Annual interest on deposit accounts calculates earnings based on the total interest accumulated over a year, providing a clear overview of potential returns. Daily interest, however, compounds interest every day, allowing funds to grow faster as accrued interest is added to the balance regularly. Choosing between annual and daily interest impacts how quickly your savings increase and can significantly affect long-term financial growth.
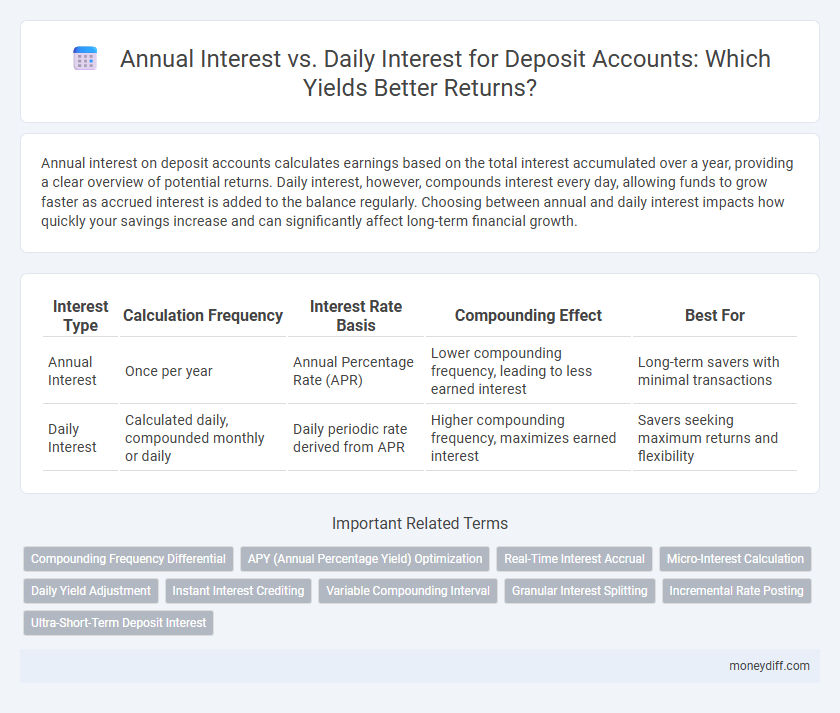
Table of Comparison
| Interest Type | Calculation Frequency | Interest Rate Basis | Compounding Effect | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Interest | Once per year | Annual Percentage Rate (APR) | Lower compounding frequency, leading to less earned interest | Long-term savers with minimal transactions |
| Daily Interest | Calculated daily, compounded monthly or daily | Daily periodic rate derived from APR | Higher compounding frequency, maximizes earned interest | Savers seeking maximum returns and flexibility |
Understanding Annual Interest and Daily Interest
Annual interest calculates the percentage earned on a deposit account over a full year, providing a straightforward measure of profitability. Daily interest divides the annual rate by 365 days, applying earnings based on the account balance each day, enhancing compounding effects. Understanding the distinction helps investors optimize returns by choosing accounts with the most beneficial interest calculation method.
How Daily Interest Works for Deposit Accounts
Daily interest for deposit accounts is calculated on the account balance at the end of each day, allowing interest to accrue every 24 hours. This method enables the compounding of interest more frequently, which can result in higher earnings compared to annual interest that is calculated once per year. Depositors benefit from daily interest as their balances grow incrementally, maximizing returns especially when deposits or withdrawals occur frequently.
Calculating Annual Interest: What You Need to Know
Calculating annual interest for deposit accounts requires understanding the principal amount, the interest rate, and the compounding frequency, which influences how interest accumulates over time. Annual interest is typically calculated using the formula A = P(1 + r/n)^(nt), where P is the principal, r is the annual interest rate, n is the number of compounding periods per year, and t is the time in years. Accurate calculation of annual interest helps depositors maximize returns by choosing accounts with favorable compounding intervals and rates.
Key Differences: Annual Interest vs Daily Interest
Annual interest calculates earnings based on the total balance over the entire year, offering a fixed rate applied once annually. Daily interest accrues interest every day by applying the rate to the daily balance, resulting in compound growth throughout the year. Understanding these differences helps depositors choose accounts that maximize returns based on their saving patterns and withdrawal frequency.
Pros and Cons of Annual Interest Compounding
Annual interest compounding accrues interest once per year, potentially resulting in lower overall returns compared to daily compounding, especially for accounts with frequent deposits or withdrawals. This method simplifies interest calculations and provides predictable earnings, which can benefit long-term savers seeking stability. However, the less frequent compounding limits the benefits of interest-on-interest growth, reducing the effective yield compared to daily compounding accounts.
The Benefits of Daily Interest for Savers
Daily interest for deposit accounts allows savers to earn interest on their balance every single day, increasing the total returns compared to annual interest calculations. This frequent compounding accelerates wealth growth, especially when interest is calculated on a balance that frequently fluctuates due to deposits or withdrawals. Savers benefit from more accurate interest calculations tied to their actual account balance, maximizing earnings without requiring a full year's wait.
