Short-term goals involve setting clear financial targets achievable within weeks or months, such as saving for a vacation or paying off a small debt, helping maintain motivation and focus. Micro-saving goals break down larger objectives into manageable daily or weekly savings, promoting consistent habits and reducing financial stress. Both methods complement each other by balancing immediate needs with gradual progress toward bigger financial aspirations.
Table of Comparison
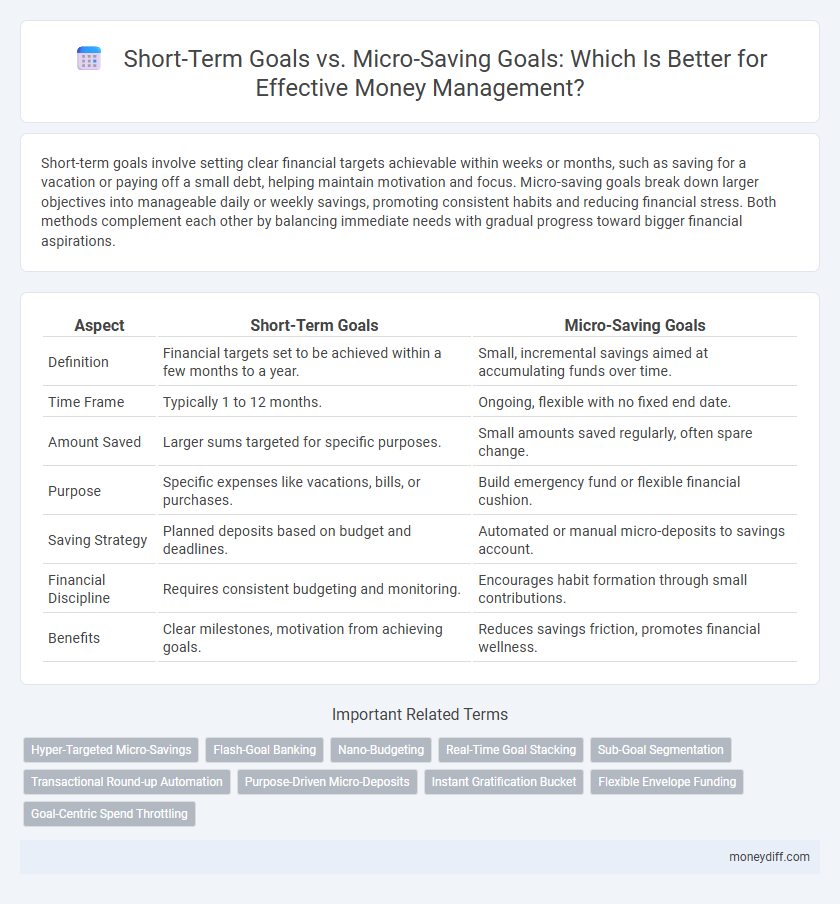
| Aspect | Short-Term Goals | Micro-Saving Goals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial targets set to be achieved within a few months to a year. | Small, incremental savings aimed at accumulating funds over time. |
| Time Frame | Typically 1 to 12 months. | Ongoing, flexible with no fixed end date. |
| Amount Saved | Larger sums targeted for specific purposes. | Small amounts saved regularly, often spare change. |
| Purpose | Specific expenses like vacations, bills, or purchases. | Build emergency fund or flexible financial cushion. |
| Saving Strategy | Planned deposits based on budget and deadlines. | Automated or manual micro-deposits to savings account. |
| Financial Discipline | Requires consistent budgeting and monitoring. | Encourages habit formation through small contributions. |
| Benefits | Clear milestones, motivation from achieving goals. | Reduces savings friction, promotes financial wellness. |
Understanding Short-Term Financial Goals
Short-term financial goals typically span from a few weeks to a year, focusing on objectives like building an emergency fund, paying off small debts, or saving for a vacation. These goals require disciplined budgeting and regular monitoring to ensure progress while maintaining liquidity. Micro-saving goals break down larger savings targets into manageable, incremental amounts, making consistent contributions more achievable within short periods.
Defining Micro-Saving Goals in Money Management
Micro-saving goals in money management involve setting small, manageable savings targets tailored to daily or weekly budgets, enabling consistent habit formation without financial strain. These goals leverage automated transfers and rounding-up techniques to accumulate funds incrementally while minimizing the impact on monthly cash flow. Defining micro-saving goals sharpens focus on achievable milestones, fostering sustained financial discipline and accelerating progress toward larger, short-term objectives.
Key Differences: Short-Term vs Micro-Saving Goals
Short-term goals typically focus on larger financial targets achievable within months to a year, such as saving for a vacation or paying off a credit card balance. Micro-saving goals involve smaller, incremental savings amounts, often automated and intended to build a habit or fund minor expenses like a coffee or a snack. The key difference lies in scale and timeframe: short-term goals require deliberate planning and commitment, while micro-saving emphasizes ease, consistency, and gradual accumulation.
Benefits of Setting Short-Term Financial Goals
Setting short-term financial goals enhances money management by providing clear, achievable targets that boost motivation and discipline. These goals improve cash flow control and enable quick adjustments to spending habits, fostering financial stability. Short-term goals also create a sense of accomplishment, encouraging consistent progress toward larger savings objectives.
Advantages of Embracing Micro-Saving Strategies
Micro-saving strategies offer the advantage of making consistent progress through small, manageable contributions, reducing the psychological burden often associated with larger short-term goals. These incremental savings can accumulate over time, fostering disciplined money management and enhancing financial security. Embracing micro-savings also promotes flexibility, allowing individuals to adjust savings habits easily without disrupting overall budgeting plans.
