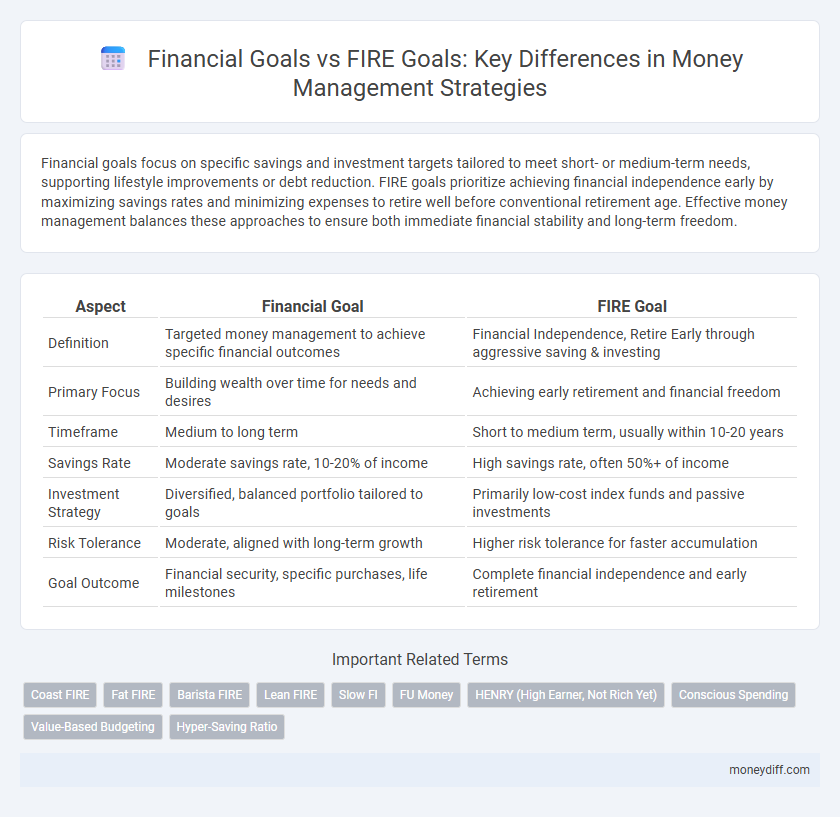
Financial goals focus on specific savings and investment targets tailored to meet short- or medium-term needs, supporting lifestyle improvements or debt reduction. FIRE goals prioritize achieving financial independence early by maximizing savings rates and minimizing expenses to retire well before conventional retirement age. Effective money management balances these approaches to ensure both immediate financial stability and long-term freedom.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Financial Goal | FIRE Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Targeted money management to achieve specific financial outcomes | Financial Independence, Retire Early through aggressive saving & investing |
| Primary Focus | Building wealth over time for needs and desires | Achieving early retirement and financial freedom |
| Timeframe | Medium to long term | Short to medium term, usually within 10-20 years |
| Savings Rate | Moderate savings rate, 10-20% of income | High savings rate, often 50%+ of income |
| Investment Strategy | Diversified, balanced portfolio tailored to goals | Primarily low-cost index funds and passive investments |
| Risk Tolerance | Moderate, aligned with long-term growth | Higher risk tolerance for faster accumulation |
| Goal Outcome | Financial security, specific purchases, life milestones | Complete financial independence and early retirement |
Understanding Financial Goals vs. FIRE Goals
Financial goals focus on achieving specific monetary milestones such as saving for retirement, buying a home, or reducing debt, emphasizing long-term stability and regular income growth. FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) goals prioritize extreme savings and investment strategies to achieve early retirement and financial freedom, often requiring higher savings rates and aggressive budget management. Understanding the difference highlights how traditional financial planning aims for steady progress, while FIRE demands a more disciplined, accelerated approach to wealth accumulation.
Defining Traditional Financial Goals
Traditional financial goals typically emphasize steady income growth, consistent savings, and long-term wealth accumulation through retirement accounts and investment portfolios. These goals prioritize stability, risk management, and achieving milestones like buying a home, funding education, or securing a comfortable retirement. Unlike FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early), traditional goals often follow conventional timelines and milestones defined by gradual wealth building and maintaining financial security.
What Is the FIRE Movement?
The FIRE movement, which stands for Financial Independence, Retire Early, emphasizes aggressive saving and investing to achieve financial independence well before traditional retirement age. Its primary goal differs from typical financial goals by focusing on minimizing expenses and maximizing passive income streams to retire decades earlier. By prioritizing a high savings rate and low spending, FIRE advocates aim to break free from the conventional work-retirement timeline.
Key Differences: Financial Goals and FIRE Goals
Financial goals typically focus on achieving specific monetary targets such as saving for a house, retirement, or education, emphasizing steady income and planned expenses. FIRE goals (Financial Independence, Retire Early) prioritize aggressive saving and investment strategies to attain financial independence at a younger age, often requiring a higher savings rate and frugal living. Key differences include the timeline, with FIRE aiming for early retirement, and the intensity of budgeting, with FIRE demanding more stringent financial discipline compared to general financial goals.
Time Horizons: Short-term vs. Early Retirement
Financial goals often emphasize short-term achievements like saving for a vacation or emergency fund, typically within a few years. FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) goals target early retirement, requiring long-term planning that spans decades and prioritizes aggressive investing and compounding growth. Time horizons directly influence strategies, risk tolerance, and saving rates, with FIRE demanding sustained commitment and a focus on maximizing investment returns over time.
