Interest Rate Swaps provide a customizable hedge against interest rate fluctuations by exchanging fixed and variable payment streams, offering stability in traditional finance portfolios. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) yield platforms generate returns through liquidity provision and staking, with exposure to smart contract and market risks. Comparing these, Interest Rate Swaps deliver precise risk management for interest rates, while DeFi yields offer potentially higher returns but with greater volatility and counterparty uncertainty.
Table of Comparison
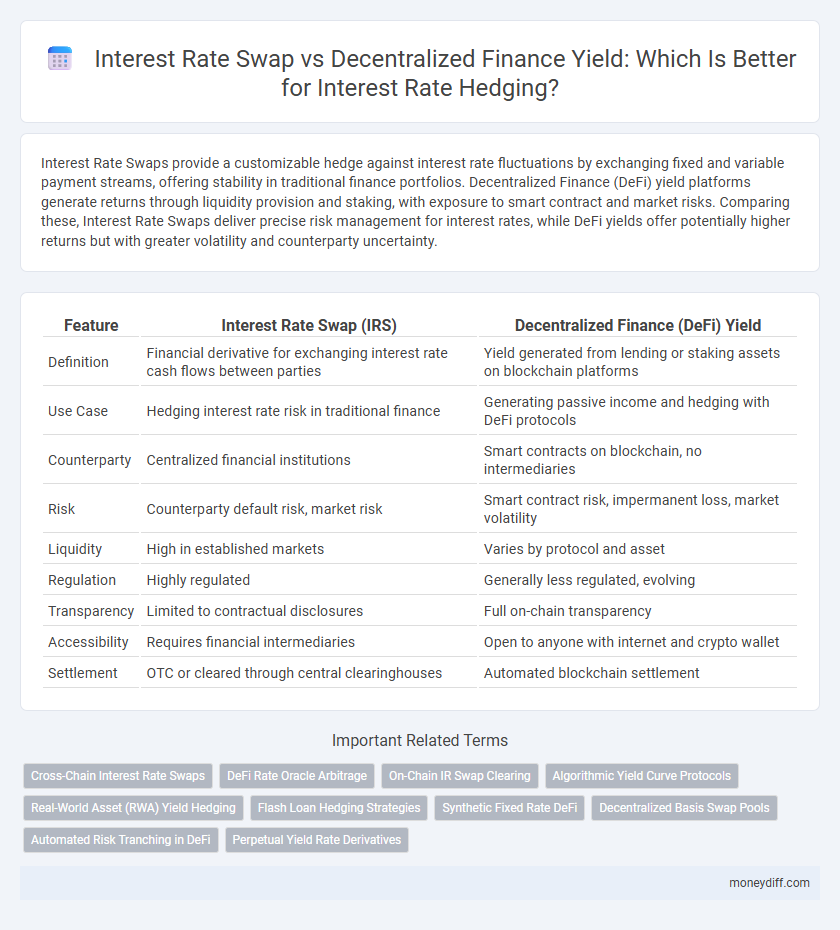
| Feature | Interest Rate Swap (IRS) | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial derivative for exchanging interest rate cash flows between parties | Yield generated from lending or staking assets on blockchain platforms |
| Use Case | Hedging interest rate risk in traditional finance | Generating passive income and hedging with DeFi protocols |
| Counterparty | Centralized financial institutions | Smart contracts on blockchain, no intermediaries |
| Risk | Counterparty default risk, market risk | Smart contract risk, impermanent loss, market volatility |
| Liquidity | High in established markets | Varies by protocol and asset |
| Regulation | Highly regulated | Generally less regulated, evolving |
| Transparency | Limited to contractual disclosures | Full on-chain transparency |
| Accessibility | Requires financial intermediaries | Open to anyone with internet and crypto wallet |
| Settlement | OTC or cleared through central clearinghouses | Automated blockchain settlement |
Understanding Interest Rate Swaps: Traditional Hedging Explained
Interest Rate Swaps (IRS) enable parties to exchange fixed interest payments for floating rate payments, effectively managing exposure to interest rate fluctuations in traditional finance. Unlike decentralized finance (DeFi) yields, which offer variable returns through liquidity provision or staking, IRS provide a more predictable cash flow structure tailored for risk mitigation. Institutions use IRS to hedge against rising interest rates by locking in fixed costs, contrasting with DeFi strategies that rely on market volatility and often lack regulatory safeguards.
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Yield?
