Disability insurance provides financial support if you become unable to work due to illness or injury, typically offering a fixed percentage of your pre-disability income. Income protection insurance covers a broader range of circumstances, including partial disabilities, and can offer more flexible benefit periods tailored to your specific needs. Both policies enhance income security, but income protection insurance often includes more comprehensive coverage to maintain your financial stability.
Table of Comparison
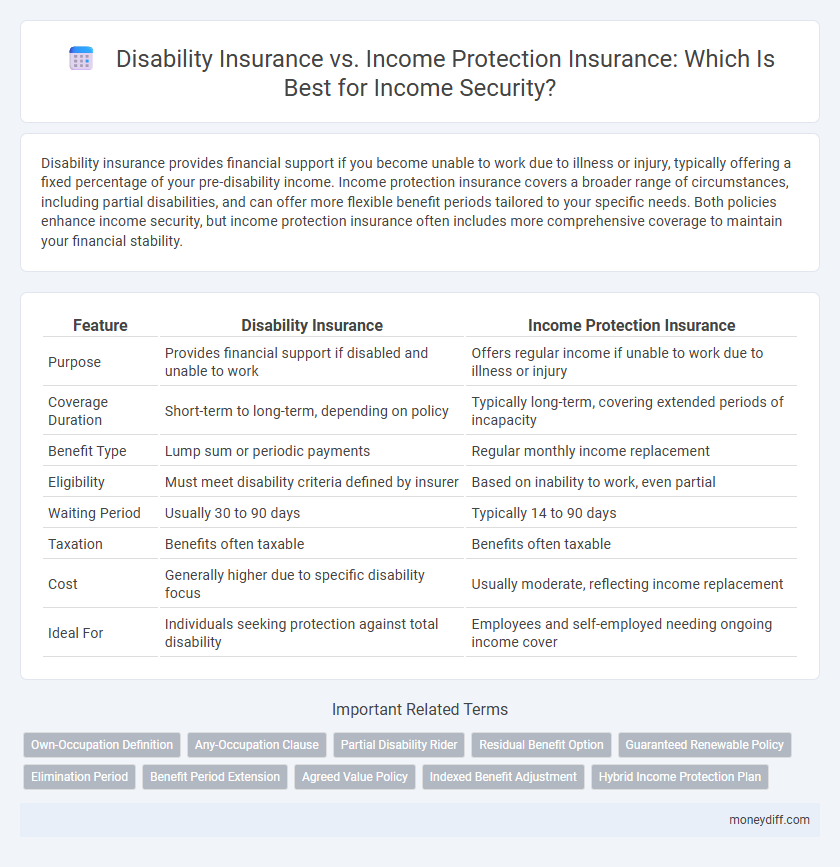
| Feature | Disability Insurance | Income Protection Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides financial support if disabled and unable to work | Offers regular income if unable to work due to illness or injury |
| Coverage Duration | Short-term to long-term, depending on policy | Typically long-term, covering extended periods of incapacity |
| Benefit Type | Lump sum or periodic payments | Regular monthly income replacement |
| Eligibility | Must meet disability criteria defined by insurer | Based on inability to work, even partial |
| Waiting Period | Usually 30 to 90 days | Typically 14 to 90 days |
| Taxation | Benefits often taxable | Benefits often taxable |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specific disability focus | Usually moderate, reflecting income replacement |
| Ideal For | Individuals seeking protection against total disability | Employees and self-employed needing ongoing income cover |
Understanding Disability Insurance and Income Protection Insurance
Disability insurance provides financial support by replacing a portion of your income if you become unable to work due to illness or injury, typically covering both short-term and long-term disabilities. Income protection insurance offers broader coverage by ensuring a steady income stream during periods when you cannot perform your job, often including benefits for partial disabilities and flexible waiting periods. Understanding the specific terms, benefit periods, and coverage limitations of each policy is crucial for securing reliable income protection tailored to individual financial needs.
Key Differences Between Disability and Income Protection Insurance
Disability insurance typically provides a fixed monthly benefit based on the policy's terms when the insured becomes unable to work due to illness or injury, often covering long-term disabilities with standardized definitions. Income protection insurance offers more flexible coverage, usually replacing a percentage of the insured's income and may include partial disability benefits, often tailored to individual earnings and employment status. Key differences include benefit structures, duration of payouts, policy definitions of disability, and eligibility criteria, impacting the choice based on personal financial security needs.
Which Insurance Offers Better Income Security?
Disability insurance provides financial support by replacing a portion of your income if you become unable to work due to illness or injury, often covering long-term disabilities with standardized benefit amounts. Income protection insurance offers more flexible coverage, typically paying a percentage of your salary up to a specified limit, and may include benefits such as adjustable terms and partial disability coverage. For better income security, income protection insurance generally delivers more tailored financial protection aligned with your actual earnings and recovery timeline.
Coverage Scope: Disability vs Income Protection
Disability insurance typically provides coverage specific to illnesses or injuries that prevent you from performing your occupational duties, often requiring medical proof of disability. Income protection insurance offers broader coverage, including protection against partial disabilities and non-occupational illnesses, ensuring a replacement income for a wider range of conditions. The scope of income protection insurance generally provides more flexible and extended income security compared to traditional disability insurance.
Eligibility Criteria and Policy Terms Compared
Disability insurance typically requires applicants to meet strict eligibility criteria, including medical evaluations and proof of current employment, while income protection insurance often has broader acceptance with less stringent health assessments. Policy terms for disability insurance usually offer longer benefit periods and higher payout ceilings, designed to cover partial or total disability, whereas income protection insurance focuses on replacing a percentage of income for shorter durations with flexible premium options. Understanding these distinctions helps secure income stability tailored to individual risk profiles and financial needs.
