Health insurance offers comprehensive coverage through established providers, ensuring access to a wide network of healthcare services and predictable claim processes. Peer-to-peer insurance for medical expenses leverages community-driven risk sharing, potentially reducing costs by eliminating traditional insurer overhead and fostering transparency. Choosing between these options depends on individual preferences for reliability, cost-effectiveness, and the value of a collective risk model in managing medical expenses.
Table of Comparison
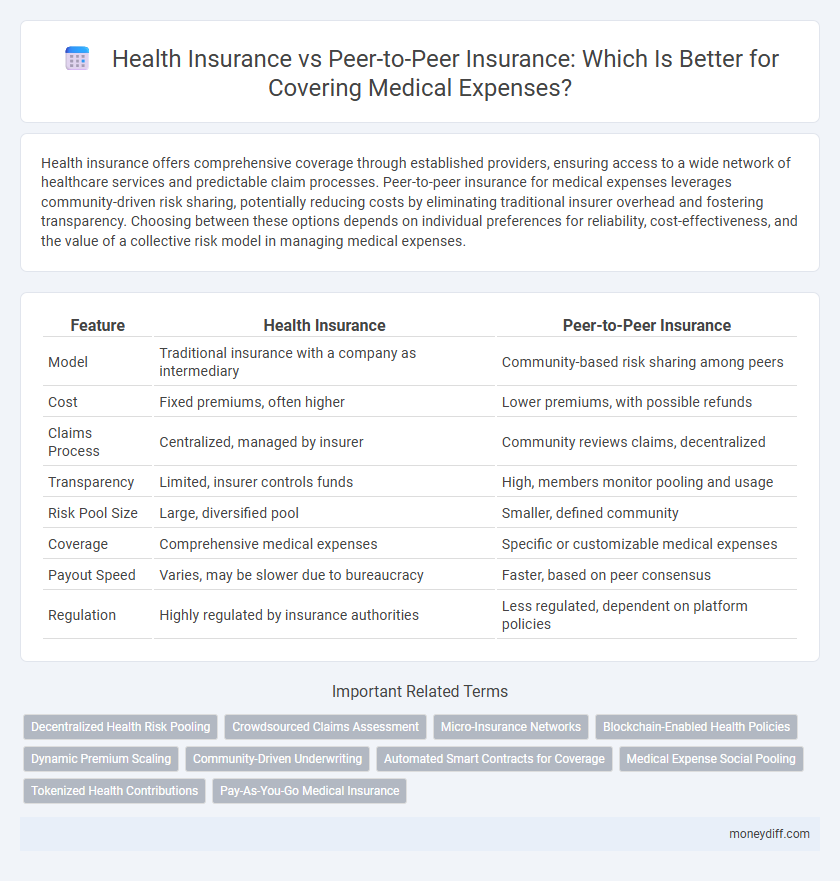
| Feature | Health Insurance | Peer-to-Peer Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Model | Traditional insurance with a company as intermediary | Community-based risk sharing among peers |
| Cost | Fixed premiums, often higher | Lower premiums, with possible refunds |
| Claims Process | Centralized, managed by insurer | Community reviews claims, decentralized |
| Transparency | Limited, insurer controls funds | High, members monitor pooling and usage |
| Risk Pool Size | Large, diversified pool | Smaller, defined community |
| Coverage | Comprehensive medical expenses | Specific or customizable medical expenses |
| Payout Speed | Varies, may be slower due to bureaucracy | Faster, based on peer consensus |
| Regulation | Highly regulated by insurance authorities | Less regulated, dependent on platform policies |
Understanding Traditional Health Insurance
Traditional health insurance typically involves a policyholder paying regular premiums to an insurance company in exchange for coverage of medical expenses, including hospital stays, surgeries, and prescription drugs. This model relies on risk pooling, where the insurer manages funds collectively from many members to cover the costs incurred by those who need medical care. It offers established networks of healthcare providers, standardized claim processes, and regulatory protections to ensure policyholder security and predictable access to medical services.
