Budgeted expenses involve forecasting and allocating funds in advance, ensuring better control over cash flow and financial planning. Pay-as-you-go expenses occur as costs arise, offering flexibility but potentially leading to unpredictable spending patterns. Understanding the balance between these approaches helps businesses optimize resource allocation and maintain financial stability.
Table of Comparison
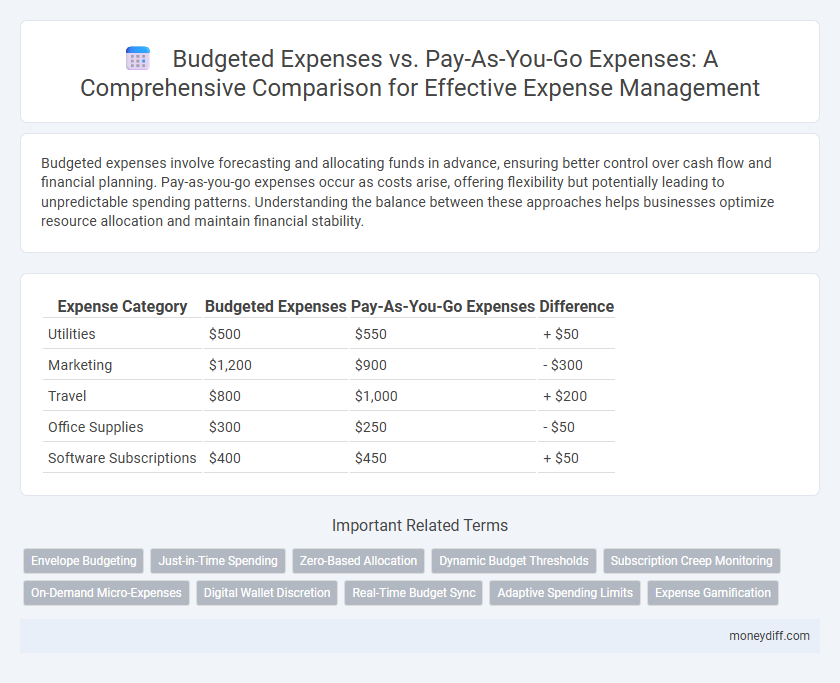
| Expense Category | Budgeted Expenses | Pay-As-You-Go Expenses | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utilities | $500 | $550 | + $50 |
| Marketing | $1,200 | $900 | - $300 |
| Travel | $800 | $1,000 | + $200 |
| Office Supplies | $300 | $250 | - $50 |
| Software Subscriptions | $400 | $450 | + $50 |
Understanding Budgeted Expenses
Budgeted expenses represent a fixed financial plan that allocates specific amounts of money for anticipated costs within a set period, providing control and predictability over spending. These expenses are essential for effective financial management as they help organizations forecast cash flow, prioritize resource allocation, and avoid overspending. Understanding budgeted expenses enables businesses to monitor financial performance, adjust strategies proactively, and ensure alignment with overall fiscal goals.
What Are Pay-As-You-Go Expenses?
Pay-as-you-go expenses refer to costs incurred only when services or resources are used, allowing businesses to avoid upfront budgeting and fixed commitments. This expense model offers flexibility by aligning payments directly with actual consumption, making it ideal for variable or unpredictable spending patterns. Unlike budgeted expenses, pay-as-you-go expenses can fluctuate significantly, reflecting real-time usage and enabling more precise cash flow management.
Key Differences Between Budgeted and Pay-As-You-Go Expenses
Budgeted expenses involve allocating a fixed amount of funds in advance for anticipated costs, providing predictable financial planning and control. Pay-as-you-go expenses are incurred only when the service or product is used, offering flexibility and avoiding upfront commitments. Key differences include predictability, with budgeted expenses allowing for better cash flow management, while pay-as-you-go expenses enable scalability and cost-efficiency based on actual usage.
Pros and Cons of Budgeted Expenses
Budgeted expenses provide financial predictability by allocating fixed amounts for specific categories, helping to prevent overspending and ensuring better cash flow management. However, they can lack flexibility, making it challenging to adapt quickly to unexpected costs or changes in spending patterns. Rigid budgeted expenses may also lead to underutilization of allocated funds if actual needs fall below estimates.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pay-As-You-Go Expenses
Pay-As-You-Go expenses offer flexibility by allowing businesses to align costs directly with usage, reducing upfront financial commitments and minimizing the risk of overspending on unused services. This model enhances cash flow management, especially for startups or companies with fluctuating demand, but can lead to higher long-term costs compared to budgeted expenses if usage is consistently high. The lack of predictable monthly expenses in Pay-As-You-Go plans may complicate financial forecasting and budgeting processes for organizations.
When to Choose Budgeted Over Pay-As-You-Go Expenses
Budgeted expenses provide financial predictability and control by allocating a fixed amount for anticipated costs, which is ideal for stable or recurring expenses. Pay-as-you-go expenses offer flexibility by charging only for actual usage, making them suitable for variable or unpredictable costs. Choose budgeted expenses when managing cash flow and long-term financial planning is critical to avoid overspending.
