Traditional health insurance offers fixed premiums and broad coverage for medical expenses, providing financial protection regardless of individual health behaviors. Usage-based health insurance adjusts premiums based on real-time health data and lifestyle choices, rewarding healthier habits with lower costs. This personalized approach can lead to more cost-effective coverage but may require continuous monitoring and data sharing.
Table of Comparison
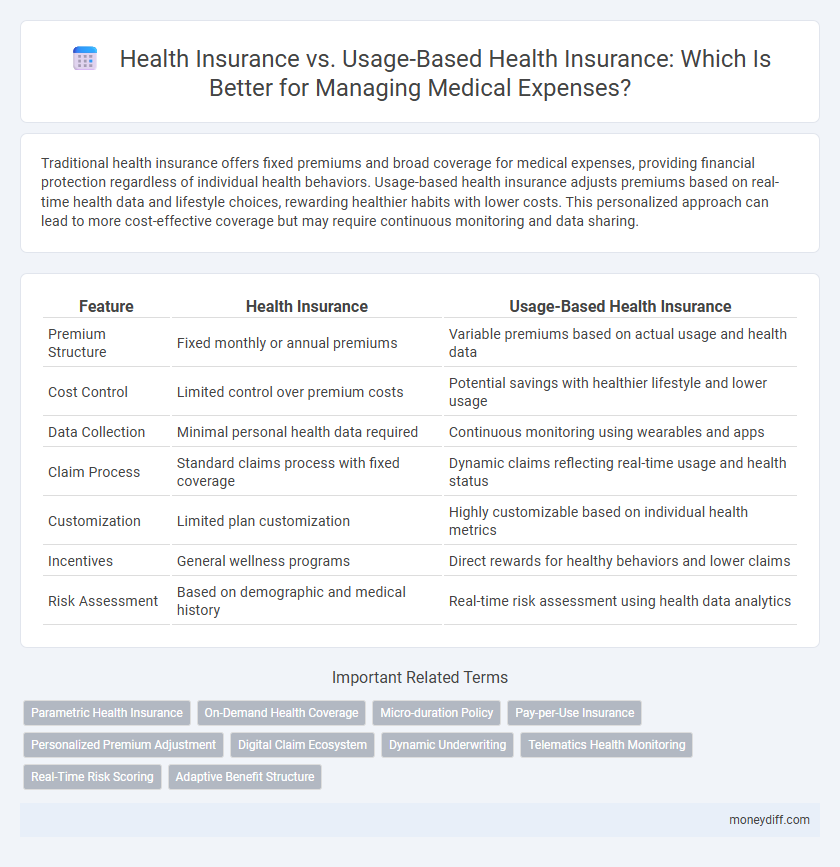
| Feature | Health Insurance | Usage-Based Health Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Premium Structure | Fixed monthly or annual premiums | Variable premiums based on actual usage and health data |
| Cost Control | Limited control over premium costs | Potential savings with healthier lifestyle and lower usage |
| Data Collection | Minimal personal health data required | Continuous monitoring using wearables and apps |
| Claim Process | Standard claims process with fixed coverage | Dynamic claims reflecting real-time usage and health status |
| Customization | Limited plan customization | Highly customizable based on individual health metrics |
| Incentives | General wellness programs | Direct rewards for healthy behaviors and lower claims |
| Risk Assessment | Based on demographic and medical history | Real-time risk assessment using health data analytics |
Understanding Traditional Health Insurance
Traditional health insurance provides comprehensive coverage with fixed premiums and copayments, offering predictable protection against a wide range of medical expenses including hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription drugs. Unlike usage-based health insurance, which adjusts costs based on individual health behaviors and real-time data, traditional plans prioritize stability and broad access without requiring lifestyle monitoring. Policyholders benefit from established networks and standardized benefits, simplifying claim processes and facilitating consistent healthcare access.
What Is Usage-Based Health Insurance?
