Traditional insurance often requires high premiums and extensive paperwork, creating barriers for low-income individuals. Microinsurance offers affordable, simplified policies designed to meet the needs of underserved populations, increasing accessibility to essential coverage. This approach enables broader financial inclusion by providing tailored protection in regions where conventional insurance is limited or unavailable.
Table of Comparison
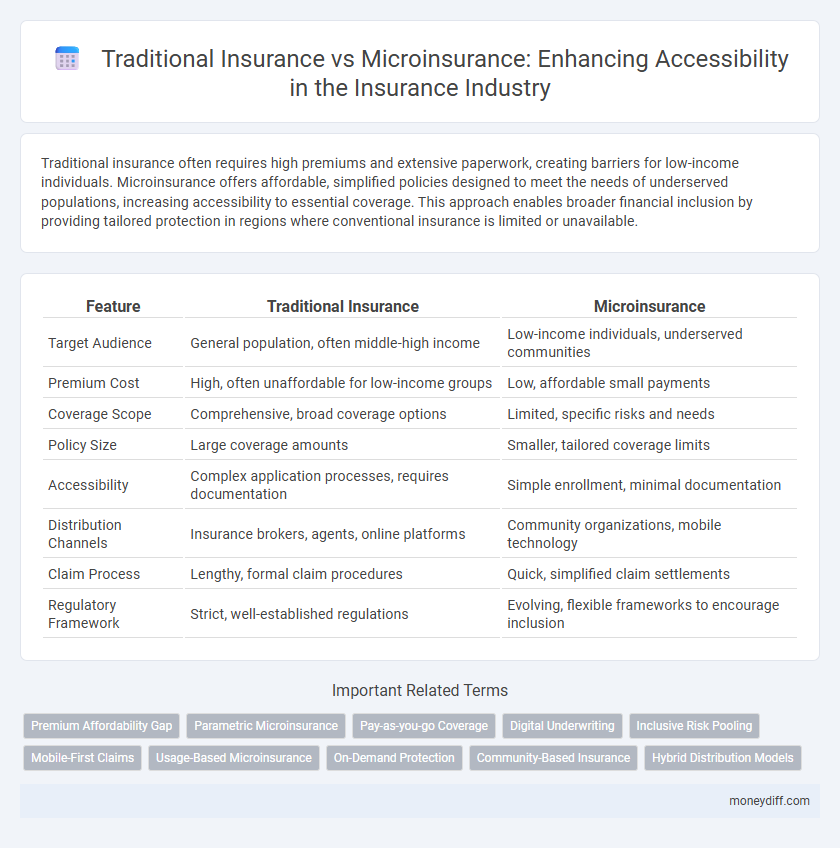
| Feature | Traditional Insurance | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | General population, often middle-high income | Low-income individuals, underserved communities |
| Premium Cost | High, often unaffordable for low-income groups | Low, affordable small payments |
| Coverage Scope | Comprehensive, broad coverage options | Limited, specific risks and needs |
| Policy Size | Large coverage amounts | Smaller, tailored coverage limits |
| Accessibility | Complex application processes, requires documentation | Simple enrollment, minimal documentation |
| Distribution Channels | Insurance brokers, agents, online platforms | Community organizations, mobile technology |
| Claim Process | Lengthy, formal claim procedures | Quick, simplified claim settlements |
| Regulatory Framework | Strict, well-established regulations | Evolving, flexible frameworks to encourage inclusion |
Understanding Traditional Insurance: Key Features
Traditional insurance typically involves comprehensive coverage plans with higher premiums and extensive underwriting processes designed for individuals and businesses with stable income streams. These policies often require long-term commitments, formal claims procedures, and provide varied protection against risks such as health, property, and liability. Accessibility challenges arise due to complex eligibility criteria, higher costs, and the need for substantial documentation, limiting reach to low-income or informal sector populations.
Introduction to Microinsurance: A New Paradigm
Microinsurance offers affordable, accessible coverage tailored to low-income populations often excluded from traditional insurance markets. Unlike traditional insurance, which requires higher premiums and complex underwriting, microinsurance simplifies product design and leverages mobile technology to reduce costs and increase reach. This new paradigm enhances financial inclusion by enabling vulnerable communities to manage risks related to health, agriculture, and property effectively.
Accessibility: Barriers in Traditional Insurance
Traditional insurance often poses significant accessibility barriers due to high premiums, complex application processes, and stringent eligibility requirements. These factors disproportionately affect low-income and rural populations, limiting their ability to obtain essential coverage. Microinsurance addresses these challenges by offering affordable, simplified, and flexible policies tailored to underserved communities.
How Microinsurance Enhances Accessibility
Microinsurance enhances accessibility by offering affordable premiums and simplified enrollment processes tailored to low-income populations and underserved communities. Unlike traditional insurance, which often requires extensive documentation and higher costs, microinsurance leverages mobile technology and community-based distribution channels to reach remote and vulnerable groups effectively. This approach not only broadens coverage but also fosters financial inclusion and risk protection for individuals who are typically excluded from conventional insurance markets.
Cost and Affordability: Comparing Both Models
Traditional insurance often involves higher premiums and extensive coverage, making it less accessible for low-income individuals due to significant upfront costs. Microinsurance provides tailored, low-cost insurance products with smaller premiums and simplified processes, enhancing affordability and accessibility for underserved populations. Cost efficiency in microinsurance models reduces financial barriers, enabling broader coverage among economically vulnerable groups.
