sectors with lower fees and transparent holdings compared to actively managed ETFs, which provide potential for outperformance through professional stock selection but may incur higher management costs. Investors seeking precise alignment with evolving market themes often prefer thematic ETFs, while those aiming for tactical flexibility might opt for actively managed alternatives.
Semi-Transparent (Non-Transparent) ETFs
Semi-transparent ETFs, a subcategory of actively managed ETFs, offer enhanced portfolio privacy by limiting daily disclosure of holdings compared to transparent ETFs, reducing front-running risks and freeing managers to execute dynamic strategies. These ETFs balance the benefits of active management with semi-transparency to attract investors seeking both strategic flexibility and protection from market exploitation.
Active Share Ratio
Active Share Ratio measures the percentage of holdings in an actively managed ETF that differ from its benchmark index, providing investors with insight into the fund's deviation from passive management. Higher Active Share Ratios often indicate greater potential for alpha generation compared to traditional ETFs, which typically track benchmarks with minimal deviation.
Factor-Based ETFs
Factor-Based ETFs systematically target specific investment factors such as value, momentum, or quality to enhance returns and manage risk, offering a transparent, cost-efficient alternative to actively managed ETFs that rely on discretionary decision-making by portfolio managers. These factor-driven ETFs provide a structured approach to capturing market anomalies with lower fees and consistently rules-based strategies, appealing to investors seeking both performance and predictability.
Direct Indexing ETFs
Direct Indexing ETFs provide personalized exposure by directly owning individual securities, offering tax-loss harvesting and customization advantages over traditional actively managed ETFs, which often rely on sector bets and manager discretion. These ETFs blend the passive benefits of indexing with active strategies, potentially enhancing returns and reducing costs compared to conventional actively managed funds.
ESG Actively Managed ETFs
ESG actively managed ETFs leverage expert portfolio management to dynamically select sustainable investments aligned with environmental, social, and governance criteria, offering greater adaptability compared to traditional index-based ESG ETFs. These funds enable investors to potentially achieve stronger impact and risk-adjusted returns by continuously assessing ESG factors and market conditions through active management strategies.
Quantitative Active ETFs
Quantitative Active ETFs leverage algorithm-driven strategies to optimize portfolio performance and risk management, differentiating them from traditional actively managed ETFs that rely on human discretion. These ETFs utilize data analysis, machine learning, and systematic models to make investment decisions, potentially enhancing returns and reducing biases inherent in manual management.
ETF Tax Efficiency Arbitrage
ETFs generally offer higher tax efficiency due to their in-kind creation and redemption process, which minimizes capital gains distributions compared to actively managed ETFs that may trigger more frequent taxable events through active trading strategies. Investors seeking tax-efficient exposure often prefer passive ETFs to leverage lower turnover and reduced capital gains tax liability, while actively managed ETFs might sacrifice some tax advantages for potential alpha generation.
Intra-day Indicative Value (IIV) for Active ETFs
Intra-day Indicative Value (IIV) provides real-time pricing transparency for actively managed ETFs, enabling investors to track the underlying asset value throughout the trading day and make informed decisions. Unlike traditional ETFs, where IIV closely reflects a passive index, active ETFs use IIV to reflect dynamic portfolio adjustments, enhancing market efficiency and trading precision.
ETFs vs Actively Managed ETFs for investment. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com