Traditional insurance relies on centralized companies that pool premiums from many policyholders to cover claims, often resulting in higher administrative costs and less transparency. Peer-to-peer insurance enables a group of individuals to collectively share risks, which can reduce costs and increase trust through direct accountability among members. This decentralized approach fosters more personalized coverage and potentially faster claims processing by minimizing intermediary involvement.
Table of Comparison
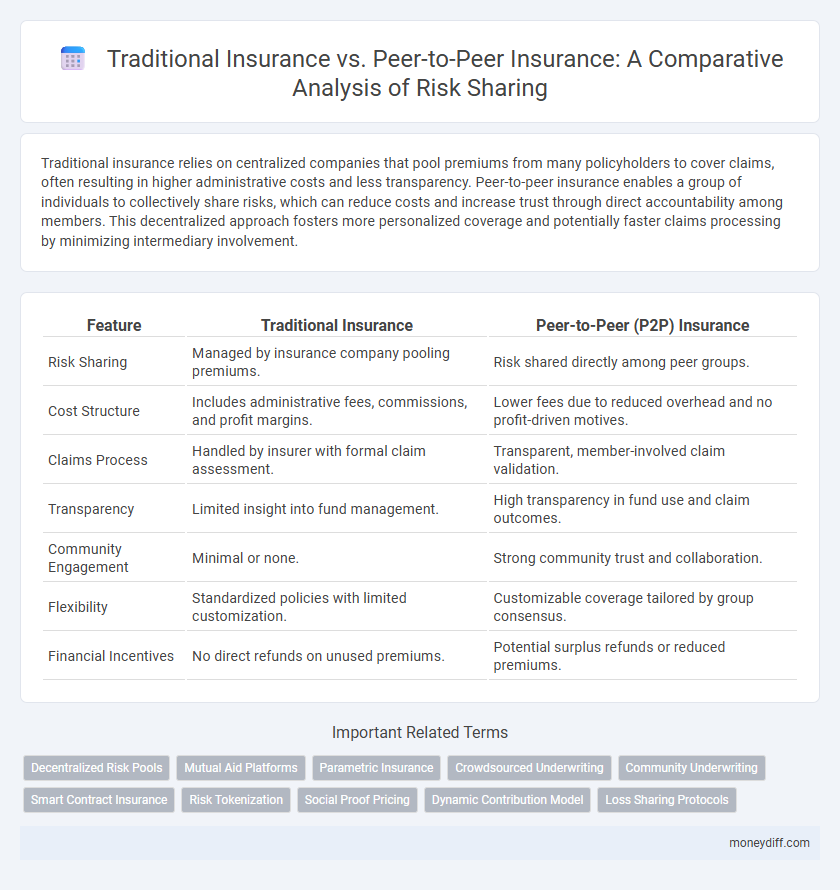
| Feature | Traditional Insurance | Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Sharing | Managed by insurance company pooling premiums. | Risk shared directly among peer groups. |
| Cost Structure | Includes administrative fees, commissions, and profit margins. | Lower fees due to reduced overhead and no profit-driven motives. |
| Claims Process | Handled by insurer with formal claim assessment. | Transparent, member-involved claim validation. |
| Transparency | Limited insight into fund management. | High transparency in fund use and claim outcomes. |
| Community Engagement | Minimal or none. | Strong community trust and collaboration. |
| Flexibility | Standardized policies with limited customization. | Customizable coverage tailored by group consensus. |
| Financial Incentives | No direct refunds on unused premiums. | Potential surplus refunds or reduced premiums. |
Understanding Traditional Insurance: The Established Model
Traditional insurance operates on a model where policyholders pay premiums to a centralized company that pools risk and manages claims through professional underwriters and actuaries. This established system relies on regulatory frameworks, risk assessment, and financial reserves to ensure solvency and protect policyholders. Traditional insurance offers widespread coverage options but often involves higher administrative costs and less transparency compared to emerging peer-to-peer models.