Savings Rates: Standard Advice vs. FIRE Strategies
Standard financial advice recommends saving 10-15% of income for long-term wealth building, ensuring steady retirement funding and emergency cushions. FIRE strategies advocate saving 50-70% or more to achieve financial independence and early retirement rapidly, emphasizing aggressive expense reduction and income optimization. Higher savings rates drastically shorten the time needed to accumulate investment assets critical for sustaining living expenses without employment income.
Risk Tolerance in Financial and FIRE Planning
Risk tolerance plays a critical role in distinguishing financial goals from FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) goals, with traditional financial planning often accommodating moderate risk exposure to balance growth and security over time. In FIRE planning, higher risk tolerance may be necessary due to aggressive saving rates and early investment strategies aiming for rapid wealth accumulation. Investors pursuing FIRE typically prioritize growth-oriented assets, accepting increased volatility to achieve financial independence sooner, whereas conventional financial goals favor a more conservative, stable approach aligned with long-term security.
Lifestyle Choices: Conventional vs. FIRE Approaches
Conventional financial goals prioritize steady income growth and gradual wealth accumulation to support a comfortable lifestyle with periodic spending. FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) goals emphasize aggressive saving and investing to achieve early retirement and maximize financial freedom, often requiring significant lifestyle adjustments and frugality. Choosing between these approaches impacts daily spending habits, investment strategies, and long-term financial planning.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Financial Goals
Traditional financial goals provide clear milestones such as saving for retirement, purchasing a home, or funding education, offering structured motivation and measurable progress. However, they may lack the flexibility and early retirement focus of FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) goals, potentially extending the timeline for financial freedom. Rigid adherence to traditional goals might also limit aggressive savings strategies and lifestyle optimizations crucial in the FIRE movement.
Pros and Cons of Pursuing FIRE
Pursuing the FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) goal offers the advantage of early retirement and increased financial freedom but requires aggressive saving and investing, which can limit current lifestyle flexibility. The FIRE approach demands strict budgeting and high savings rates, potentially leading to burnout or reduced enjoyment of present experiences. Compared to traditional financial goals focused on balanced wealth growth and risk management, FIRE emphasizes rapid asset accumulation but may sacrifice long-term sustainability and adaptability to changing life circumstances.
Related Important Terms
Coast FIRE
Coast FIRE emphasizes reaching a financial milestone early so that investments grow passively to cover retirement without additional contributions, contrasting with traditional financial goals that focus on continuous saving and earning until full retirement. This approach allows individuals to maintain financial freedom sooner by minimizing active work years while ensuring long-term wealth accumulation aligns with personal lifestyle targets.
Fat FIRE
Fat FIRE emphasizes achieving financial independence with a lifestyle of luxury and comfort, requiring a higher savings target compared to traditional Financial Independence, Retire Early (FIRE) goals. This strategy involves maximizing investment returns and generating multiple income streams to sustain elevated expenses without compromising long-term wealth.
Barista FIRE
Barista FIRE focuses on achieving financial independence through part-time work combined with investment income, striking a balance between traditional financial goals and full FIRE by reducing expenses while maintaining steady cash flow. This approach provides flexibility and stability by allowing individuals to cover living costs with part-time income while their investment portfolio grows, making it a practical alternative to complete early retirement.
Lean FIRE
Financial goals center on building wealth for security and lifestyle enhancement, while Lean FIRE focuses on achieving financial independence with minimal expenses, enabling early retirement on a frugal budget. Emphasizing Lean FIRE requires precise budgeting, aggressive savings rates often exceeding 50%, and strategic investments to sustain a modest but fulfilling lifestyle without depleting resources.
Slow FI
Slow FI emphasizes steady, disciplined savings and investment over aggressive early retirement targets, prioritizing sustainable wealth growth and financial flexibility. This approach balances long-term financial goals with lifestyle satisfaction, contrasting with traditional Financial Independence, Retire Early (FIRE) strategies that often require rapid accumulation of assets.
FU Money
FU Money represents a financial goal emphasizing sufficient wealth accumulation to ensure independence and the freedom to make life choices without financial constraints. Unlike traditional FIRE goals centering on early retirement, FU Money prioritizes building a secure money reserve that empowers confident decision-making and stress-free money management.
HENRY (High Earner, Not Rich Yet)
HENRYs balance aggressive savings and investments to achieve FIRE goals while managing immediate financial objectives like debt reduction and lifestyle inflation control. Prioritizing liquid assets and diversified income streams supports both short-term financial stability and long-term financial independence.
Conscious Spending
Conscious spending plays a critical role in both financial goals and FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) goals by ensuring money is aligned with personal values and long-term objectives. Prioritizing essential expenses and mindful investments accelerates wealth accumulation while avoiding lifestyle inflation that hinders achieving financial freedom.
Value-Based Budgeting
Financial goals prioritize specific monetary targets such as saving for retirement or debt repayment, while FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) goals emphasize achieving a lifestyle aligned with early retirement through aggressive saving and investing. Value-Based Budgeting enhances money management by allocating funds toward expenses that reflect personal values, ensuring that financial and FIRE goals support meaningful, long-term fulfillment.
Hyper-Saving Ratio
A high Hyper-Saving Ratio accelerates progress toward FIRE (Financial Independence, Retire Early) goals by maximizing savings and investment rates, surpassing conventional financial goals that prioritize moderate saving and long-term wealth accumulation. Prioritizing aggressive saving strategies dramatically shortens the timeline to financial independence compared to traditional money management focused on steady income growth and controlled expenses.
Financial goal vs FIRE goal for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com