Blue-chip stocks offer stable returns and established market positions, making them attractive for conservative investors seeking reliable income. ESG stocks prioritize environmental, social, and governance factors, appealing to those aiming to align investments with ethical values while potentially benefiting from sustainable growth trends. Balancing blue-chip stability with ESG innovation can create a diversified portfolio that addresses both financial performance and social responsibility goals.
Table of Comparison
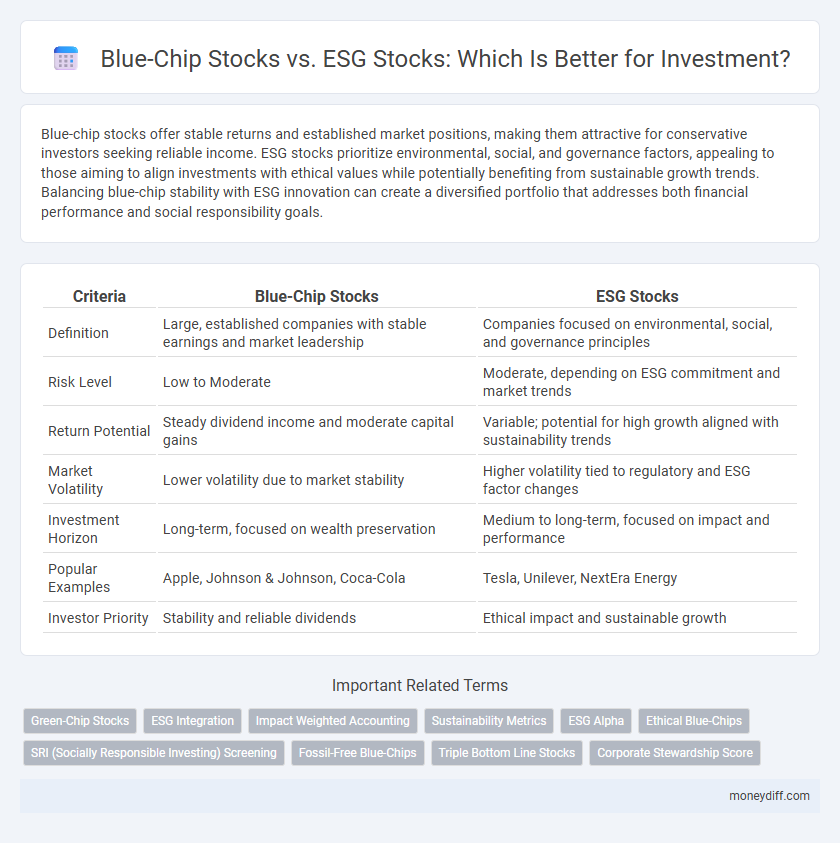
| Criteria | Blue-Chip Stocks | ESG Stocks |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large, established companies with stable earnings and market leadership | Companies focused on environmental, social, and governance principles |
| Risk Level | Low to Moderate | Moderate, depending on ESG commitment and market trends |
| Return Potential | Steady dividend income and moderate capital gains | Variable; potential for high growth aligned with sustainability trends |
| Market Volatility | Lower volatility due to market stability | Higher volatility tied to regulatory and ESG factor changes |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term, focused on wealth preservation | Medium to long-term, focused on impact and performance |
| Popular Examples | Apple, Johnson & Johnson, Coca-Cola | Tesla, Unilever, NextEra Energy |
| Investor Priority | Stability and reliable dividends | Ethical impact and sustainable growth |
Understanding Blue-Chip Stocks: Foundations of Stability
Blue-chip stocks represent shares in well-established companies with a history of reliable earnings, strong market capitalization, and consistent dividend payments, making them foundations of stability in an investment portfolio. These stocks typically belong to industry leaders with proven resilience during economic downturns, offering lower volatility compared to emerging or sector-specific equities such as ESG stocks. Investors seeking long-term capital preservation and steady income often prioritize blue-chip stocks for their dependable performance and risk mitigation characteristics.
What Are ESG Stocks? Principles and Criteria
ESG stocks represent companies that adhere to Environmental, Social, and Governance criteria, ensuring sustainable and ethical business practices. These stocks are evaluated based on principles such as reducing carbon emissions, promoting social responsibility, maintaining transparent governance, and fostering diversity and inclusion. Investors seek ESG stocks to align their portfolios with sustainability goals while pursuing long-term financial performance.
Historical Performance: Blue-Chip vs ESG Stocks
Blue-chip stocks have historically delivered consistent dividends and steady long-term growth, driven by established companies with strong financial stability. ESG stocks, while exhibiting higher volatility, have shown accelerated growth in recent years due to increasing investor demand for sustainable and socially responsible practices. Studies indicate that integrating ESG criteria does not necessarily compromise returns, with ESG portfolios often matching or outperforming traditional blue-chip benchmarks over the past decade.
Risk Factors: Stability versus Sustainability
Blue-chip stocks offer investors stability through established market presence and consistent dividends, minimizing volatility and risk. ESG stocks incorporate environmental, social, and governance criteria, appealing to those prioritizing sustainability but often experiencing higher short-term volatility. Evaluating risk factors between these options requires balancing predictable returns from blue-chip stocks against the long-term impact and regulatory risks associated with ESG investments.
Dividend Yields: Comparing Blue-Chip and ESG Payouts
Blue-chip stocks traditionally offer higher and more stable dividend yields due to their established profitability and consistent cash flow. ESG stocks, while growing in popularity for their sustainability focus, often reinvest earnings for growth, resulting in lower or more variable dividend payouts. Investors seeking steady income typically prefer blue-chip dividends, whereas those prioritizing ethical impact may accept lower yields with ESG equities.