Which Accounts Offer Daily Interest?
Savings accounts, money market accounts, and certain high-yield checking accounts typically offer daily interest, calculating earnings based on the account balance each day. Daily interest allows funds to grow faster compared to annual interest, as the interest compounds more frequently. Checking account types with features like rewards or high balances often provide daily interest to attract depositors seeking optimized returns.
Maximizing Returns: Choosing Daily or Annual Interest
Maximizing returns on deposit accounts depends significantly on choosing between daily and annual interest calculations. Daily interest accrues and compounds more frequently, enhancing the effective yield compared to annual interest, which compounds just once per year. Opting for daily interest accounts accelerates the growth of principal, especially with higher deposit balances and longer investment durations.
Daily vs Annual Interest: Impact on Earnings
Daily interest calculation on deposit accounts compounds earnings more frequently than annual interest, resulting in higher overall returns. When interest is credited daily, deposit balances grow incrementally, leveraging the power of compounding interest throughout the year. In contrast, annual interest compounding applies interest once per year, which may limit potential earnings compared to daily compounding methods.
Tips for Choosing the Best Interest Compounding Method
Choosing the best interest compounding method for deposit accounts depends on the frequency of interest calculation and its impact on overall returns. Daily interest compounding typically yields higher effective annual returns compared to annual compounding due to interest being calculated and added to the principal more frequently, which accelerates growth. Prioritize accounts with daily interest compounding when seeking maximum growth potential, especially for long-term deposits.
Related Important Terms
Compounding Frequency Differential
Annual interest compounds once per year, resulting in interest earned solely on the principal and previously accumulated interest at year-end, whereas daily interest compounds every day, allowing interest to accrue on an increasingly larger balance and thereby enhancing overall returns. The compounding frequency differential significantly impacts total earnings, with daily compounding providing a higher effective yield compared to annual compounding due to interest being calculated and added more frequently.
APY (Annual Percentage Yield) Optimization
Annual Percentage Yield (APY) optimization depends significantly on whether interest is compounded annually or daily, with daily compounding typically yielding higher returns due to interest earning interest every day. Depositors seeking maximum growth in deposit accounts should prioritize daily interest compounds, which enhance APY by calculating and crediting interest on a more frequent basis than annual compounding.
Real-Time Interest Accrual
Annual interest on deposit accounts is calculated once per year, leading to slower growth compared to daily interest, which accrues in real-time by compounding interest every day, maximizing returns. Real-time interest accrual enhances the compound effect, allowing deposit balances to grow faster and providing greater flexibility for withdrawals or additional deposits.
Micro-Interest Calculation
Annual interest calculates earnings based on the total deposit over a year, while daily interest computes returns on a micro-level by applying interest rates to daily balances, allowing for more precise growth tracking and potentially higher returns through compounding. Micro-interest calculation enhances accuracy by considering daily fluctuations, making it ideal for accounts with frequent transactions or varying balances.
Daily Yield Adjustment
Daily interest calculates earnings by adjusting the deposit balance every day based on the annual interest rate divided by 365, allowing for precise yield growth reflecting daily market fluctuations. This method contrasts with annual interest, which applies a fixed rate once per year, potentially missing opportunities to capitalize on short-term variations in interest rates or account balances.
Instant Interest Crediting
Instant interest crediting in deposit accounts enhances liquidity by calculating daily interest and crediting it immediately, allowing account holders to benefit from compounded earnings faster than traditional annual interest calculations. This method leverages daily interest compounding, increasing overall returns compared to the fixed once-a-year annual interest crediting system.
Variable Compounding Interval
Variable compounding intervals in deposit accounts influence the effective annual interest rate by calculating interest either daily or annually, with daily compounding typically yielding higher returns due to more frequent application of interest to the principal. Understanding the impact of these intervals on interest accumulation helps investors maximize earnings by choosing accounts with compounding frequencies aligned with their financial goals.
Granular Interest Splitting
Annual interest compounds less frequently, potentially reducing the benefits of granular interest splitting compared to daily interest calculations that allocate earnings on a daily basis, allowing more precise accrual and reinvestment. Daily interest maximizes returns by applying interest to the principal more regularly, thereby enhancing growth through frequent interest capitalization in deposit accounts.
Incremental Rate Posting
Annual interest on deposit accounts compounds once per year, resulting in a fixed return rate based on the total principal and accumulated interest over 12 months. Daily interest accrues incrementally each day, allowing for more frequent rate posting and potentially higher returns due to compounding on the accrued balance every day.
Ultra-Short-Term Deposit Interest
Ultra-short-term deposit interest rates typically offer annual interest figures quoted for convenience, but daily interest calculations provide a more precise measure of earnings by compounding interest on a daily basis. Comparing annual and daily interest rates allows depositors to optimize returns by understanding the effects of compounding frequency on their ultra-short-term investments.
Annual Interest vs Daily Interest for deposit accounts. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com