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Yield refers to the returns generated from lending, staking, or providing liquidity on blockchain-based platforms without intermediaries. Unlike traditional interest rate swaps that hedge interest rate risks through derivative contracts in regulated markets, DeFi Yield leverages smart contracts and decentralized protocols to offer variable interest rates often influenced by supply and demand dynamics. Investors seeking hedging strategies must consider the inherent volatility and platform risks associated with DeFi Yield compared to the more predictable cash flows of interest rate swaps.
Comparing Risk Profiles: Interest Rate Swaps vs DeFi Yield
Interest rate swaps provide a customizable tool for hedging interest rate exposure with counterparty risk mitigated by regulated financial institutions, whereas DeFi yield strategies rely on smart contracts with inherent smart contract and platform risks. Interest rate swaps offer predictable cash flows and legal enforceability, contrasting with DeFi yields, which face volatility from market fluctuations and protocol vulnerabilities. Evaluating these risk profiles is crucial for investors seeking balance between traditional regulatory safeguards and the autonomous yet riskier environment of decentralized finance.
Accessibility: Banks vs Blockchain in Financial Hedging
Interest rate swaps in traditional banking offer tailored hedging with established regulatory frameworks and deep liquidity but often require high entry thresholds and counterparty credit risk management. Decentralized finance (DeFi) yield protocols provide more accessible financial hedging by enabling anyone with internet access to participate without intermediaries, leveraging blockchain transparency and smart contracts. However, DeFi faces challenges in scalability, regulatory uncertainty, and potential vulnerability to smart contract exploits compared to the regulated and mature banking environment.
Cost Structures: Fees and Hidden Expenses
Interest Rate Swaps typically involve upfront negotiation, counterparty credit risk, and intermediary fees that can increase overall hedging costs, while decentralized finance (DeFi) yields offer transparent, algorithm-driven returns but may incur gas fees, slippage, and platform-specific hidden expenses. Swap agreements often have fixed fee schedules and potential margin calls, whereas DeFi protocols may charge variable fees based on network congestion and smart contract interactions. Understanding the distinct fee frameworks and hidden costs in both mechanisms is essential for effective hedging strategies and optimized cost management.
Regulatory Environment: Compliance in Swaps vs DeFi
Interest rate swaps operate within a well-established regulatory environment governed by bodies such as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), ensuring compliance with standardized reporting, clearing, and margin requirements. In contrast, decentralized finance (DeFi) yield protocols function in a largely unregulated space, facing regulatory uncertainty and evolving legal scrutiny regarding securities laws and anti-money laundering (AML) standards. This regulatory divergence influences counterparty risk management and compliance costs, making swaps more predictable for institutional hedging while DeFi yields offer innovation but with higher legal and operational risks.
Counterparty Risk: Centralized vs Decentralized Solutions
Interest rate swaps involve counterparty risk due to reliance on centralized financial institutions that may default or fail to meet obligations, potentially causing significant losses. Decentralized finance (DeFi) yield protocols operate on blockchain technology with smart contracts that mitigate counterparty risk by eliminating intermediaries and providing transparent, automated execution. However, DeFi carries smart contract vulnerabilities and platform risks, requiring careful assessment compared to traditional centralized counterparties.
Yield Volatility: Fixed Swap Rates vs Variable DeFi Returns
Interest rate swaps offer fixed, predictable rates that minimize yield volatility, making them ideal for hedging against fluctuating interest expenses. In contrast, decentralized finance (DeFi) yields are variable and often subject to high volatility due to market demand, liquidity changes, and protocol risks. Fixed swap rates provide stability and risk mitigation, while DeFi returns require active management to handle unpredictable yield fluctuations.
Liquidity Considerations for Hedging Strategies
Interest rate swaps offer deep liquidity through established over-the-counter markets, providing precise hedging against interest rate fluctuations, while decentralized finance (DeFi) yields often face liquidity fragmentation across multiple protocols and smart contract risks. The concentrated liquidity pools in interest rate swaps reduce slippage and counterparty risk, essential for large-scale hedging strategies, whereas DeFi yields may experience volatility and impermanent loss due to market fragmentation and lower capital reserves. Effective hedging requires balancing the robust liquidity and credit control of traditional swaps with the innovative but less liquid and more volatile environment of DeFi yield instruments.
Choosing the Right Hedging Tool: Key Decision Factors
Interest rate swaps offer tailored hedging solutions with customizable fixed and floating rates, providing precise exposure management for institutional investors. Decentralized Finance yields present alternative liquidity options with variable returns, leveraging blockchain transparency and automation but higher volatility. Key decision factors include counterparty risk, regulatory environment, liquidity, and customization flexibility to align with specific risk profiles and portfolio goals.
