Health insurance provides comprehensive coverage for a wide range of medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and preventive care, typically involving fixed premiums. Usage-based insurance for medical coverage adjusts premiums based on individual healthcare usage or health data, offering a more personalized and potentially cost-effective option for those with healthier lifestyles. Choosing between these options depends on balancing predictable costs against the benefits of customized pricing tied to actual medical needs.
Table of Comparison
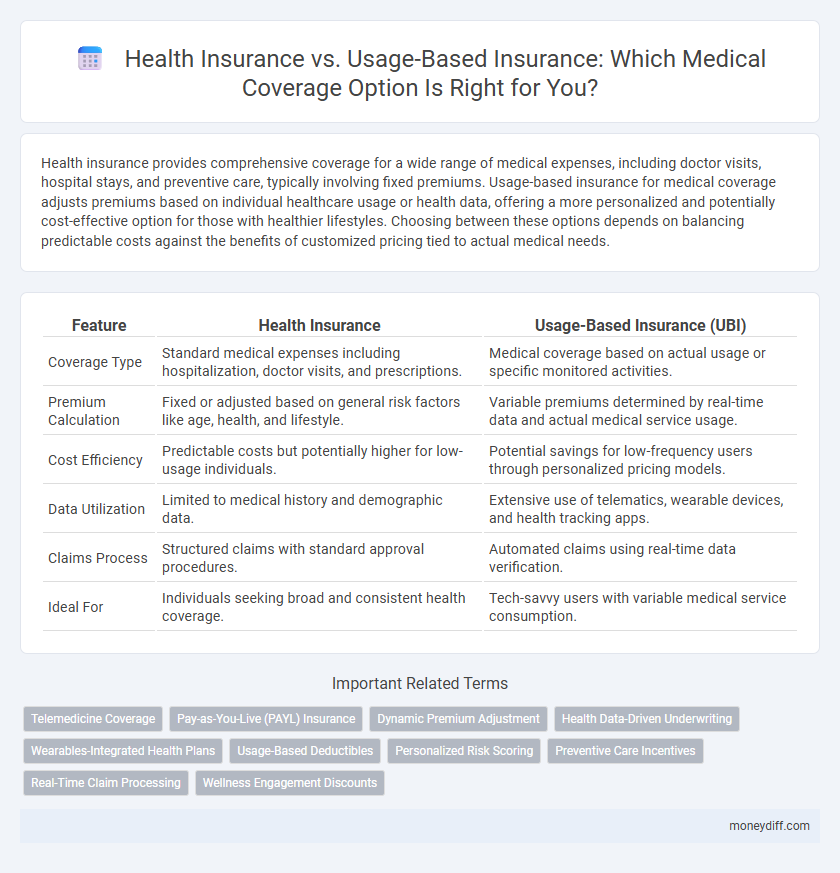
| Feature | Health Insurance | Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Type | Standard medical expenses including hospitalization, doctor visits, and prescriptions. | Medical coverage based on actual usage or specific monitored activities. |
| Premium Calculation | Fixed or adjusted based on general risk factors like age, health, and lifestyle. | Variable premiums determined by real-time data and actual medical service usage. |
| Cost Efficiency | Predictable costs but potentially higher for low-usage individuals. | Potential savings for low-frequency users through personalized pricing models. |
| Data Utilization | Limited to medical history and demographic data. | Extensive use of telematics, wearable devices, and health tracking apps. |
| Claims Process | Structured claims with standard approval procedures. | Automated claims using real-time data verification. |
| Ideal For | Individuals seeking broad and consistent health coverage. | Tech-savvy users with variable medical service consumption. |
Understanding Health Insurance: Key Features and Benefits
Health insurance provides comprehensive medical coverage with fixed premiums and predictable out-of-pocket costs, including access to a broad network of healthcare providers and preventive care benefits. Usage-based insurance for medical coverage offers personalized premiums based on real-time health data and individual risk factors, promoting healthier behaviors and potentially lowering costs. Key features of traditional health insurance include coverage for hospitalization, prescription drugs, and chronic disease management, whereas usage-based models emphasize tailored pricing and incentivized wellness.
What is Usage-Based Insurance for Medical Coverage?
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) for medical coverage leverages real-time data from wearable devices and health monitoring apps to customize premiums based on individual health behaviors and lifestyle choices. This model incentivizes healthier habits by offering lower costs to policyholders who maintain regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and medication adherence. Unlike traditional health insurance with fixed rates, UBI provides dynamic pricing reflecting actual health risk, enhancing personalized medical coverage and cost efficiency.
Cost Comparison: Health Insurance vs Usage-Based Insurance
Health insurance typically involves fixed premiums and predictable out-of-pocket costs, offering financial stability for routine medical care and emergencies. Usage-based insurance adjusts premiums based on individual healthcare utilization and behavior, potentially lowering costs for healthy individuals but risking higher expenses for frequent medical users. Comparing costs requires analyzing personal health risk factors, frequency of medical needs, and willingness to accept variable premiums tied to healthcare consumption.
Coverage Flexibility: Which Option Suits Your Needs?
Health insurance offers comprehensive coverage with fixed premiums and predictable benefits, ideal for individuals seeking broad protection and budget stability. Usage-based insurance adjusts premiums based on actual healthcare utilization, providing cost savings for low-users but potentially higher expenses for frequent medical visits. Choosing between these depends on your health risk profile and preference for premium predictability versus cost-efficient, tailored coverage.