Usage-Based Health Insurance (UBHI) is a novel approach to medical expense coverage that tailors premiums and benefits according to individual health behaviors and real-time data collected through wearable devices and health apps. Unlike traditional health insurance, which charges fixed rates based on generalized risk factors, UBHI incentivizes healthier lifestyles by adjusting costs and coverage dynamically based on metrics like physical activity, heart rate, and medication adherence. This model promotes personalized healthcare management, potentially lowering out-of-pocket expenses and improving overall wellness through continuous monitoring and proactive interventions.
Coverage Scope: Standard vs. Usage-Based Plans
Standard health insurance typically offers comprehensive coverage for a wide range of medical expenses, including hospital stays, preventive care, and prescription drugs, regardless of the insured's health behavior. Usage-based health insurance adjusts premiums and coverage based on the actual utilization of healthcare services, promoting cost efficiency for low users but potentially limiting benefits for frequent medical needs. Coverage scope in standard plans is broad and predictable, while usage-based plans provide personalized coverage that may fluctuate with the policyholder's health service consumption.
Premium Structure and Cost Differences
Traditional health insurance typically charges fixed premiums based on factors like age, health status, and coverage level, resulting in predictable monthly costs regardless of medical usage. Usage-based health insurance adjusts premiums dynamically by tracking actual healthcare utilization or lifestyle behaviors, which can lower costs for healthier individuals but may increase expenses for those with frequent medical needs. This cost structure incentivizes preventive care in usage-based models while offering stability in traditional plans.
Flexibility and Customization in Both Models
Health insurance plans offer standard coverage with fixed premiums and predefined benefits, providing predictable costs but limited customization. Usage-based health insurance uses data from wearable devices or health apps to adjust premiums and coverage based on individual health behaviors, enhancing flexibility and personalization. This model allows policyholders to tailor plans according to their lifestyle, potentially lowering costs while promoting healthier choices.
Claims Process: Traditional vs. Usage-Based
Traditional health insurance typically involves submitting claims through providers or policyholders, with fixed premiums and deductibles impacting out-of-pocket costs. Usage-based health insurance leverages real-time data from wearable devices and health apps to adjust coverage dynamically, streamlining claims processing and potentially reducing fraud. This model emphasizes personalized risk assessment, accelerating approvals and lowering administrative overhead compared to the conventional claims system.
Health Data and Privacy Concerns
Traditional health insurance generally relies on fixed premiums and broad health risk assessments, whereas usage-based health insurance (UBHI) leverages real-time health data collected through wearable devices and mobile apps to tailor coverage and premiums. The extensive use of personal health information in UBHI raises significant privacy concerns, including potential data breaches, unauthorized sharing, and misuse of sensitive medical data by insurers or third parties. Ensuring robust data encryption, clear consent protocols, and strict compliance with regulations like HIPAA is crucial to protect policyholders' privacy in usage-based health insurance models.
Suitability for Different Lifestyles
Health insurance provides comprehensive coverage suitable for individuals seeking predictable expenses and stable premiums, ideal for those with consistent healthcare needs. Usage-based health insurance offers cost-efficient plans tailored to low-risk lifestyles, rewarding healthy behavior through dynamic pricing models based on real-time health data. Choosing between traditional and usage-based options depends on lifestyle factors such as activity levels, chronic conditions, and willingness to share personal health metrics.
Long-Term Financial Implications
Health insurance provides predictable monthly premiums and comprehensive coverage, offering financial stability for long-term medical expenses. Usage-based health insurance adjusts costs based on actual healthcare utilization, potentially lowering premiums but introducing variability in future expenses. Evaluating long-term financial implications requires assessing health status, risk tolerance, and the likelihood of frequent medical needs to determine the most cost-effective option.