Related Important Terms
Cross-Chain Interest Rate Swaps
Cross-chain interest rate swaps enable seamless hedging of interest rate risk by leveraging decentralized finance protocols across multiple blockchain networks, mitigating counterparty risk and enhancing liquidity. This innovation contrasts traditional interest rate swaps by providing transparent, programmable, and trustless execution with real-time, on-chain settlement, driving efficiency in interest rate derivative markets.
DeFi Rate Oracle Arbitrage
Interest rate swaps offer fixed-to-floating rate hedging traditionally used by institutional investors, while decentralized finance (DeFi) yield opportunities leverage real-time data from DeFi rate oracles to exploit arbitrage across lending protocols. DeFi rate oracle arbitrage captures discrepancies in interest rates on-chain, enabling dynamic risk management and potentially higher returns compared to conventional swaps through transparent, programmable smart contracts.
On-Chain IR Swap Clearing
On-chain interest rate swap clearing in decentralized finance (DeFi) offers transparent, automated execution of derivative contracts with reduced counterparty risk compared to traditional interest rate swaps, enabling efficient hedging of interest rate exposure directly on blockchain platforms. DeFi yield strategies leverage smart contracts for liquidity aggregation and staking rewards, but on-chain IR swap clearing provides more precise risk management and price discovery by decentralizing swap settlement and collateralization processes.
Algorithmic Yield Curve Protocols
Interest rate swaps provide customizable hedging through fixed and floating rate exchanges based on OTC derivatives, whereas decentralized finance yields leverage algorithmic yield curve protocols that dynamically adjust returns via smart contracts and on-chain liquidity pools. Algorithmic yield curve protocols optimize risk and return by automatically balancing rates across diverse maturities using decentralized oracles and automated market makers, offering enhanced transparency and composability compared to traditional interest rate swap mechanisms.
Real-World Asset (RWA) Yield Hedging
Interest rate swaps offer customizable hedging solutions for Real-World Asset (RWA) yield fluctuations by enabling parties to exchange fixed and floating rates, reducing exposure to interest rate volatility. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) yield strategies provide transparent, blockchain-based alternatives with programmable smart contracts, but they face challenges in liquidity and regulatory uncertainty compared to traditional interest rate swaps for RWA yield hedging.
Flash Loan Hedging Strategies
Interest rate swaps offer customizable hedging against interest rate fluctuations by exchanging fixed and variable rates between parties, providing precise risk management suited for institutional investors. Flash loan hedging strategies in decentralized finance leverage instant, uncollateralized borrowing to execute arbitrage or hedge positions within a single blockchain transaction, minimizing slippage and exposure duration in volatile markets.
Synthetic Fixed Rate DeFi
Synthetic Fixed Rate DeFi protocols offer a decentralized alternative to traditional interest rate swaps by enabling users to hedge interest rate risk with on-chain assets, eliminating counterparty risk and enhancing transparency. These DeFi instruments synthetically replicate fixed rate exposure through smart contracts, providing customizable and efficient interest rate hedging in volatile markets.
Decentralized Basis Swap Pools
Decentralized Basis Swap Pools in DeFi offer flexible interest rate hedging by enabling users to exchange floating rate exposure without centralized intermediaries, providing enhanced liquidity and transparency compared to traditional Interest Rate Swaps. These pools leverage blockchain protocols to efficiently manage basis risk while delivering competitive yields, attracting participants seeking decentralized alternatives for risk management and yield optimization.
Automated Risk Tranching in DeFi
Interest rate swaps provide customizable, bilateral contracts for hedging interest rate exposure, while decentralized finance (DeFi) yield strategies utilize automated risk tranching to distribute risk across multiple asset tiers, enhancing capital efficiency and transparency. Automated risk tranching in DeFi protocols leverages smart contracts to dynamically allocate yields and risks, enabling more flexible and decentralized interest rate hedging compared to traditional swap agreements.
Perpetual Yield Rate Derivatives
Interest rate swaps offer customizable cash flow hedging through fixed-to-floating rate exchanges, enabling precise risk management against interest rate fluctuations. Decentralized finance perpetual yield rate derivatives provide continuous, on-chain yield exposure with enhanced liquidity and transparency but carry smart contract and market volatility risks.
Interest Rate Swap vs Decentralized Finance Yield for hedging Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com