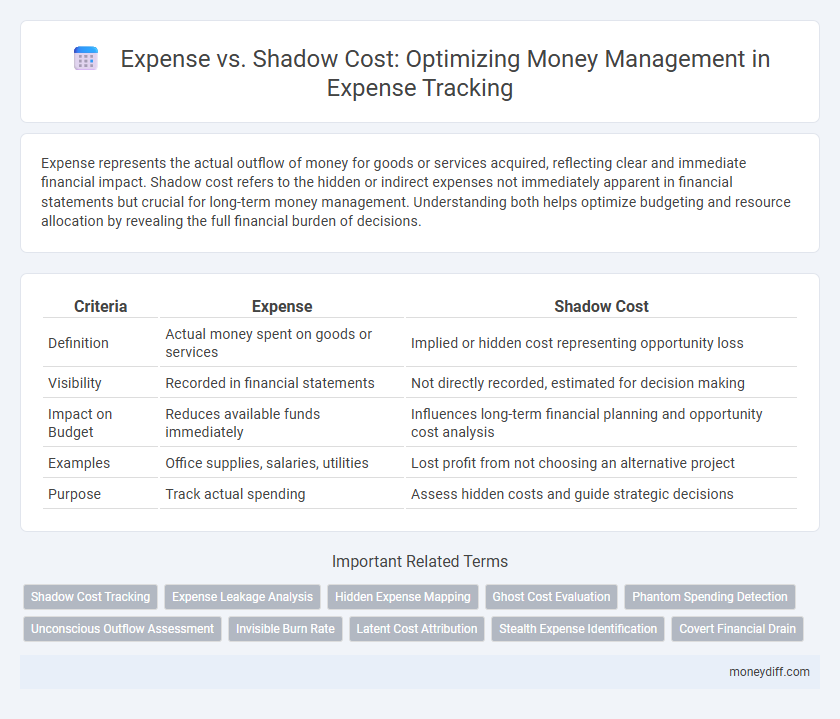
Expense represents the actual outflow of money for goods or services acquired, reflecting clear and immediate financial impact. Shadow cost refers to the hidden or indirect expenses not immediately apparent in financial statements but crucial for long-term money management. Understanding both helps optimize budgeting and resource allocation by revealing the full financial burden of decisions.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Expense | Shadow Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Actual money spent on goods or services | Implied or hidden cost representing opportunity loss |
| Visibility | Recorded in financial statements | Not directly recorded, estimated for decision making |
| Impact on Budget | Reduces available funds immediately | Influences long-term financial planning and opportunity cost analysis |
| Examples | Office supplies, salaries, utilities | Lost profit from not choosing an alternative project |
| Purpose | Track actual spending | Assess hidden costs and guide strategic decisions |
Understanding Expense vs Shadow Cost in Money Management
Expense refers to the actual monetary outflow recorded in financial statements, while shadow cost represents the hidden or indirect costs not immediately reflected in accounting records. Understanding the distinction between expense and shadow cost is crucial for accurate budgeting and effective money management, as shadow costs can impact resource allocation and profitability. Proper identification and analysis of both enable businesses to optimize financial performance and make more informed decisions.
Defining Expenses: Direct Outflows Explained
Expenses represent direct outflows of cash or assets from a business, reflecting the actual costs incurred during operations. Shadow costs, in contrast, are implicit or opportunity costs not directly recorded in financial statements but essential for comprehensive money management decisions. Understanding the distinction between explicit expenses and shadow costs ensures accurate budgeting and financial analysis.
What Is Shadow Cost? Hidden Factors in Spending
Shadow cost refers to the hidden or indirect expenses associated with a purchase or investment that are not immediately apparent in the initial price. These costs include opportunity costs, such as the value of foregone alternatives, and additional expenses like maintenance, time, and resource consumption. Accurately accounting for shadow costs in money management leads to more informed financial decisions and a clearer understanding of the true impact of spending.
The Psychological Impact of Shadow Costs
Shadow costs create a hidden psychological burden by influencing spending decisions beyond the visible expense, leading individuals to undervalue future financial consequences. These intangible costs, such as stress or lost opportunities, can skew money management, causing inefficient allocation of resources. Understanding shadow costs helps improve financial discipline by making individuals more aware of the true impact of their spending habits.
Comparing Real Expenses and Shadow Costs
Real expenses represent actual cash outflows recorded in financial statements, reflecting true monetary transactions. Shadow costs, often intangible or indirect, encompass opportunity costs and hidden financial impacts not captured in traditional accounting. Comparing real expenses to shadow costs enables more comprehensive money management by revealing the full economic consequences of decisions beyond immediate expenditures.
