Corporate insurance provides businesses with externally managed risk coverage through traditional insurance providers, offering standardized policies and broad market access. Captive insurance allows companies to create their own insurance subsidiary, granting greater control over policy terms, claims handling, and potential cost savings by retaining underwriting profits. Choosing between corporate and captive insurance depends on the business's risk profile, financial capacity, and desire for customized coverage solutions.
Table of Comparison
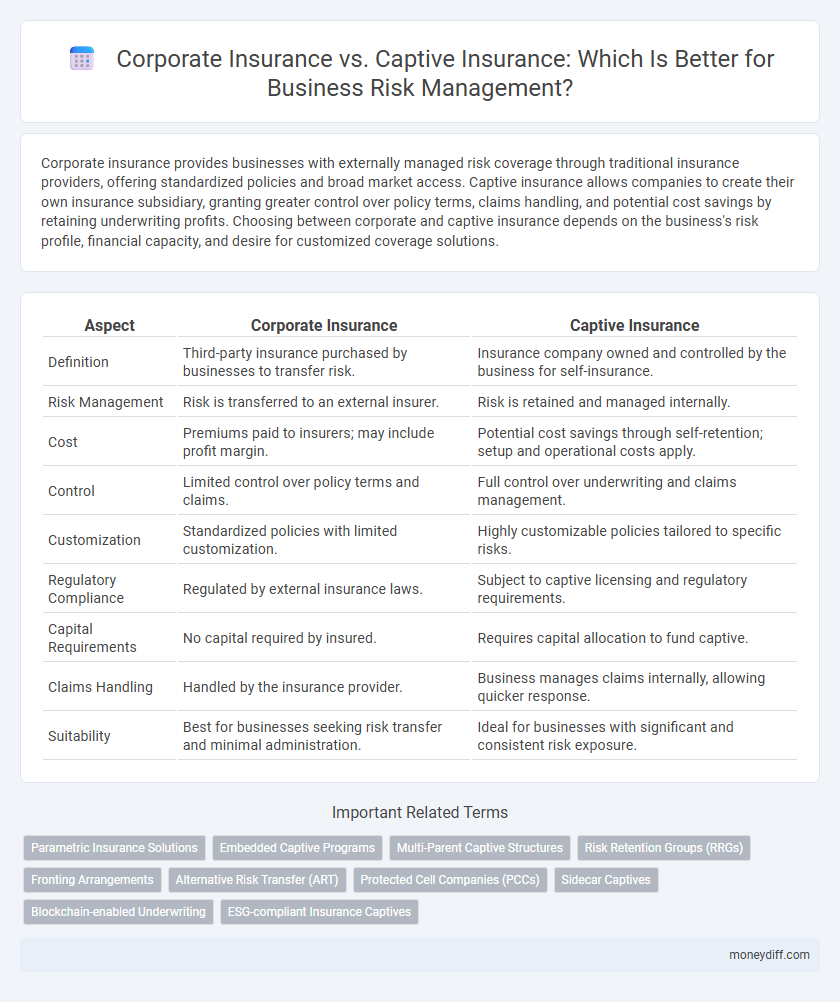
| Aspect | Corporate Insurance | Captive Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Third-party insurance purchased by businesses to transfer risk. | Insurance company owned and controlled by the business for self-insurance. |
| Risk Management | Risk is transferred to an external insurer. | Risk is retained and managed internally. |
| Cost | Premiums paid to insurers; may include profit margin. | Potential cost savings through self-retention; setup and operational costs apply. |
| Control | Limited control over policy terms and claims. | Full control over underwriting and claims management. |
| Customization | Standardized policies with limited customization. | Highly customizable policies tailored to specific risks. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Regulated by external insurance laws. | Subject to captive licensing and regulatory requirements. |
| Capital Requirements | No capital required by insured. | Requires capital allocation to fund captive. |
| Claims Handling | Handled by the insurance provider. | Business manages claims internally, allowing quicker response. |
| Suitability | Best for businesses seeking risk transfer and minimal administration. | Ideal for businesses with significant and consistent risk exposure. |
Understanding Corporate Insurance: Definition and Benefits
Corporate insurance involves purchasing risk coverage from third-party insurers, transferring financial liability for business risks such as property damage, liability claims, and employee injuries. It provides businesses with comprehensive protection, regulatory compliance, and risk management expertise, ensuring stability and continuity. By leveraging standardized policies and industry-specific solutions, corporate insurance helps mitigate unforeseen losses while preserving cash flow and creditworthiness.