Claim Process: Traditional vs Usage-Based Insurance
Traditional health insurance claim processes require extensive paperwork, pre-authorization, and longer settlement times due to manual verification and fixed policy terms. Usage-based insurance leverages telematics and real-time data to streamline claims, enabling faster approvals and personalized coverage adjustments. This data-driven approach reduces fraud, accelerates reimbursements, and enhances transparency in medical claim settlements.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Predictability and Control
Health insurance offers predictable out-of-pocket expenses through fixed premiums and copayments, providing financial stability for routine medical care. Usage-based insurance adjusts costs based on actual service utilization, potentially lowering expenses for healthy individuals but increasing unpredictability during high medical needs. Choosing between these plans depends on prioritizing expense control and risk tolerance within personal healthcare management.
Accessibility and Eligibility Criteria Explained
Health insurance typically offers broad accessibility with eligibility based on factors like age, employment status, and pre-existing conditions, providing comprehensive medical coverage. Usage-based insurance for medical coverage requires the insured to meet specific behavior or usage criteria, such as wearable health device data or doctor visit frequency, often limiting accessibility to tech-savvy or health-conscious individuals. Eligibility for usage-based models is more restrictive but can result in personalized premiums aligned with actual health habits and risk profiles.
Customization Options for Policyholders
Health insurance offers a range of predefined plans with limited customization, primarily focusing on coverage tiers and deductible choices. Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) for medical coverage leverages real-time health data from wearable devices and mobile apps, allowing policyholders to tailor premiums and benefits based on actual medical usage and lifestyle. This data-driven customization enhances personalized risk assessment and incentivizes healthier behaviors, resulting in more accurate premium pricing and potentially lower costs for consumers.
Financial Security: Long-Term Considerations
Health insurance provides predictable premiums and comprehensive coverage that supports long-term financial security by protecting against high medical expenses. Usage-based insurance adapts costs to actual healthcare consumption, potentially lowering short-term expenses but risking unpredictability in future financial planning. Choosing between these options requires evaluating stability needs, budget flexibility, and anticipated medical care frequency.
Choosing the Right Medical Coverage for Smart Money Management
Health insurance offers comprehensive medical coverage with fixed premiums and predictable out-of-pocket costs, suiting individuals seeking stability in managing healthcare expenses. Usage-based insurance adapts premiums based on actual medical service utilization, providing cost savings for those with infrequent healthcare needs and encouraging mindful consumption of medical resources. Evaluating personal health conditions, risk tolerance, and financial goals helps optimize medical coverage selection for effective money management and minimized unexpected healthcare costs.
Related Important Terms
Telemedicine Coverage
Health insurance plans traditionally offer comprehensive telemedicine coverage, providing access to virtual consultations, remote diagnostics, and mental health services without additional costs. Usage-based insurance for medical coverage tailors telemedicine benefits based on real-time usage patterns and health data, potentially lowering premiums for low-utilization individuals while encouraging proactive health management.
Pay-as-You-Live (PAYL) Insurance
Pay-as-You-Live (PAYL) insurance integrates real-time lifestyle data to personalize health coverage, promoting preventive care and reducing premiums based on healthy behaviors. Unlike traditional health insurance with fixed rates, PAYL incentivizes wellness through continuous monitoring, resulting in cost-efficient, tailored medical coverage that adapts to individual health patterns.
Dynamic Premium Adjustment
Health insurance with dynamic premium adjustment tailors costs based on real-time health data and lifestyle changes, promoting personalized medical coverage and cost efficiency. Usage-based insurance leverages wearable devices and health tracking to continuously assess risk, enabling premiums to fluctuate with actual health behavior and medical needs.
Health Data-Driven Underwriting
Health data-driven underwriting in health insurance utilizes detailed medical histories and biometric data to tailor premiums and coverage, enhancing risk assessment accuracy compared to traditional methods. Usage-based insurance for medical coverage relies on real-time health behavior tracking through wearable devices, promoting personalized plans that incentivize healthier lifestyles while dynamically adjusting costs.
Wearables-Integrated Health Plans
Wearables-integrated health plans leverage real-time biometric data to personalize premiums and incentivize healthy behaviors, contrasting traditional health insurance that relies on fixed rates based on general risk pools. Usage-based insurance enhances medical coverage by using continuous health monitoring from devices like smartwatches, improving risk assessment and promoting proactive healthcare management.
Usage-Based Deductibles
Usage-based deductibles in health insurance adjust according to the policyholder's healthcare utilization and lifestyle data, promoting cost efficiency and personalized medical coverage. This dynamic structure contrasts with traditional fixed deductibles by incentivizing healthier behaviors and potentially lowering out-of-pocket expenses based on real-time health monitoring and claims history.
Personalized Risk Scoring
Health insurance leverages personalized risk scoring through comprehensive medical histories and demographic data to tailor coverage and premiums, while usage-based insurance incorporates real-time health behavior and biometric data, enabling dynamic adjustments in medical coverage. This integration of personalized risk scoring enhances predictive accuracy and aligns insurance costs more closely with individual health profiles and lifestyle choices.
Preventive Care Incentives
Health insurance plans often include preventive care incentives such as free annual check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings to reduce long-term medical costs and improve patient outcomes. Usage-based insurance for medical coverage leverages real-time health data through wearable devices to personalize incentives, encouraging healthier behaviors and proactive management of chronic conditions.
Real-Time Claim Processing
Health insurance with real-time claim processing leverages advanced data analytics and electronic health records to expedite reimbursements and reduce administrative delays. Usage-based insurance for medical coverage utilizes telematics and patient data to dynamically adjust premiums while enabling instant verification and settlement of claims based on actual healthcare usage.
Wellness Engagement Discounts
Health insurance plans offering wellness engagement discounts incentivize policyholders to maintain healthy lifestyles through activities tracked by wearable devices or health apps, reducing overall premiums. Usage-based insurance for medical coverage similarly adjusts costs based on real-time health data and individual behavior, promoting proactive health management and personalized discount opportunities.
Health Insurance vs Usage-Based Insurance for medical coverage. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com