What Is Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Insurance?
Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance is a decentralized risk-sharing model where individuals pool their premiums to cover mutual claims, reducing reliance on traditional insurance companies. Unlike conventional insurance, which involves a middleman and profit-driven motives, P2P insurance emphasizes transparency, lower costs, and community-driven trust. This model leverages technology platforms to facilitate direct connections among policyholders, enhancing efficiency and aligning incentives for fair claims handling.
Risk Pooling: How Each Model Distributes Risk
Traditional insurance pools risk by collecting premiums from a large group of policyholders and transferring the aggregated risk to the insurer's reserves, where losses are paid out from a centralized fund. Peer-to-peer insurance decentralizes risk pooling by allowing members of a smaller community to collectively share and cover each other's losses, often using a transparent platform that reduces administrative costs. Risk distribution in peer-to-peer models is more direct and personalized, with unclaimed premiums potentially refunded to members, contrasting with the fixed premium structure of traditional insurers.
Cost Structure Comparison: Premiums and Payouts
Traditional insurance typically involves fixed premiums determined by actuaries to cover administrative costs, profit margins, and risk pools, often resulting in higher overall costs for policyholders. Peer-to-peer insurance reduces administrative overhead by pooling members' premiums directly, which can lead to lower premiums and faster payouts when claims are valid. This model encourages transparency and potential premium rebates, as unused funds are shared among participants rather than retained by a central insurer.
Claims Process: Traditional vs P2P Approaches
Traditional insurance claims processes often involve multiple intermediaries, lengthy assessments, and fixed premiums, leading to slower payouts and less transparency. Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance streamlines claims handling by fostering direct member involvement and automated verification through blockchain or smart contracts, accelerating settlements and reducing administrative costs. Data from industry reports indicate P2P models can reduce claim processing time by up to 40% compared to traditional insurers.
Transparency and Trust: Which Model Offers More?
Peer-to-peer insurance offers enhanced transparency and trust by allowing members to directly share risks and monitor the use of funds, reducing the opacity often found in traditional insurance. Traditional insurance relies on intermediaries and complex policies, which can obscure cost structures and claim processes, potentially undermining consumer confidence. The decentralized nature of peer-to-peer insurance fosters a collective accountability that strengthens trust among participants compared to conventional insurers.
Technology’s Role in Peer-to-Peer Insurance
Peer-to-peer insurance leverages blockchain technology and smart contracts to automate claim processing and enhance transparency, reducing administrative costs and fraud risks compared to traditional insurance models. By using digital platforms, peer-to-peer insurance enables real-time risk assessment and community-based risk pooling, fostering trust and faster settlements among policyholders. Advanced data analytics and decentralized networks improve risk sharing efficiency, positioning peer-to-peer insurance as a disruptive alternative to conventional insurers reliant on centralized control.
Community Engagement: Social Dynamics in P2P Insurance
Peer-to-peer insurance harnesses community engagement to foster trust and transparency among members, enhancing risk-sharing effectiveness compared to traditional insurance models. Social dynamics in P2P insurance create stronger accountability as members collaboratively manage claims and premiums, reducing fraud and moral hazard. This decentralized approach aligns incentives within the community, promoting shared responsibility and improving overall claim outcomes.
Regulatory Landscape: Legal Considerations for Both Models
Traditional insurance operates under well-established regulatory frameworks that mandate strict compliance with solvency requirements, capital reserves, and consumer protection laws, ensuring policyholder security and market stability. Peer-to-peer insurance presents novel regulatory challenges as it blurs the lines between insured individuals and insurers, requiring adaptive legal frameworks addressing decentralized risk-sharing, transparency, and fraud prevention. Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly developing tailored guidelines for peer-to-peer models to balance innovation with risk management and consumer safeguards.
