Traditional insurance calculates premiums based on broad factors such as age, location, and driving history, often leading to generalized risk assessments. Usage-based insurance (UBI) leverages real-time data from telematics devices to analyze individual driving behavior, enabling more personalized and potentially lower premiums. This data-driven approach encourages safer driving habits while aligning premiums more closely with actual risk exposure.
Table of Comparison
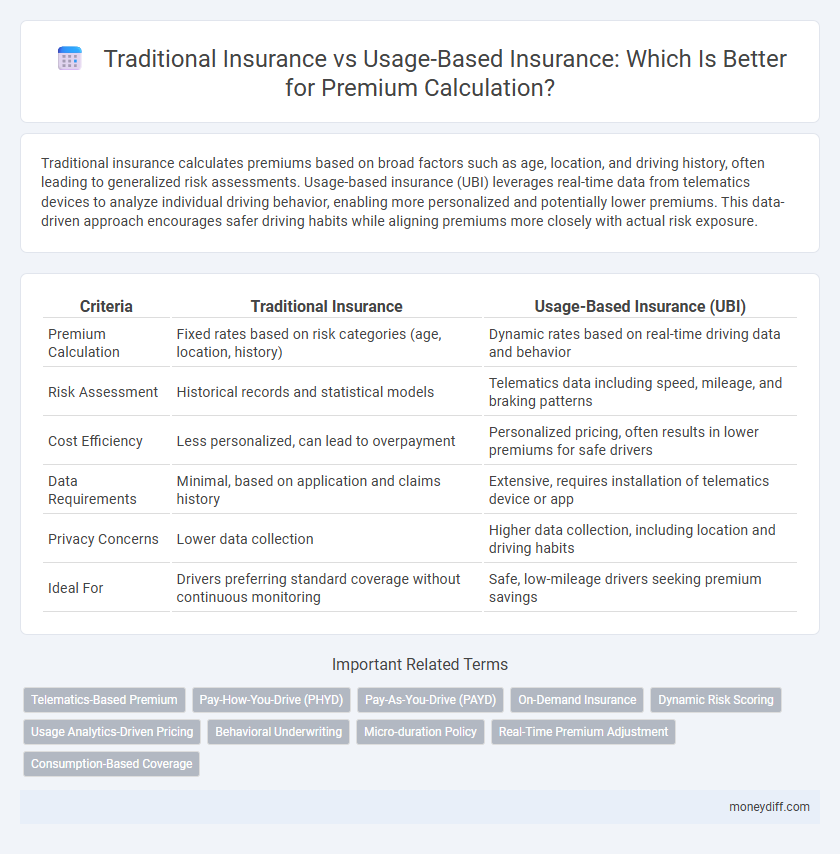
| Criteria | Traditional Insurance | Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) |
|---|---|---|
| Premium Calculation | Fixed rates based on risk categories (age, location, history) | Dynamic rates based on real-time driving data and behavior |
| Risk Assessment | Historical records and statistical models | Telematics data including speed, mileage, and braking patterns |
| Cost Efficiency | Less personalized, can lead to overpayment | Personalized pricing, often results in lower premiums for safe drivers |
| Data Requirements | Minimal, based on application and claims history | Extensive, requires installation of telematics device or app |
| Privacy Concerns | Lower data collection | Higher data collection, including location and driving habits |
| Ideal For | Drivers preferring standard coverage without continuous monitoring | Safe, low-mileage drivers seeking premium savings |
Understanding Traditional Insurance Premiums
Traditional insurance premiums are calculated based on general risk factors including age, location, driving history, and vehicle type, relying on historical data and statistical models. This approach uses fixed criteria and broad categorizations to estimate potential risk, often resulting in less personalized pricing. Understanding traditional premiums helps consumers compare how static risk assessments differ from dynamic, real-time data used in usage-based insurance models.
What Is Usage-Based Insurance (UBI)?
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) utilizes real-time driving data collected through telematics devices or mobile apps to calculate premiums based on individual driving behavior, such as speed, braking patterns, and mileage. Unlike traditional insurance models that rely primarily on historical data like age, location, and credit scores, UBI offers personalized rates that reward safer drivers with lower premiums. This approach enhances accuracy in risk assessment, encourages safer driving habits, and can reduce overall insurance costs for low-risk policyholders.
Key Differences: Standard vs Usage-Based Premiums
Standard insurance premiums are calculated primarily based on fixed factors such as age, location, and driving history, which remain static over the policy term. Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) leverages real-time driving data collected through telematics devices to assess risk more dynamically, enabling premiums to fluctuate based on actual driving behavior. The key difference lies in the precision of risk assessment, where UBI offers personalized, usage-driven pricing, potentially lowering costs for safe drivers compared to the traditional standardized approach.
Factors Affecting Traditional Insurance Rates
Traditional insurance premium calculation relies heavily on demographic factors such as age, gender, marital status, and credit history, alongside the type and value of the insured asset. Geographic location and driving history also play crucial roles in determining risk levels and subsequent premiums within conventional insurance models. Unlike usage-based insurance that tracks real-time behavior, traditional insurance primarily uses historical and static data to assess risk and set rates.