Identifying Hidden Costs in Daily Purchases
Identifying hidden costs in daily purchases requires understanding the difference between explicit expenses and shadow costs, which include indirect factors like time spent, opportunity loss, and future maintenance fees. Shadow costs often go unnoticed but significantly impact overall money management by inflating the true cost of what seems like a simple purchase. Accurate budgeting demands factoring in these latent expenses to avoid underestimating the real financial burden.
How Shadow Costs Influence Budgeting
Shadow costs represent hidden or indirect expenses that are not immediately visible in traditional accounting but significantly affect overall budgeting accuracy. Incorporating shadow costs, such as opportunity costs or long-term maintenance expenses, allows for more comprehensive money management and prevents underestimating true financial requirements. Recognizing these factors improves strategic allocation of resources and enhances financial planning outcomes.
Mitigating Shadow Costs in Personal Finance
Shadow costs represent hidden or indirect expenses not immediately visible in personal finance but significantly impact overall budgeting. Mitigating shadow costs involves identifying overlooked charges such as subscription fees, impulse purchases, and opportunity costs linked to financial decisions. Effective money management requires regularly auditing spending habits and employing tools to track and minimize these concealed financial drains.
Expense Tracking vs Shadow Cost Awareness
Expense tracking involves recording and analyzing all actual financial outflows to maintain accurate budgets and manage cash flow effectively. Shadow cost awareness captures hidden or indirect expenses, such as opportunity costs and unrecorded time investments, which traditional expense tracking may overlook. Integrating both approaches enhances money management by providing a comprehensive view of financial impact beyond explicit expenditures.
Optimizing Money Decisions: Balancing Expense and Shadow Cost
Optimizing money decisions requires a clear understanding of both explicit expenses and hidden shadow costs, such as lost opportunities or deferred maintenance. Evaluating the true cost of financial choices includes factoring in indirect impacts that affect long-term budget health and resource allocation. Balancing these elements enhances strategic spending by aligning immediate payments with future financial implications.
Related Important Terms
Shadow Cost Tracking
Shadow cost tracking reveals the hidden expenses associated with resource allocation, enabling more accurate financial management beyond explicit monetary outflows. By identifying opportunity costs and indirect losses, organizations optimize budget decisions and improve overall expense control.
Expense Leakage Analysis
Expense leakage analysis identifies hidden costs and inefficiencies within an organization's spending, which often result from untracked shadow costs not reflected in formal expense reports. Understanding the disparity between recorded expenses and shadow costs enables businesses to optimize cash flow, improve budgeting accuracy, and reduce financial waste.
Hidden Expense Mapping
Hidden expense mapping reveals shadow costs often overlooked in traditional money management, such as opportunity costs and indirect fees that inflate overall expenditure. Identifying these concealed financial burdens enables more accurate budgeting and strategic allocation of resources, enhancing expense control and profitability.
Ghost Cost Evaluation
Expense represents actual monetary outflows recorded in financial statements, whereas shadow cost, or ghost cost, refers to hidden or indirect costs such as opportunity costs and untracked resource usage that impact overall money management. Effective ghost cost evaluation uncovers these invisible expenditures, enabling more precise budgeting and strategic financial planning.
Phantom Spending Detection
Expense tracking distinguishes actual outflows from shadow costs by identifying phantom spending--hidden or unnoticed expenses that erode budgets without visible transactions. Implementing advanced analytics and AI-driven tools enables effective phantom spending detection, improving financial accuracy and optimizing money management.
Unconscious Outflow Assessment
Unconscious outflow assessment reveals hidden shadow costs that significantly impact money management beyond explicit expenses, encompassing overlooked fees, opportunity costs, and inefficiencies. Identifying these latent financial drains sharpens budget accuracy and enhances strategic allocation of resources.
Invisible Burn Rate
Expense refers to the explicit money spent on business operations, while shadow cost encompasses the invisible burn rate, including hidden expenses like lost productivity and opportunity costs. Effectively managing shadow costs is crucial for accurate financial forecasting and optimizing money management strategies.
Latent Cost Attribution
Expense represents the explicit monetary outflow recorded in financial statements, whereas shadow cost captures latent cost attribution encompassing hidden or indirect expenses such as opportunity costs and untracked resource consumption. Accurate money management requires integrating shadow cost analysis to reveal true economic impact beyond conventional expense reporting.
Stealth Expense Identification
Stealth expense identification uncovers hidden costs often overlooked in traditional expense tracking, enabling more precise money management by revealing shadow costs such as indirect fees, maintenance, and opportunity losses. Recognizing these concealed expenses allows businesses and individuals to optimize budgets, reduce financial leaks, and improve overall fiscal efficiency.
Covert Financial Drain
Shadow costs represent covert financial drains that are not immediately visible in expense reports but significantly impact overall money management. These hidden expenses, such as opportunity costs and unquantified resource utilization, reduce profitability and distort true financial health beyond traditional expense tracking.
Expense vs Shadow Cost for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com