Payout Structure and Benefit Period Explained
Disability insurance typically offers a fixed monthly benefit based on a percentage of your pre-disability income, lasting until you return to work, reach a specified age (often 65), or meet the policy's maximum benefit period. Income protection insurance provides payouts designed to replace a portion of your earnings while you're unable to work due to illness or injury, with flexible benefit periods that may range from a few years to up to retirement age. The choice between these insurances depends on the desired payout structure and length of income replacement needed to ensure financial stability.
Cost and Premium Considerations
Disability insurance premiums often reflect the insured's occupation, age, and health, making coverage costly for high-risk professions compared to income protection insurance, which typically offers more flexible pricing tailored to broader employment categories. Income protection insurance generally provides adjustable benefit periods and waiting times, allowing policyholders to manage premiums more effectively based on their financial needs and risk tolerance. Cost efficiency between the two depends on individual circumstances, with income protection insurance often presenting a more affordable option for long-term income security due to its customizable features.
Exclusions and Limitations to Watch For
Disability insurance typically excludes coverage for pre-existing conditions, self-inflicted injuries, and certain high-risk activities, limiting payout eligibility. Income protection insurance often imposes waiting periods before benefits begin and may exclude mental health conditions or chronic illnesses from claims. Understanding these exclusions and limitations is crucial for securing reliable income protection and avoiding unexpected claim denials.
How to Choose the Right Insurance for Your Needs
Selecting the right insurance requires evaluating your financial obligations and employment status to determine if disability insurance or income protection insurance best suits your needs. Disability insurance typically offers benefits for long-term disabilities resulting from sickness or accidents, while income protection insurance provides regular income replacement during temporary inability to work. Assess policy terms, waiting periods, benefit limits, and coverage duration to ensure adequate income security tailored to your personal and professional circumstances.
Final Thoughts: Securing Your Income Against Disability
Disability insurance provides a crucial safety net by replacing a portion of your income if illness or injury prevents you from working, ensuring financial stability during challenging times. Income protection insurance often offers more comprehensive coverage with longer benefit periods and additional features like rehabilitation support, tailored to maintain your lifestyle despite income loss. Securing the right policy involves assessing your specific needs, understanding benefit triggers, and prioritizing coverage that aligns with your long-term income security goals.
Related Important Terms
Own-Occupation Definition
Own-Occupation Definition in disability insurance provides coverage if the insured cannot perform their specific job, ensuring income security tailored to their profession. Income protection insurance may use a broader definition, paying benefits only if the insured cannot work any job suited to their skills, potentially limiting financial support.
Any-Occupation Clause
Disability insurance with an Any-Occupation clause provides benefits only if the insured cannot work in any job suited to their education, experience, or training, offering narrower coverage but often lower premiums. Income protection insurance typically pays out if the insured is unable to perform their own occupation, ensuring more comprehensive income security by covering partial disabilities within their specific profession.
Partial Disability Rider
The Partial Disability Rider in disability insurance provides crucial benefits by covering partial loss of income when the policyholder can work in a limited capacity, offering more tailored income security than standard income protection insurance. This rider ensures ongoing financial support during recovery phases, mitigating gaps in earnings while maintaining essential lifestyle expenses.
Residual Benefit Option
Disability insurance with a Residual Benefit Option provides income security by covering partial disabilities, allowing policyholders to receive benefits proportional to their reduced earnings. Income protection insurance typically offers broader coverage but may lack tailored residual benefits, making disability insurance more suitable for maintaining financial stability during partial work capacity.
Guaranteed Renewable Policy
Guaranteed renewable policies in disability insurance ensure ongoing income protection by allowing policyholders to renew coverage without medical requalification, preserving financial security during unexpected income loss. Unlike income protection insurance, guaranteed renewable disability policies often provide stronger contractual guarantees and stability in premium rates, enhancing long-term income replacement reliability.
Elimination Period
Disability insurance typically features an elimination period ranging from 30 to 90 days, during which no benefits are paid, whereas income protection insurance often offers customizable elimination periods that can extend up to 180 days, allowing for tailored premium costs and coverage duration. Understanding the elimination period is crucial for income security, as it determines the waiting time before benefit payouts commence, directly impacting an insured individual's financial stability during a disability.
Benefit Period Extension
Disability insurance typically offers a fixed benefit period extension, often up to 2 years or until retirement age, providing long-term income security during extended incapacity. Income protection insurance, however, usually features flexible benefit period extensions tailored to individual needs, allowing policyholders to select coverage ranging from 1 to 5 years or more, ensuring customized financial support.
Agreed Value Policy
Disability insurance with an agreed value policy guarantees a predetermined benefit amount, providing certainty in income replacement regardless of income fluctuations before disability. Income protection insurance typically pays a percentage of pre-disability earnings but may vary with income changes, making agreed value disability insurance more reliable for long-term income security.
Indexed Benefit Adjustment
Indexed Benefit Adjustment in disability insurance ensures monthly payouts keep pace with inflation, preserving the insured's purchasing power over time. Income protection insurance may offer fixed benefits without indexing, potentially reducing real income security during long-term claims.
Hybrid Income Protection Plan
Hybrid Income Protection Plans combine the benefits of Disability Insurance and Income Protection Insurance by offering comprehensive coverage that ensures stable income during both partial and total disability periods, safeguarding financial security. These plans cover a broader range of conditions and include flexible payout options, making them an optimal choice for maintaining consistent income in unpredictable health scenarios.
Disability insurance vs Income protection insurance for income security. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com