Choosing the Best Risk-Sharing Solution for Your Money Management
Traditional insurance pools premiums from a large base of policyholders to spread risk, often leading to higher administrative costs and less transparency. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages smaller groups to share risks directly, reducing overhead and promoting trust among members through collective responsibility. Selecting the best risk-sharing solution depends on evaluating cost-efficiency, claims processing speed, and the level of control desired over your money management.
Related Important Terms
Decentralized Risk Pools
Traditional insurance relies on centralized risk pools managed by insurers to distribute risk and collect premiums, often resulting in higher administrative costs and less transparency. Peer-to-peer insurance utilizes decentralized risk pools where members share risks directly, leveraging blockchain technology to enhance trust, reduce intermediaries, and enable more efficient claim settlements.
Mutual Aid Platforms
Traditional insurance relies on centralized companies to pool premiums and manage risk, while peer-to-peer insurance leverages mutual aid platforms that enable groups of individuals to share risks directly, reducing overhead and increasing transparency. Mutual aid platforms foster community-driven protection by allowing participants to contribute to a shared fund, which is used to pay claims collectively, enhancing trust and promoting fair cost distribution among members.
Parametric Insurance
Parametric insurance offers predefined payouts based on specific event triggers, enhancing transparency and efficiency in risk sharing compared to traditional insurance, which relies on claims adjustment and indemnity processes. Peer-to-peer insurance leverages parametric models to distribute risk among a community, reducing administrative costs and enabling faster compensation for insured events.
Crowdsourced Underwriting
Peer-to-peer insurance leverages crowdsourced underwriting by pooling premiums from a community to share risks directly, reducing reliance on traditional insurers' centralized risk assessment and potentially lowering costs. This model enhances transparency and aligns incentives as policyholders collectively evaluate risks and claims, contrasting with traditional insurance's top-down risk management approach.
Community Underwriting
Traditional insurance relies on centralized risk pools managed by companies, while peer-to-peer insurance embraces community underwriting by enabling groups to collectively pool premiums and share risks, reducing administrative costs and enhancing transparency. This decentralized approach aligns individual incentives within the community, fostering trust and potentially lowering premiums through mutual accountability.
Smart Contract Insurance
Smart Contract Insurance leverages blockchain technology to facilitate decentralized risk sharing, automating claims and payouts without intermediaries, contrasting with traditional insurance's reliance on centralized entities and manual processes. This innovation reduces fraud, increases transparency, and lowers administrative costs by embedding contract terms directly into code executed on a blockchain network.
Risk Tokenization
Risk tokenization in peer-to-peer insurance transforms traditional risk pooling by converting individual risk shares into digital tokens, enhancing transparency and liquidity compared to conventional insurance models reliant on centralized underwriting. This blockchain-based approach enables decentralized risk distribution, reducing intermediaries while increasing efficiency in claims processing and capital utilization.
Social Proof Pricing
Traditional insurance relies on actuarial data to set premiums, whereas peer-to-peer insurance leverages social proof pricing by pooling risk among a community of members with similar profiles, resulting in potentially lower costs and increased transparency. Social proof pricing in peer-to-peer models reduces moral hazard by aligning incentives within the group, fostering trust and collective responsibility in risk sharing.
Dynamic Contribution Model
Traditional insurance relies on fixed premiums set by actuaries, while peer-to-peer insurance employs a dynamic contribution model where members' contributions adjust based on collective risk and claims experience, promoting fairness and transparency in risk sharing. This dynamic model incentivizes loss prevention and aligns member interests, reducing moral hazard compared to static premium structures in conventional insurance.
Loss Sharing Protocols
Traditional insurance relies on centralized loss sharing protocols where the insurer pools premiums to cover claims, often leading to higher administrative costs and less transparency. Peer-to-peer insurance uses decentralized loss sharing mechanisms that distribute risks directly among members, enhancing transparency, reducing overhead, and aligning incentives for more efficient risk management.
Traditional insurance vs Peer-to-peer insurance for risk sharing. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com