Choosing the Right Insurance for Your Needs
Choosing the right health insurance involves evaluating traditional health insurance plans that offer fixed premiums and broad coverage against usage-based health insurance models that adjust costs according to medical expenses incurred. Usage-based health insurance leverages data from health tracking devices to customize premiums, potentially lowering costs for healthier individuals while encouraging preventive care. Assessing your medical history, lifestyle, and financial flexibility helps determine whether a predictable premium or a dynamic, expense-driven approach better suits your healthcare needs.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Health Insurance
Parametric Health Insurance offers predetermined payouts triggered by specific health events or metrics, providing faster claims processing and reducing administrative costs compared to traditional Health Insurance, which reimburses actual medical expenses after claim approval. Usage-Based Health Insurance leverages real-time health data and wearable technology to tailor premiums and coverage, enhancing personalized risk assessment and cost efficiency in managing medical expenses.
On-Demand Health Coverage
On-demand health coverage offers flexible, usage-based health insurance that aligns premiums directly with actual medical expenses, providing cost-efficient protection tailored to individual healthcare needs. This model contrasts traditional health insurance by enabling policyholders to activate or pause coverage as needed, reducing unnecessary costs while maintaining access to essential medical services.
Micro-duration Policy
Micro-duration health insurance policies offer coverage for short-term medical expenses, providing flexibility and cost-efficiency compared to traditional health insurance with long-term commitment. Usage-based health insurance customizes premiums based on individual health behaviors and medical usage, optimizing affordability and personalized care management.
Pay-per-Use Insurance
Usage-based health insurance, also known as pay-per-use insurance, tailors premiums to individual health behaviors and medical service utilization, potentially lowering costs for low-frequency users by charging based on actual usage rather than fixed monthly rates. Traditional health insurance offers predictable coverage with fixed premiums but may result in higher overall costs for healthier individuals who use fewer medical services.
Personalized Premium Adjustment
Traditional health insurance typically sets fixed premiums based on general risk categories, while usage-based health insurance adjusts premiums dynamically according to an individual's actual medical expenses and health behavior data. This personalized premium adjustment enables more accurate cost alignment and incentivizes healthier lifestyle choices, potentially lowering overall out-of-pocket costs for policyholders.
Digital Claim Ecosystem
Health insurance traditionally relies on predefined premiums and coverage limits, while usage-based health insurance leverages digital claim ecosystems to process real-time data from wearable devices and health apps, enabling more personalized and dynamic premium adjustments. This digital claim ecosystem enhances accuracy, reduces fraud, and accelerates reimbursement by automating claims through blockchain and AI-powered verification.
Dynamic Underwriting
Dynamic underwriting in usage-based health insurance leverages real-time health data and behavioral analytics to tailor premiums and coverage, contrasting with traditional health insurance's fixed underwriting model based on static risk assessments. This approach enables more personalized risk management, potentially lowering costs and improving medical expense coverage by continuously adjusting to policyholders' health changes and medical usage patterns.
Telematics Health Monitoring
Traditional health insurance offers fixed premiums and coverage regardless of individual behavior, whereas usage-based health insurance leverages telematics health monitoring to adjust premiums and benefits based on real-time data such as heart rate, activity levels, and sleep patterns. This data-driven approach enhances risk assessment accuracy and promotes preventive care by incentivizing healthier lifestyle choices through personalized pricing models.
Real-Time Risk Scoring
Real-time risk scoring in usage-based health insurance leverages continuous monitoring of biometric data and lifestyle habits to dynamically adjust premiums and coverage, enhancing personalized healthcare management. Traditional health insurance often relies on static risk assessments, making usage-based models more responsive and cost-effective in managing medical expenses.
Adaptive Benefit Structure
Health insurance with an adaptive benefit structure tailors coverage to individual health needs, whereas usage-based health insurance dynamically adjusts premiums and benefits based on real-time medical usage patterns. This flexibility enables more personalized expense management, promoting cost efficiency and improved healthcare access.
Health Insurance vs Usage-Based Health Insurance for medical expenses. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com