Coverage Scope: Traditional vs. Microinsurance
Traditional insurance offers extensive coverage scopes including comprehensive health, property, life, and auto insurance, typically requiring higher premiums and extensive documentation. Microinsurance targets underserved populations with affordable policies focusing on specific risks like crop failure, basic health, or funeral expenses, emphasizing accessibility and simplified claims processes. The limited but tailored coverage scope of microinsurance bridges the protection gap for low-income groups often excluded from traditional insurance markets.
Distribution Channels: Expanding Reach in Microinsurance
Microinsurance leverages diverse distribution channels such as mobile technology, local agents, and community organizations to significantly enhance accessibility for low-income populations, contrasting traditional insurance's reliance on conventional brokers and physical offices. Mobile platforms facilitate quick policy enrollment and claims processing, overcoming geographic barriers common in underserved areas. Partnerships with local entities ensure greater trust and penetration, making microinsurance a more inclusive solution for vulnerable groups.
Claims Process: Simplicity and Transparency
Traditional insurance often involves complex claims processes with extensive documentation and prolonged settlement periods, which can deter low-income or rural clients. Microinsurance prioritizes simplicity and transparency by streamlining claim submissions through mobile platforms and offering quicker payouts tailored to underserved populations. Emphasizing user-friendly procedures and clear communication enhances accessibility, ensuring more individuals can benefit from insurance protection.
Target Audience: Who Benefits Most?
Traditional insurance primarily targets middle to high-income individuals and businesses with substantial assets, offering comprehensive coverage but often at higher costs and complex terms that limit accessibility for low-income populations. Microinsurance serves low-income individuals and underserved communities by providing affordable, simplified, and flexible insurance products tailored to their specific risks and financial capabilities. This accessibility empowers vulnerable groups such as rural farmers, daily wage earners, and small entrepreneurs, ensuring they gain financial protection and resilience against unforeseen events.
The Future of Insurance Accessibility: Trends and Innovations
Microinsurance is revolutionizing insurance accessibility by offering affordable, flexible coverage especially tailored for low-income populations often neglected by traditional insurance. Leveraging digital platforms, mobile technology, and data analytics, microinsurance providers can deliver rapid, convenient service without extensive paperwork or high premiums. Emerging trends like AI-driven underwriting and blockchain-based claims processing promise to further democratize insurance access, ensuring broader protection in an increasingly connected world.
Related Important Terms
Premium Affordability Gap
Traditional insurance often carries high premium costs that create a significant affordability gap for low-income populations, limiting their access to necessary coverage. Microinsurance addresses this gap by offering lower premiums and tailored policies designed to meet the financial constraints of underserved communities, thus improving accessibility and financial protection.
Parametric Microinsurance
Parametric microinsurance offers enhanced accessibility compared to traditional insurance by providing instant, data-driven payouts triggered by predefined events such as natural disasters, reducing claim processing time and administrative costs. This approach leverages technology and satellite data to deliver affordable coverage to underserved populations in remote or low-income areas, improving financial inclusion and resilience.
Pay-as-you-go Coverage
Traditional insurance typically requires high premiums and long-term commitments, limiting accessibility for low-income individuals, while microinsurance offers pay-as-you-go coverage with flexible, low-cost premiums tailored to meet the needs of underserved populations. Pay-as-you-go microinsurance increases financial inclusion by enabling policyholders to pay small amounts incrementally, reducing upfront costs and expanding access to essential protection in emerging markets.
Digital Underwriting
Digital underwriting in traditional insurance often involves complex data requirements and longer processing times, limiting accessibility for low-income or underserved populations. Microinsurance leverages streamlined digital underwriting techniques with minimal data inputs and automated risk assessments, enhancing accessibility and affordability for vulnerable groups.
Inclusive Risk Pooling
Traditional insurance often excludes low-income populations due to high premiums and extensive coverage requirements, limiting accessibility. Microinsurance enhances inclusive risk pooling by offering affordable, targeted coverage that aggregates smaller risks from underserved communities, increasing access to financial protection.
Mobile-First Claims
Traditional insurance often faces challenges of accessibility and high costs, whereas microinsurance leverages mobile-first claims processes to enable fast, affordable, and user-friendly access to coverage for low-income and underinsured populations. Mobile platforms streamline claim submissions, reduce administrative overhead, and increase transparency, making insurance more inclusive and efficient in emerging markets.
Usage-Based Microinsurance
Usage-Based Microinsurance leverages telematics and real-time data to provide affordable, tailored coverage for low-income populations, enhancing accessibility by aligning premiums with actual risk behavior. Unlike traditional insurance with fixed rates and high entry barriers, this model promotes financial inclusion through flexible, usage-sensitive policies that adapt to customer needs and usage patterns.
On-Demand Protection
Microinsurance offers on-demand protection with lower premiums and flexible coverage tailored for low-income and underserved populations, enhancing accessibility compared to traditional insurance, which often requires higher upfront payments and rigid policies. Digital platforms enable instant policy activation and claims processing in microinsurance, making protection more affordable and accessible for those with limited resources.
Community-Based Insurance
Community-Based Insurance enhances accessibility by leveraging local networks and trust to provide affordable coverage tailored to underserved populations. Microinsurance, compared to traditional insurance, offers lower premiums and simplified claims processes, making it more inclusive for low-income communities.
Hybrid Distribution Models
Hybrid distribution models in insurance combine traditional channels with digital platforms to enhance accessibility, bridging gaps for underserved populations. By integrating agents, brokers, and mobile technology, these models optimize outreach and affordability, particularly in microinsurance markets targeting low-income communities.
Traditional insurance vs Microinsurance for accessibility. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com