Practical Examples of Short-Term Money Goals
Short-term money goals typically include saving for a vacation, paying off credit card debt, or building an emergency fund within six months to a year. Micro-saving goals focus on small, consistent deposits, such as rounding up daily expenses to the nearest dollar or saving $5 each day, which gradually accumulate without significant lifestyle changes. These practical approaches help improve financial discipline, increase savings incrementally, and prepare for immediate financial needs.
Micro-Saving Techniques for Everyday Expenses
Micro-saving techniques for everyday expenses involve setting aside small, manageable amounts of money regularly to build savings without impacting daily budgets significantly. These methods include rounding up purchases to the nearest dollar, automating transfers of spare change into savings accounts, and tracking micro-deposits through budgeting apps. Consistently applying these strategies helps create a financial cushion and supports long-term wealth accumulation while maintaining short-term financial flexibility.
Choosing Between Short-Term and Micro-Saving Goals
Choosing between short-term and micro-saving goals depends on financial priorities and time horizon. Short-term goals target expenses within months to a year, such as vacations or emergency funds, while micro-saving goals focus on incremental daily or weekly deposits that accumulate over time. Prioritizing short-term goals provides immediate financial security, whereas micro-saving supports consistent habit-building for long-term financial stability.
Integrating Both Goal Types for Effective Money Management
Integrating short-term goals with micro-saving goals enhances money management by combining immediate financial targets with consistent, small-scale saving habits. Short-term goals provide clear milestones such as paying bills or purchasing essentials, while micro-saving promotes incremental wealth accumulation through automated transfers or round-up apps. This synergy ensures disciplined budgeting, reduces financial stress, and builds a sustainable savings foundation.
Measuring Progress: Tracking Short-Term and Micro-Saving Success
Tracking progress in short-term goals involves setting specific milestones and regularly reviewing account balances to ensure targets are met on time. Micro-saving goals require monitoring small, frequent deposits and analyzing cumulative growth to maintain motivation and adjust saving strategies. Using financial apps to visualize achievements enhances accountability and promotes consistent money management habits.
Related Important Terms
Hyper-Targeted Micro-Savings
Hyper-targeted micro-savings focus on setting specific, actionable financial targets within short time frames, allowing individuals to accumulate funds gradually without impacting daily expenses. This method leverages small, frequent deposits aligned with precise goals, enhancing discipline and accelerating progress compared to traditional short-term goals.
Flash-Goal Banking
Flash-Goal Banking revolutionizes money management by integrating short-term goals with micro-saving strategies, enabling users to set precise financial targets and automatically allocate small amounts toward achieving them quickly. This method enhances cash flow control and boosts motivation by providing real-time progress tracking for both immediate expenses and incremental savings.
Nano-Budgeting
Short-term goals often involve specific financial targets like saving for a vacation or paying off a credit card, whereas micro-saving goals emphasize small, frequent deposits focusing on nano-budgeting techniques that track even the smallest expenses to build savings steadily. Nano-budgeting enhances money management by breaking down income into minuscule allocations, optimizing cash flow, and fostering disciplined saving habits that contribute substantially to both immediate and long-term financial objectives.
Real-Time Goal Stacking
Real-time goal stacking enhances money management by allowing users to simultaneously allocate funds toward short-term goals such as emergency savings while incrementally contributing to micro-saving goals like daily coffee expenses, optimizing financial discipline and progress tracking. This dynamic approach leverages automated adjustments based on spending behavior, maximizing resource allocation efficiency without compromising immediate financial needs.
Sub-Goal Segmentation
Breaking down short-term goals into micro-saving sub-goals enhances financial discipline by creating manageable, targeted savings tasks that increase motivation and tracking efficiency. This sub-goal segmentation leverages behavioral insights to reduce spending impulses and accelerate progress toward larger financial objectives through incremental achievements.
Transactional Round-up Automation
Transactional round-up automation enhances short-term and micro-saving goals by automatically rounding up purchases and transferring the difference to savings, promoting consistent, effortless money accumulation. This method leverages small, frequent transactions to build savings without impacting daily spending habits, optimizing financial discipline and goal achievement.
Purpose-Driven Micro-Deposits
Purpose-driven micro-deposits enhance money management by targeting specific short-term goals with small, consistent contributions that build momentum and reinforce saving habits. This approach offers greater flexibility and psychological motivation compared to traditional short-term goals, making micro-saving goals more achievable and sustainable.
Instant Gratification Bucket
Short-term goals target immediate financial needs or desires, often linked to the instant gratification bucket, enabling quick rewards that motivate consistent saving habits. Micro-saving goals break these targets into manageable daily or weekly amounts, reducing temptation by limiting impulsive spending and fostering sustainable money management.
Flexible Envelope Funding
Flexible envelope funding enhances short-term goals by allowing dynamic allocation of savings toward immediate financial priorities, adapting quickly to changing expenses. Micro-saving goals benefit from this method through incremental contributions that accumulate seamlessly within designated envelopes, promoting disciplined yet adjustable money management.
Goal-Centric Spend Throttling
Goal-centric spend throttling prioritizes allocating funds toward micro-saving goals that accumulate small, consistent amounts to achieve short-term financial targets efficiently. This method prevents impulsive spending by aligning daily expenses with clearly defined monetary objectives, enhancing disciplined money management.
Short-Term Goals vs Micro-Saving Goals for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com