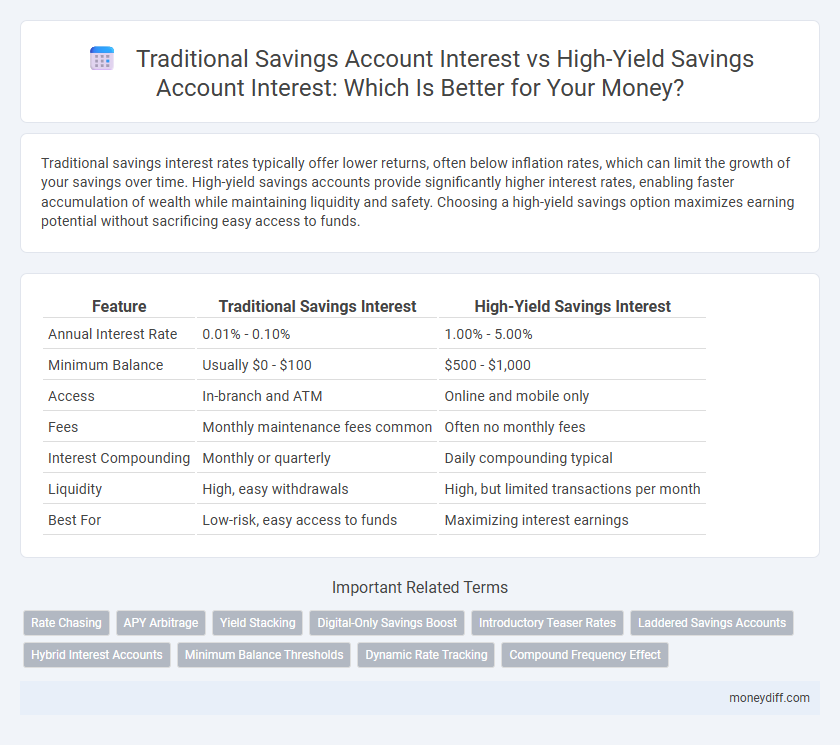
Traditional savings interest rates typically offer lower returns, often below inflation rates, which can limit the growth of your savings over time. High-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher interest rates, enabling faster accumulation of wealth while maintaining liquidity and safety. Choosing a high-yield savings option maximizes earning potential without sacrificing easy access to funds.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Savings Interest | High-Yield Savings Interest |
|---|---|---|
| Annual Interest Rate | 0.01% - 0.10% | 1.00% - 5.00% |
| Minimum Balance | Usually $0 - $100 | $500 - $1,000 |
| Access | In-branch and ATM | Online and mobile only |
| Fees | Monthly maintenance fees common | Often no monthly fees |
| Interest Compounding | Monthly or quarterly | Daily compounding typical |
| Liquidity | High, easy withdrawals | High, but limited transactions per month |
| Best For | Low-risk, easy access to funds | Maximizing interest earnings |
Understanding Traditional Savings Interest Rates
Traditional savings interest rates typically range from 0.01% to 0.10% APY, reflecting lower returns due to minimal risk and high liquidity. These rates are influenced by the Federal Reserve's benchmark rates and tend to stay stable over time, making them predictable for long-term savers. Understanding the modest growth potential and ease of access helps individuals balance the benefits of safety versus higher yields found in alternative accounts.
What Sets High-Yield Savings Accounts Apart
High-yield savings accounts offer interest rates significantly above the national average, often ranging from 0.40% to over 4.00% APY, compared to traditional savings rates typically below 0.10% APY. These accounts leverage online banking platforms and lower overhead costs to pass on better returns to customers, making them an attractive choice for savers seeking faster growth on their deposits. FDIC insurance protects funds up to $250,000, ensuring safety alongside higher interest gains.
Comparing Interest Rates: Traditional vs High-Yield
Traditional savings accounts typically offer interest rates ranging from 0.01% to 0.10%, providing minimal growth on deposited funds. In contrast, high-yield savings accounts feature significantly higher interest rates, often between 3.00% and 4.50%, allowing for faster accumulation of savings. This stark difference makes high-yield accounts more advantageous for maximizing interest earnings over time.
Accessibility and Convenience in Savings Accounts
Traditional savings accounts often offer widespread accessibility through extensive branch networks and widely available ATMs, ensuring convenience for routine transactions. High-yield savings accounts primarily operate online, providing limited physical locations but enhanced digital access, including mobile apps and instant transfers. The choice between the two depends on whether users prioritize physical banking presence or streamlined online management for savings growth.
Security and FDIC Insurance for Your Savings
Traditional savings accounts offer basic interest rates with full FDIC insurance coverage, ensuring your funds remain secure up to $250,000 per depositor. High-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher interest rates while maintaining the same FDIC protection, making them a safe option for maximizing returns. Both account types prioritize security, but high-yield accounts leverage competitive rates to grow savings faster without sacrificing insured protection.
Minimum Balance Requirements and Fees
Traditional savings accounts often have low or no minimum balance requirements but typically offer lower interest rates, making them suitable for basic saving needs. High-yield savings accounts usually require higher minimum balances to avoid fees, but they provide significantly better interest rates, enhancing overall returns. Understanding the trade-off between minimum balance thresholds and associated fees is crucial for maximizing savings growth in both account types.