Impact on Financial Planning and Control
Budgeted expenses enable precise financial planning by allocating fixed amounts for anticipated costs, ensuring disciplined spending and reducing the risk of budget overruns. Pay-as-you-go expenses offer flexibility by aligning costs directly with actual usage, helping businesses avoid unnecessary expenditures but requiring vigilant monitoring to prevent unexpected financial strain. Effective financial control balances these approaches, optimizing cash flow management while maintaining adaptability to changing operational demands.
Practical Examples of Each Expense Type
Budgeted expenses include fixed costs like monthly rent, salaries, and insurance premiums that are planned and allocated in advance to maintain financial stability. Pay-as-you-go expenses arise from variable costs such as utility bills, raw materials, and freelance services, which fluctuate based on actual usage or consumption. Businesses benefit from budgeting fixed expenses to predict cash flow while managing pay-as-you-go expenses flexibly to control real-time spending.
How to Transition Between Expense Strategies
Transitioning between budgeted expenses and pay-as-you-go expenses requires a detailed assessment of current cash flow patterns and expense predictability. Businesses should implement tracking systems that categorize expenditures by type and timing to inform whether fixed budget allocations or variable expense models yield better financial control. Gradual adoption of a hybrid strategy allows monitoring responsiveness and cost efficiency before full transition, minimizing financial disruptions.
Tips for Managing Both Types of Expenses
Effective management of budgeted expenses requires detailed tracking and regular reviews to ensure spending aligns with set financial limits, preventing overspending. For pay-as-you-go expenses, maintaining accurate records and immediate payment helps avoid interest charges and late fees, improving cash flow control. Combining these approaches involves using budgeting software that can categorize and monitor both fixed and variable expenses, enabling comprehensive financial oversight and informed decision-making.
Related Important Terms
Envelope Budgeting
Envelope budgeting allocates funds into predefined categories, ensuring budgeted expenses align with available cash, preventing overspending and improving financial control. Pay-as-you-go expenses require immediate payment from current funds without prior allocation, increasing the risk of depleting resources and undermining budgeting discipline.
Just-in-Time Spending
Budgeted expenses allocate fixed funds in advance, enabling planned financial control, while pay-as-you-go expenses promote just-in-time spending by incurring costs only when services or resources are used, optimizing cash flow and reducing wastage. Just-in-time spending in pay-as-you-go models aligns expenditures directly with actual usage, enhancing flexibility and minimizing idle budget allocations.
Zero-Based Allocation
Zero-based allocation ensures budgeted expenses are justified from zero each period, promoting precise financial control compared to pay-as-you-go expenses that fluctuate based on actual usage. This method optimizes resource allocation by eliminating unnecessary costs and aligning spending directly with organizational goals.
Dynamic Budget Thresholds
Dynamic budget thresholds enable organizations to adjust budgeted expenses in real-time, aligning financial limits with actual pay-as-you-go expenses to prevent overspending. This approach enhances expense management by providing flexible control mechanisms that respond to fluctuating costs and usage patterns.
Subscription Creep Monitoring
Budgeted expenses provide a fixed financial framework for subscription services, helping organizations avoid overspending by setting clear limits, whereas pay-as-you-go expenses fluctuate based on actual usage, requiring vigilant subscription creep monitoring to detect and control unexpected cost increases. Implementing automated tools for subscription creep monitoring helps identify redundant or underutilized subscriptions in real-time, optimizing expenditure management and ensuring budget adherence.
On-Demand Micro-Expenses
Budgeted expenses provide a fixed allocation for predictable costs, while pay-as-you-go expenses enable flexible spending based on actual usage, crucial for managing on-demand micro-expenses. On-demand micro-expenses allow precise control over small, variable costs by aligning expenses directly with consumption patterns, optimizing cash flow and reducing waste.
Digital Wallet Discretion
Budgeted expenses provide a fixed allocation for digital wallet discretionary spending, enabling predictable financial planning and control over discretionary purchases. Pay-as-you-go expenses offer flexibility by allowing users to spend within their digital wallet based on real-time needs, often resulting in more variable but adaptable discretionary expense management.
Real-Time Budget Sync
Budgeted expenses provide a fixed financial framework for planned costs, while pay-as-you-go expenses fluctuate based on actual usage, requiring dynamic tracking to avoid overspending. Real-time budget sync ensures that expense data is continuously updated, enabling accurate monitoring and immediate adjustments to maintain financial control.
Adaptive Spending Limits
Adaptive spending limits optimize budgeted expenses by setting predefined thresholds while allowing flexibility for pay-as-you-go expenses to adjust dynamically based on real-time usage patterns. This approach ensures controlled financial planning without sacrificing the agility needed for variable, consumption-based costs.
Expense Gamification
Budgeted expenses provide a fixed financial plan that controls spending limits, while pay-as-you-go expenses offer flexibility by charging costs based on actual usage, enhancing responsiveness to real-time financial needs. Integrating expense gamification can motivate users to stay within budget by rewarding cost-saving behaviors and promoting financial discipline through interactive challenges and goals.
Budgeted Expenses vs Pay-As-You-Go Expenses for Expense Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com