Growth Potential: Market Trends and Opportunities
Blue-chip stocks typically offer stable growth driven by established market presence and consistent earnings, appealing to investors seeking lower volatility. ESG stocks demonstrate significant growth potential as market trends increasingly favor sustainable and socially responsible companies, attracting capital inflows and regulatory incentives. Emerging opportunities in renewable energy, clean technology, and social impact sectors position ESG stocks for accelerated expansion compared to traditional blue-chip equities.
Ethical Considerations in Investment Choices
Blue-chip stocks represent financially stable companies with a long track record of reliability and steady dividends, appealing to investors seeking consistent returns. ESG stocks prioritize environmental, social, and governance criteria, reflecting a commitment to sustainable and ethical business practices. Ethical considerations in investment choices have led many investors to balance financial performance with social responsibility by integrating ESG factors into blue-chip portfolios.
Portfolio Diversification: Mixing Blue-Chip and ESG
Incorporating both blue-chip stocks and ESG stocks enhances portfolio diversification by balancing stability with sustainable growth potential. Blue-chip stocks provide reliable dividends and lower volatility, while ESG stocks offer exposure to innovative companies committed to environmental, social, and governance principles. This combination mitigates risk and aligns investment strategies with evolving market trends and values.
Impact of Regulations on Blue-Chip and ESG Stocks
Regulations increasingly shape the performance and investment appeal of blue-chip and ESG stocks, with stricter environmental and social governance requirements boosting demand for ESG-compliant companies. Blue-chip stocks, traditionally valued for stability and dividends, face rising compliance costs and operational adjustments due to evolving regulatory frameworks targeting sustainability and corporate responsibility. Investors increasingly evaluate regulatory risk and alignment with global climate agreements when choosing between blue-chip stability and ESG growth potential.
Which is Right for You? Investor Profiles and Goals
Investors seeking stable, long-term growth typically benefit from blue-chip stocks known for consistent dividends and strong market positions, while ESG stocks attract those prioritizing ethical impact alongside returns. Conservative profiles aiming for reliability often favor blue-chip investments, whereas socially conscious investors with moderate risk tolerance may prefer ESG portfolios aligning with environmental, social, and governance criteria. Matching stock choices to personal values and financial goals ensures a tailored investment strategy suitable for varied investor profiles.
Related Important Terms
Green-Chip Stocks
Green-chip stocks, a subset of ESG stocks, specifically target companies with strong commitments to environmental sustainability, often offering competitive returns alongside positive ecological impact. Investors seeking long-term growth and risk mitigation may prefer green-chip stocks for their potential to align financial performance with global trends towards renewable energy and carbon neutrality.
ESG Integration
Blue-chip stocks offer stable returns from established companies, while ESG stocks integrate environmental, social, and governance criteria to align investments with sustainable and ethical practices. Incorporating ESG integration into a portfolio enhances long-term risk management and capitalizes on growing market demand for responsible investing.
Impact Weighted Accounting
Impact Weighted Accounting enhances the evaluation of blue-chip stocks by incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance metrics, providing investors with a comprehensive understanding of long-term value beyond traditional financial indicators. ESG stocks benefit from this framework by quantifying their societal and environmental contributions, enabling impact-focused investment decisions that align profit with purpose.
Sustainability Metrics
Blue-chip stocks typically offer stability and long-term growth backed by established companies with strong financials, while ESG stocks emphasize environmental, social, and governance criteria, often integrating sustainability metrics such as carbon footprint reduction, diversity scores, and ethical supply chain practices. Investors prioritizing sustainability metrics may prefer ESG stocks for their targeted impact on social responsibility, whereas blue-chip stocks balance profitability with moderate sustainability initiatives.
ESG Alpha
ESG stocks often deliver ESG alpha by combining strong environmental, social, and governance performance with competitive financial returns, outperforming traditional blue-chip stocks in sustainable growth metrics. Investors seeking long-term value and risk mitigation can benefit from integrating ESG criteria, which enhances portfolio resilience and aligns investments with evolving regulatory and consumer trends.
Ethical Blue-Chips
Ethical blue-chip stocks combine the financial stability and strong market performance of established companies with adherence to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, offering investors both robust returns and responsible investment practices. Prioritizing ethical blue-chips allows for portfolio growth aligned with sustainable development goals, reducing risks related to regulatory changes and reputational damage associated with non-ESG-compliant firms.
SRI (Socially Responsible Investing) Screening
Blue-chip stocks offer stable returns with established market performance, while ESG stocks are evaluated based on environmental, social, and governance criteria, aligning investments with ethical standards. In Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) screening, ESG stocks are prioritized to exclude industries like fossil fuels and tobacco, promoting sustainable and impactful investment portfolios.
Fossil-Free Blue-Chips
Fossil-free blue-chip stocks combine the stability and strong financial performance of established blue-chip companies with a commitment to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, excluding investments in fossil fuels. This strategic approach appeals to investors seeking long-term value while supporting sustainable and ethical business practices.
Triple Bottom Line Stocks
Blue-chip stocks offer stable returns and long-term growth potential, appealing to conservative investors prioritizing financial performance. ESG stocks, particularly those aligned with triple bottom line principles, integrate environmental, social, and governance factors to deliver sustainable value and positive societal impact alongside financial gains.
Corporate Stewardship Score
Blue-chip stocks often exhibit strong corporate stewardship scores due to their established governance frameworks and consistent financial performance, appealing to investors seeking stability. ESG stocks, however, may offer higher corporate stewardship scores by integrating environmental, social, and governance factors, aligning investments with ethical and sustainable business practices.
Blue-Chip Stocks vs ESG Stocks for investment Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com