What Is Peer-to-Peer Insurance?
Peer-to-peer insurance is a decentralized model where groups of individuals pool their premiums to cover medical expenses collectively, reducing administrative costs and increasing transparency. Unlike traditional health insurance, which relies on large corporations and complex underwriting, peer-to-peer insurance leverages trust networks and technology platforms to facilitate claims and risk sharing. This approach often results in lower premiums and cash-back incentives for members who have fewer claims, aligning interests and enhancing community support in healthcare coverage.
Key Differences Between Health and P2P Insurance
Health insurance typically involves a contract with an insurer that guarantees coverage for medical expenses through premiums, deductibles, copayments, and established networks of providers. Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance operates by pooling funds from members to cover claims collectively, often promoting transparency and reduced administrative costs. Key differences include the traditional risk transfer model in health insurance versus the shared risk and community-driven approach of P2P insurance, impacting cost structure, claim processing, and member engagement.
Cost Comparison: Premiums and Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Health insurance typically involves higher premiums but offers broader coverage and predictable out-of-pocket expenses, while peer-to-peer insurance often features lower premiums by pooling risk among members, potentially reducing administrative fees. Out-of-pocket costs in peer-to-peer models can vary more due to claim-sharing among participants, whereas traditional health insurance sets defined copayments and deductibles. Choosing between the two depends on balancing premium affordability against the certainty of personal medical expense coverage.
Coverage Options and Flexibility
Health insurance offers comprehensive coverage options with standardized benefits tailored to a wide range of medical expenses, often including preventive care, hospitalization, and specialist services. Peer-to-peer insurance provides greater flexibility by allowing members to customize their coverage levels and share risk directly within a community, often resulting in lower premiums and more personalized benefits. This model encourages transparency and member control, unlike traditional health insurance plans that follow strict regulatory frameworks and predefined coverage structures.
Claims Process and Payout Procedures
Health insurance typically involves a structured claims process where policyholders submit medical bills and receive reimbursements or direct payments according to predetermined coverage limits and network agreements. Peer-to-peer insurance uses a decentralized model where members pool funds and approve claims collectively, often resulting in faster payouts but less standardized procedures. The transparency and community-driven nature of peer-to-peer insurance can reduce administrative overhead, whereas traditional health insurance provides regulatory protections and consistent claim adjudication.
Transparency and Trust in Insurance Models
Peer-to-peer insurance offers increased transparency by allowing members to directly oversee claim processes and fund usage, fostering greater trust compared to traditional health insurance models where opaque profit motives often obscure financial flows. Health insurance typically operates through centralized entities with complex regulations, potentially leading to mistrust due to limited insight into how premiums are allocated and claims are managed. Emphasizing transparency and mutual accountability, peer-to-peer insurance builds stronger trust among participants by aligning incentives and promoting open communication of medical expense handling.
Community Support vs. Corporate Backing
Health insurance provides corporate backing with established financial reserves and regulatory oversight, ensuring reliable coverage and claims processing for medical expenses. Peer-to-peer insurance emphasizes community support, pooling member contributions to cover healthcare costs collectively and fostering transparency and mutual trust. While corporate plans offer structured benefits and risk management, peer-to-peer models leverage social connections to reduce costs and promote shared responsibility in medical expense coverage.
Pros and Cons of Health Insurance
Health insurance offers comprehensive coverage with predictable premiums and access to a wide network of healthcare providers, ensuring financial protection against high medical expenses. However, it often involves complex policies, deductibles, and copayments that can lead to out-of-pocket costs, and some plans have limited flexibility in choosing providers. While health insurance provides regulatory oversight and consumer protections, its higher premiums and administrative costs may not suit everyone compared to alternative models like peer-to-peer insurance.
