Interest on savings accounts offers a stable and low-risk way to grow assets with predictable returns, ideal for conservative investors seeking security. Yield farming interest, on the other hand, provides higher potential returns by leveraging decentralized finance protocols but involves greater risk and volatility. Balancing the two can optimize asset growth by combining the safety of traditional savings with the dynamic opportunities of yield farming.
Table of Comparison
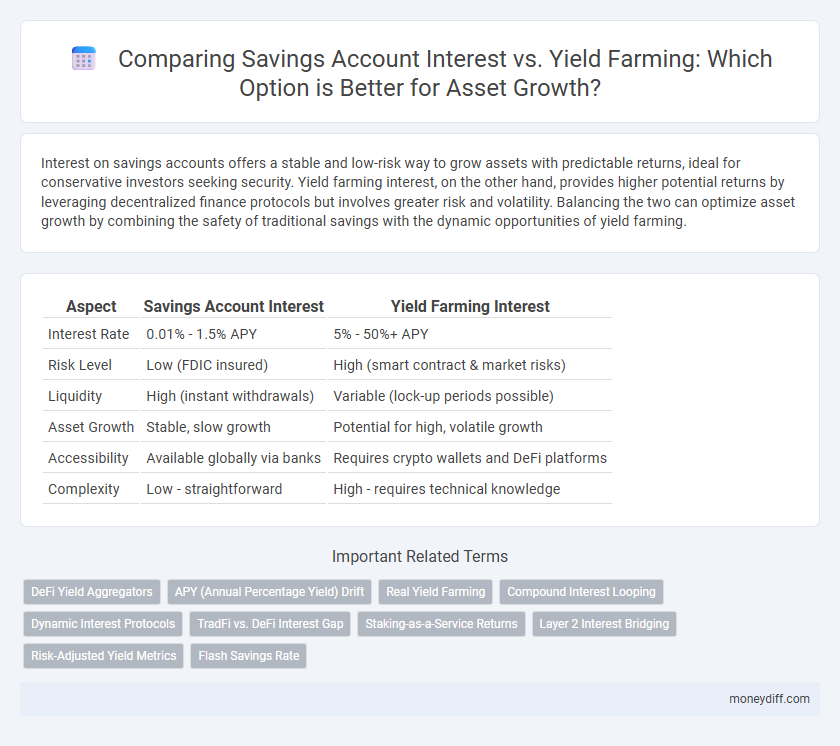
| Aspect | Savings Account Interest | Yield Farming Interest |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | 0.01% - 1.5% APY | 5% - 50%+ APY |
| Risk Level | Low (FDIC insured) | High (smart contract & market risks) |
| Liquidity | High (instant withdrawals) | Variable (lock-up periods possible) |
| Asset Growth | Stable, slow growth | Potential for high, volatile growth |
| Accessibility | Available globally via banks | Requires crypto wallets and DeFi platforms |
| Complexity | Low - straightforward | High - requires technical knowledge |
Understanding Interest: Savings Accounts vs Yield Farming
Savings account interest typically offers lower, fixed returns with high security and federal insurance protection, making it suitable for conservative asset growth. Yield farming interest leverages decentralized finance protocols to provide significantly higher, variable returns by lending or staking assets, but it involves greater risk including smart contract vulnerabilities and market fluctuations. Understanding these differences helps investors balance risk tolerance with growth objectives when choosing between traditional savings accounts and yield farming strategies.
Comparing Traditional and DeFi Interest Mechanisms
Interest on savings accounts typically offers lower, fixed rates determined by central banks and financial institutions, providing stable but modest asset growth. Yield farming in DeFi platforms leverages smart contracts to offer variable, often higher returns by utilizing liquidity pools and decentralized protocols. Traditional savings provide security and regulatory oversight, whereas DeFi yield farming presents higher risk with potential for greater interest through innovative, algorithm-driven mechanisms.
Safety and Risk: Where Is Your Money Safer?
Interest on savings accounts offers greater safety due to FDIC insurance protecting deposits up to $250,000, minimizing risk of loss. Yield farming interest, while potentially higher, carries significant risks including smart contract vulnerabilities and market volatility, which can result in loss of principal. Evaluating risk tolerance and prioritizing capital preservation helps determine where your money is safer for asset growth.
Calculating Returns: APY and Compound Interest Explained
Annual Percentage Yield (APY) quantifies savings account growth by incorporating compound interest, reflecting the true return over a year. Yield farming interest often offers higher APYs by reinvesting rewards, accelerating asset growth through compounding cycles. Calculating returns requires considering frequency of compounding to compare traditional savings accounts with yield farming outcomes accurately.
Liquidity Considerations: Accessing Your Funds
Savings account interest provides immediate liquidity, allowing account holders to withdraw funds anytime without penalties or delays, which is crucial for emergency access. Yield farming interest, while often offering higher returns, typically involves locking assets in decentralized finance protocols, limiting immediate access and increasing the risk of impermanent loss. Understanding liquidity constraints helps investors balance asset growth objectives with the need for financial flexibility.
Security and Regulation: Banking vs Crypto Protocols
Interest on savings accounts is typically secured by government-backed insurance programs such as the FDIC, offering strong regulatory oversight and risk mitigation. Yield farming interest in crypto protocols, while potentially higher, operates in a less regulated environment with smart contract vulnerabilities and no formal insurance. Investors seeking asset growth must weigh the stability and regulatory protections of traditional banking against the innovative but riskier crypto yield farming landscape.