How Usage-Based Insurance Calculates Premiums
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) calculates premiums by analyzing real-time driving behaviors such as speed, acceleration, braking patterns, and mileage using telematics devices or mobile apps. These precise data points enable insurers to customize rates based on individual risk profiles rather than generalized statistics, resulting in more accurate premium pricing. By continuously monitoring driving habits, UBI rewards safer drivers with lower costs while identifying riskier patterns that may increase premiums.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Insurance
Traditional insurance offers predictable premium payments based on general risk factors such as age, location, and driving history, providing simplicity and ease of understanding for policyholders. It lacks customization, often resulting in higher costs for safe drivers who do not benefit from individualized data. However, traditional insurance eliminates privacy concerns related to data tracking and avoids potential inaccuracies in usage-based assessments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Usage-Based Insurance
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) offers personalized premium calculation by leveraging telematics data such as driving behavior, mileage, and time of use, leading to potential cost savings for safe drivers. Advantages include increased fairness, promotion of safer driving habits, and real-time risk assessment, while disadvantages involve privacy concerns, data security risks, and potential higher costs for risky drivers. Traditional insurance relies on static factors like age and location, lacking the dynamic adaptability of UBI-based premiums.
Who Should Consider Usage-Based Insurance?
Usage-based insurance (UBI) is ideal for low-mileage drivers, safe drivers, and those seeking personalized premium rates based on actual driving behavior. Individuals who regularly use telematics devices or smartphone apps to monitor speed, braking, and distance benefit from potential cost savings and increased control over premiums. Drivers with variable or unpredictable travel patterns may find traditional insurance policies more stable, whereas UBI suits those aiming to maximize discounts through responsible driving habits.
Impact on Personal Money Management
Traditional insurance policies use fixed premiums based on general risk factors, often leading to overpayment for low-risk drivers. Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) calculates premiums dynamically by monitoring actual driving behavior, resulting in more personalized and cost-efficient rates. This approach enhances personal money management by offering real-time control over insurance expenses and incentivizing safer driving habits.
Choosing the Right Insurance Model for Your Needs
Traditional insurance calculates premiums based on demographic factors, driving history, and risk categories, offering predictable costs but less personalization. Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) leverages telematics data such as mileage, driving behavior, and time of use to create more accurate, usage-centered premium pricing. Selecting between these models depends on individual driving patterns, preference for cost transparency, and desire for tailored coverage, making UBI ideal for low-mileage or safe drivers while traditional insurance suits those valuing simplicity.
Related Important Terms
Telematics-Based Premium
Telematics-based premium calculation uses real-time driving data such as speed, braking patterns, and mileage to tailor insurance costs more accurately than traditional methods relying on demographic factors alone. This usage-based insurance model incentivizes safer driving behaviors and provides personalized premiums reflecting individual risk profiles.
Pay-How-You-Drive (PHYD)
Pay-How-You-Drive (PHYD) insurance leverages telematics data such as driving behavior, speed, and mileage to tailor premium calculations more accurately than traditional insurance models that rely on static factors like age and location. This usage-based insurance approach reduces costs for safer drivers and incentivizes responsible driving by aligning premiums directly with real-time risk profiles.
Pay-As-You-Drive (PAYD)
Traditional insurance calculates premiums based on fixed factors like age, location, and driving history, while Usage-Based Insurance (UBI), specifically Pay-As-You-Drive (PAYD), determines premiums by tracking actual miles driven and driving behavior through telematics. PAYD models offer personalized pricing, reducing costs for low-mileage drivers and incentivizing safer driving habits, resulting in more accurate risk assessment and potential savings.
On-Demand Insurance
On-Demand Insurance offers flexible, pay-as-you-go premium calculation based on actual usage, contrasting with traditional Insurance's fixed-rate premiums determined by broad risk factors. Usage-Based Insurance leverages telematics data for personalized pricing, enhancing cost-efficiency and customer control.
Dynamic Risk Scoring
Traditional insurance premium calculation relies on static factors such as age, location, and driving history, while Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) leverages dynamic risk scoring by continuously analyzing real-time driving behavior data like speed, acceleration, and braking patterns. Dynamic risk scoring enhances premium accuracy by adapting to individual risk profiles over time, promoting safer driving habits and potentially lowering costs for low-risk drivers.
Usage Analytics-Driven Pricing
Usage-based insurance leverages real-time driving data such as speed, distance, and braking patterns to create customized premium calculations tailored to individual behavior. This analytics-driven pricing model enhances risk assessment accuracy, promotes safer driving habits, and often results in more competitive premiums compared to traditional insurance methods.
Behavioral Underwriting
Behavioral underwriting in usage-based insurance leverages real-time driving data such as speed, braking patterns, and mileage to calculate premiums, offering a more personalized and accurate risk assessment than traditional insurance methods. This data-driven approach reduces reliance on demographic factors and historical claims, enhancing fairness and incentivizing safer driving habits.
Micro-duration Policy
Micro-duration policies in insurance offer precise premium calculation by charging based on short, specific coverage intervals, contrasting traditional insurance that uses broader risk assessments over extended periods. Usage-based insurance leverages telematics data to tailor premiums according to actual driving behavior, enhancing cost efficiency and personalized risk management for micro-duration coverage.
Real-Time Premium Adjustment
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) leverages telematics and real-time driving data to adjust premiums dynamically, reflecting individual risk more accurately than traditional insurance methods that rely on historical and static factors. This real-time premium adjustment enables insurers to reward safe driving behaviors instantly, potentially lowering costs for low-risk drivers while promoting safer roads.
Consumption-Based Coverage
Traditional insurance calculates premiums using fixed factors like age, location, and driving history, often leading to generalized rates that may not reflect individual risk accurately. Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) employs telematics data such as mileage, driving behavior, and time of use, enabling consumption-based coverage that dynamically adjusts premiums based on actual usage patterns, resulting in fairer pricing and incentivizing safer driving habits.
Insurance vs Usage-Based Insurance for premium calculation. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com