Pros and Cons of Peer-to-Peer Insurance
Peer-to-peer insurance offers increased transparency and reduced administrative costs by directly connecting policyholders, potentially lowering premiums compared to traditional health insurance. This model enhances community trust and claim accountability but may face challenges in risk pooling and coverage consistency, leading to potential gaps in extensive medical expense coverage. Limited regulatory oversight and smaller risk pools can increase financial vulnerability during high-cost medical events, making it essential to evaluate peer-to-peer insurance against comprehensive health insurance policies for critical healthcare needs.
Related Important Terms
Decentralized Health Risk Pooling
Decentralized health risk pooling in peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance enables members to share medical expenses directly, reducing reliance on traditional health insurers and enhancing transparency. This model leverages blockchain technology to create secure, automated claims processing while lowering administrative costs and minimizing fraud risks.
Crowdsourced Claims Assessment
Health insurance relies on traditional claim evaluation by professionals, whereas peer-to-peer insurance leverages crowdsourced claims assessment to increase transparency and reduce fraud through collective verification by policyholders. This decentralized approach enhances claim accuracy and promotes trust within the insured community while potentially lowering administrative costs.
Micro-Insurance Networks
Micro-insurance networks within health insurance offer scalable coverage tailored for low-income populations, enabling affordable access to essential medical services through pooled risk and community-based support. Peer-to-peer insurance for medical expenses leverages decentralized groups to reduce administrative costs and foster trust among members, providing a flexible alternative that often results in faster claims processing and personalized coverage options.
Blockchain-Enabled Health Policies
Blockchain-enabled health policies revolutionize medical expense coverage by enhancing transparency and reducing fraud in both traditional health insurance and peer-to-peer insurance models. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages decentralized networks to lower costs and improve trust among participants, while blockchain integration in health insurance streamlines claims processing and fosters secure sharing of medical data.
Dynamic Premium Scaling
Dynamic premium scaling in health insurance adjusts rates based on individual risk factors and medical history to provide personalized coverage, whereas peer-to-peer insurance uses collective risk-sharing among members to stabilize premiums and reduce costs through mutual incentives. This mechanism in peer-to-peer models promotes transparency and community-driven claims management, contrasting with the actuarial risk assessments typical of traditional health insurance.
Community-Driven Underwriting
Health insurance typically relies on traditional actuarial risk assessments and insurer underwriting, whereas peer-to-peer insurance emphasizes community-driven underwriting, allowing members to pool funds and share medical expenses collaboratively. This model fosters transparency, reduces administrative overhead, and aligns incentives by leveraging collective risk evaluation and member accountability.
Automated Smart Contracts for Coverage
Automated smart contracts in health insurance streamline claims processing by verifying coverage and payments instantly, reducing administrative costs and fraud. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages blockchain-based smart contracts to transparently manage pooled funds and enable decentralized, trustless medical expense reimbursements among members.
Medical Expense Social Pooling
Medical expense social pooling in health insurance centralizes risk by spreading costs across a large group, ensuring predictable premiums and comprehensive coverage. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages decentralized social pooling, allowing members to contribute directly to each other's medical expenses, promoting transparency and potentially lowering costs through reduced administrative fees.
Tokenized Health Contributions
Tokenized health contributions in peer-to-peer insurance enable transparent, real-time tracking of premiums and claims through blockchain technology, reducing administrative costs compared to traditional health insurance. This decentralized approach fosters community-driven risk pooling and faster reimbursements, enhancing efficiency in managing medical expenses.
Pay-As-You-Go Medical Insurance
Pay-As-You-Go medical insurance in Peer-to-Peer (P2P) models offers flexibility by allowing members to pay premiums based on actual medical expenses, reducing upfront costs compared to traditional Health Insurance with fixed monthly premiums. This method enhances transparency and cost-efficiency by pooling contributions within a community to cover claims directly, minimizing administrative fees and insurer profits.
Health Insurance vs Peer-to-Peer Insurance for medical expenses. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com