How Interest Compounds in Different Savings Accounts
Traditional savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates with interest compounded monthly or quarterly, resulting in modest growth over time. High-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher interest rates, often compounded daily, which accelerates the accumulation of earnings through more frequent interest-on-interest effects. Understanding the compounding frequency and rate differences is crucial for maximizing returns and optimizing savings strategies in banking.
Online Banks vs Brick-and-Mortar Banks: Where is the Yield?
Online banks typically offer higher savings interest rates compared to brick-and-mortar banks due to lower overhead costs and operational expenses. Traditional banks often provide average interest rates around 0.01% to 0.10%, while online banks can offer high-yield savings accounts with rates ranging from 3% to 4% or more. This significant difference in yield emphasizes the growing advantage of online banking for savers seeking better returns on their deposits.
Pros and Cons of High-Yield Savings Accounts
High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts, enabling faster growth of deposited funds through compound interest. These accounts often come with limitations such as minimum balance requirements and limited monthly withdrawals, which can restrict accessibility. While high-yield accounts provide enhanced returns, potential fees and access constraints should be carefully evaluated against individual financial goals.
Choosing the Right Savings Account for Your Financial Goals
Traditional savings accounts typically offer interest rates around 0.01% to 0.10%, making them suitable for short-term savings with immediate access. High-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher rates, often between 0.40% to 4.00%, which can maximize returns for long-term financial goals. Choosing the right savings account depends on balancing liquidity needs and desired growth, ensuring the interest rate aligns with your personal financial objectives.
Related Important Terms
Rate Chasing
Traditional savings interest rates typically range from 0.01% to 0.10%, providing minimal growth on deposits, while high-yield savings accounts offer rates between 0.40% and 1.50%, significantly increasing potential earnings through interest compounding. Rate chasing involves frequently moving funds to accounts with the highest available interest rates, but it can incur risks such as withdrawal limits, potential fees, and the instability of promotional rates.
APY Arbitrage
High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher Annual Percentage Yields (APY) compared to traditional savings accounts, enabling consumers to benefit from APY arbitrage by shifting funds to accounts with superior interest rates. This strategy maximizes returns by exploiting the interest rate differential without increased risk, effectively enhancing passive income through optimized banking choices.
Yield Stacking
Traditional savings accounts typically offer low-interest rates around 0.01% to 0.10%, limiting yield potential, while high-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher rates ranging from 3% to 5%, enabling enhanced yield stacking through compounded returns and strategic fund allocations. Yield stacking in high-yield savings maximizes overall interest earnings by layering multiple accounts or combining savings with certificates of deposit (CDs) to capitalize on varying rate tiers and promotional offers.
Digital-Only Savings Boost
Digital-only savings accounts typically offer high-yield interest rates that significantly outperform traditional savings accounts, leveraging lower overhead costs to pass increased returns directly to customers. This shift enables savers to maximize earnings through seamless online access and higher APYs, revolutionizing conventional banking interest models.
Introductory Teaser Rates
Traditional savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates, often around 0.01% to 0.10%, whereas high-yield savings accounts provide introductory teaser rates that can range from 3% to 5% annually for a limited period. These promotional rates attract new customers but usually revert to standard rates after a few months, making it essential to compare long-term yields.
Laddered Savings Accounts
Laddered savings accounts strategically spread funds across multiple traditional and high-yield savings accounts with staggered maturity dates, optimizing interest earnings by balancing liquidity and higher rates. This approach leverages the stable returns of traditional savings interest while capturing the elevated yields offered by high-yield accounts, enhancing overall portfolio growth.
Hybrid Interest Accounts
Hybrid interest accounts combine the steady reliability of traditional savings interest rates with the enhanced returns typical of high-yield savings accounts, offering account holders a balanced approach to growing savings efficiently. These accounts typically feature tiered interest rates that increase with higher balances, optimizing earnings while maintaining liquidity and minimizing risk compared to purely high-yield options.
Minimum Balance Thresholds
Traditional savings accounts typically require lower minimum balance thresholds, often around $100, making them accessible to most customers but offering lower interest rates. High-yield savings accounts usually have higher minimum balance requirements, ranging from $1,000 to $5,000, to qualify for significantly higher interest rates and maximize earnings.
Dynamic Rate Tracking
High-yield savings accounts offer dynamic rate tracking that adjusts interest rates based on market conditions, often resulting in higher returns compared to traditional savings accounts with fixed rates. This adaptive interest calculation enhances savings growth potential by aligning with fluctuating economic trends and benchmark rates like the federal funds rate.
Compound Frequency Effect
High-yield savings accounts typically offer more frequent compound interest--daily or monthly--compared to traditional savings accounts, which often compound interest quarterly or annually, resulting in significantly higher returns over time. The increased compound frequency accelerates the growth of principal and interest earnings, maximizing the effective annual yield and enhancing long-term savings performance.
Traditional Savings Interest vs High-Yield Savings Interest for banking. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com