What is Captive Insurance? Structure and Purpose
Captive insurance is a risk management strategy where a business creates a licensed insurance company to insure its own risks, reducing reliance on external insurers. This insurance subsidiary enables tailored coverage, cost control, and profit retention within the corporate group. Captive insurance structures vary, including single-parent captives, group captives, and agency captives, each designed to meet specific business risk profiles and financial objectives.
Key Differences Between Corporate and Captive Insurance
Corporate insurance involves purchasing risk coverage from third-party insurers, providing businesses with standardized policies and broad risk diversification. Captive insurance, by contrast, is a self-insurance mechanism where a company creates its own insurance subsidiary, allowing tailored risk management and potential cost savings through retained premiums. Key differences include risk control, premium costs, regulatory requirements, and potential for profit from underwriting results, with captives offering greater customization but requiring more capital and administrative oversight.
Cost Implications: Corporate vs Captive Insurance
Corporate insurance typically involves higher premiums and administrative expenses due to third-party risk transfer, while captive insurance can reduce long-term costs by allowing businesses to retain and manage their own risk more efficiently. Captive insurance often leads to improved cash flow, tax advantages, and customized coverage, which can lower the total cost of risk compared to traditional corporate policies. However, initial setup and regulatory compliance for captives require significant investment, making cost-effectiveness dependent on the scale and risk profile of the business.
Risk Control and Customization Options
Corporate insurance offers standardized risk control measures with limited customization, relying on broad policy frameworks designed for diverse businesses. Captive insurance enables businesses to develop tailored risk management strategies, providing greater flexibility in coverage terms and proactive loss prevention specific to organizational needs. Enhanced customization in captive insurance supports precise risk control, allowing companies to adjust policies dynamically based on evolving risk profiles.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance Issues
Corporate insurance requires businesses to adhere to standard regulatory frameworks established by state and federal agencies, ensuring strict compliance with licensing, financial solvency, and reporting obligations. Captive insurance offers greater flexibility but demands meticulous compliance with domicile-specific regulations and comprehensive risk management protocols to avoid penalties and maintain operational legitimacy. Navigating regulatory considerations effectively involves balancing statutory requirements with strategic risk retention to optimize financial and legal outcomes for the business.
Financial Stability and Capital Requirements
Corporate insurance typically offers broader risk coverage with established financial stability due to regulatory oversight and pooled resources from multiple policyholders. Captive insurance allows businesses to retain risk and potentially reduce premiums by self-insuring, but it requires substantial capital reserves and strict compliance to maintain solvency and regulatory approval. Effective management of capital requirements is crucial for captive insurers to ensure financial stability while optimizing risk retention strategies.
Claims Handling and Administration Efficiency
Corporate insurance provides businesses with external claims handling and established administrative processes, ensuring standardized and often quicker resolution times through professional underwriters and adjusters. Captive insurance allows companies to customize claims management and administration, enhancing control and potentially reducing costs, but may require more internal resources and specialized expertise to maintain efficiency. Efficient claims handling in captive insurance depends heavily on the firm's ability to integrate advanced claims systems and knowledgeable personnel, while corporate insurance benefits from streamlined, outsourced administration.
Tax Advantages and Implications
Corporate insurance offers businesses straightforward tax deductions on premium payments as ordinary business expenses, reducing taxable income in the policy year. Captive insurance, structured as an owned insurance company, can provide greater tax flexibility by allowing premium payments to accumulate within the captive, potentially deferring taxes and optimizing risk management expenses. Both frameworks require careful compliance with tax regulations, including transfer pricing rules and risk distribution standards, to maximize tax advantages and avoid IRS scrutiny.