Inflation Impact: Preserving Value in Both Options
Interest on savings accounts typically lags behind inflation, eroding real purchasing power over time despite nominal gains. Yield farming interest, though volatile, often offers higher returns that can better outpace inflation, preserving and growing the real value of assets. Assessing inflation impact is crucial to choosing between the stability of savings interest and the potentially higher, but riskier, inflation-beating yields in yield farming.
Fees and Hidden Costs: What’s Eating Your Earnings?
Interest on savings accounts typically offers low returns with minimal fees, ensuring most earnings remain intact. Yield farming interest can generate higher yields but often involves complex fees, impermanent loss, and hidden transaction costs that reduce net profits. Understanding fee structures and potential hidden charges is essential to accurately compare asset growth between these two options.
Tax Implications for Interest Earned
Interest earned on savings accounts is typically subject to standard income tax rates, with banks reporting interest income to tax authorities annually. In contrast, yield farming interest is often considered taxable as ordinary income or capital gains depending on jurisdiction, and investors must track complex transactions for accurate tax reporting. The tax implications of yield farming can be more complex due to frequent token transactions, requiring detailed record-keeping to comply with tax regulations and optimize asset growth strategies.
Choosing the Best Strategy for Asset Growth
Interest on savings accounts offers stable, low-risk returns typically ranging from 0.01% to 1.5% annually, suitable for conservative asset growth and emergency funds. Yield farming interest, often exceeding 10% APY, involves higher risks like smart contract vulnerabilities and market volatility but can significantly accelerate asset growth when managed carefully. Evaluating risk tolerance, investment horizon, and liquidity needs is essential to choose between the security of savings accounts and the high-yield potential of yield farming.
Related Important Terms
DeFi Yield Aggregators
DeFi yield aggregators offer significantly higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts by leveraging automated strategies across multiple protocols to maximize asset growth. While savings accounts provide steady but low-interest returns often below inflation, yield farming interest through these platforms can exponentially increase yields due to compounding rewards and liquidity incentives in decentralized finance ecosystems.
APY (Annual Percentage Yield) Drift
Savings account interest rates typically offer a stable but low APY averaging around 0.5% to 1.5%, whereas yield farming can provide significantly higher APYs, often ranging from 10% to over 100%, though with increased volatility and risk. APY drift in yield farming occurs as market conditions and liquidity incentives fluctuate, making asset growth unpredictable compared to the consistent compounding offered by traditional savings accounts.
Real Yield Farming
Interest on savings accounts offers stable but typically low returns, often below inflation rates, limiting long-term asset growth. Real yield farming leverages decentralized finance protocols to generate higher, often compounding returns by providing liquidity or staking assets, significantly enhancing portfolio growth potential through active management and strategic risk exposure.
Compound Interest Looping
Interest on savings accounts typically offers low, fixed compound interest rates, providing steady but modest asset growth, whereas yield farming interest leverages high, variable compound returns through decentralized finance protocols, enabling accelerated asset accumulation by reinvesting earnings in a compound interest looping process. This looping strategy exponentially increases yields by continuously cycling rewards back into the principal, maximizing the growth potential far beyond traditional savings account compounding.
Dynamic Interest Protocols
Dynamic interest protocols offer adaptive yield farming strategies that often outperform traditional savings account interest rates by leveraging decentralized finance mechanisms for asset growth. Savings accounts provide fixed, low-interest returns with minimal risk, while dynamic protocols adjust rates based on market conditions, maximizing potential earnings through liquidity provision and staking incentives.
TradFi vs. DeFi Interest Gap
Interest on traditional savings accounts typically offers low annual percentage yields (APYs) averaging around 0.05% to 0.5%, reflecting the conservative risk and regulatory frameworks of traditional finance (TradFi). Yield farming in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms can provide significantly higher returns, often ranging from 5% to over 100% APY, though these gains come with increased risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities and market volatility, highlighting the substantial interest gap between TradFi and DeFi asset growth opportunities.
Staking-as-a-Service Returns
Staking-as-a-Service offers significantly higher returns compared to traditional savings account interest rates, often yielding annual percentages ranging from 5% to 15%, depending on the blockchain network and asset staked. While savings accounts typically offer less than 1% APY, yield farming through staking leverages decentralized finance protocols to maximize asset growth, albeit with increased market and platform risks.
Layer 2 Interest Bridging
Interest on savings accounts offers stable but low returns, typically around 0.5% to 2% annually, while yield farming on Layer 2 networks delivers significantly higher yields, often ranging from 10% to 30% through decentralized finance protocols. Layer 2 interest bridging optimizes asset growth by reducing transaction fees and latency, enabling more efficient compounding opportunities compared to traditional savings.
Risk-Adjusted Yield Metrics
Interest on savings accounts offers stable, low-risk returns typically around 0.01% to 1.5% annually, providing capital preservation but limited growth potential. Yield farming interest, while capable of delivering significantly higher annual percentage yields (APYs) exceeding 10% to 100%, involves increased risk exposure such as smart contract vulnerabilities and market volatility, making risk-adjusted yield metrics like the Sharpe ratio crucial for evaluating true asset growth potential.
Flash Savings Rate
Flash Savings Rate on traditional savings accounts typically offers low, fixed interest rates often below 1%, limiting asset growth potential compared to yield farming strategies. Yield farming leverages decentralized finance protocols to provide variable, higher returns by staking or lending assets, but carries increased risk and market volatility.
Interest on Savings Account vs Yield Farming Interest for asset growth. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com