Choosing the Right Insurance Model for Your Business
Corporate insurance provides businesses with risk transfer through third-party insurers, offering broad coverage and financial stability, while captive insurance allows companies to self-insure by creating their own insurance subsidiaries, enhancing risk control and potential cost savings. Selecting the right insurance model depends on factors such as risk appetite, financial capacity, regulatory environment, and long-term strategic goals. Businesses with consistent, predictable risks may benefit from captive insurance, whereas those seeking external risk management and simplicity often prefer traditional corporate insurance solutions.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Insurance Solutions
Parametric insurance solutions offer businesses an efficient alternative to traditional corporate insurance and captive insurance by providing predefined payouts based on specific triggers such as weather events or market indices, reducing claims processing time and uncertainty. These solutions enhance risk management strategies by delivering transparent, fast, and data-driven compensation, enabling businesses to mitigate financial losses from volatile risks without the administrative complexity of captive insurance structures.
Embedded Captive Programs
Embedded captive programs integrate captive insurance solutions directly within a corporation's risk management strategy, offering tailored coverage and enhanced control over underwriting profits compared to traditional corporate insurance policies. These programs reduce reliance on external insurers by financing specific risks internally, improving cost predictability and optimizing capital allocation for business risk management.
Multi-Parent Captive Structures
Multi-Parent Captive (MPC) structures enable multiple unrelated organizations to share ownership in a captive insurance company, optimizing risk retention and cost-efficiency compared to traditional corporate insurance policies. MPCs provide customized coverage and improved risk management flexibility for businesses seeking alternatives to conventional insurance market limitations.
Risk Retention Groups (RRGs)
Risk Retention Groups (RRGs) enable businesses to self-insure by pooling resources to retain and manage shared risks, offering greater control over premiums and coverage compared to traditional corporate insurance. Corporate insurance transfers risk to third-party insurers with fixed premiums but generally lacks the customizable risk retention benefits and potential cost savings provided by RRGs.
Fronting Arrangements
Fronting arrangements in corporate insurance involve a licensed insurer issuing policies and transferring most risks to a reinsurer, commonly a captive insurance company that provides risk retention and cost control for businesses. This setup enables companies to access regulatory compliance and market credibility while effectively managing risk through their captive, optimizing financial performance and coverage customization.
Alternative Risk Transfer (ART)
Corporate insurance typically involves transferring business risk to third-party insurers, while captive insurance, a form of Alternative Risk Transfer (ART), allows companies to self-insure by establishing a wholly owned insurance subsidiary. Captive insurance offers enhanced control over risk management, potential cost savings, and tailored coverage compared to traditional corporate insurance solutions.
Protected Cell Companies (PCCs)
Protected Cell Companies (PCCs) structure allows businesses to segregate assets and liabilities within distinct cells, optimizing risk management compared to traditional corporate insurance. Captive insurance through PCCs offers tailored coverage and cost-efficiency by isolating risks from other cell liabilities, enhancing financial protection and regulatory flexibility for multi-line businesses.
Sidecar Captives
Sidecar captives offer a flexible risk financing solution by allowing businesses to share exposure with third-party investors while maintaining control over underwriting and claims management, combining benefits of corporate insurance with captive insurance structures. These arrangements enhance capital efficiency and risk retention strategies by leveraging external capital without fully relying on traditional corporate insurance providers.
Blockchain-enabled Underwriting
Blockchain-enabled underwriting enhances transparency and efficiency in both corporate insurance and captive insurance by securely automating risk assessment and claims processing. This technology reduces fraud and operational costs while enabling businesses to tailor coverage through real-time data analysis and decentralized risk management.
ESG-compliant Insurance Captives
Corporate insurance transfers risk to external insurers, providing standardized coverage but limited control over ESG criteria, while ESG-compliant insurance captives enable businesses to retain risk internally, customize policies to meet environmental, social, and governance standards, and enhance transparency and sustainability in risk management. This approach aligns corporate risk strategies with sustainability goals, promotes responsible investment, and supports corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Corporate insurance vs Captive insurance for business risk. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com