Impulse purchases often lead to unplanned expenses driven by emotional triggers and immediate gratification, disrupting budgets and financial goals. Intentional spending, characterized by careful planning and deliberate decision-making, promotes financial discipline and helps buyers align their expenses with priorities. Understanding this distinction empowers consumers to manage their resources more effectively and avoid unnecessary debt.
Table of Comparison
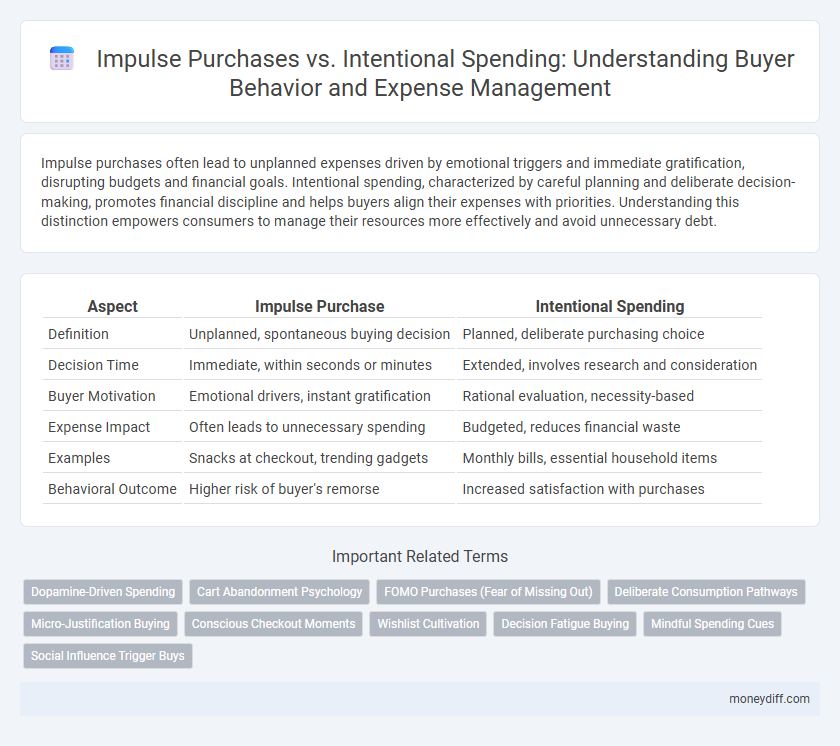
| Aspect | Impulse Purchase | Intentional Spending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unplanned, spontaneous buying decision | Planned, deliberate purchasing choice |
| Decision Time | Immediate, within seconds or minutes | Extended, involves research and consideration |
| Buyer Motivation | Emotional drivers, instant gratification | Rational evaluation, necessity-based |
| Expense Impact | Often leads to unnecessary spending | Budgeted, reduces financial waste |
| Examples | Snacks at checkout, trending gadgets | Monthly bills, essential household items |
| Behavioral Outcome | Higher risk of buyer's remorse | Increased satisfaction with purchases |
Understanding Impulse Purchases: What Drives Instant Spending?
Impulse purchases are driven by emotional triggers such as stress, excitement, or social influence, leading to spontaneous buying decisions without prior planning. Neurological studies indicate that the reward system in the brain releases dopamine during impulse buying, which creates a pleasurable sensation and reinforces the behavior. Retail strategies such as product placement, limited-time offers, and personalized marketing capitalize on these psychological drivers to increase instant spending.
The Psychology Behind Intentional Spending Decisions
Intentional spending decisions are driven by deliberate evaluation of needs, long-term benefits, and value maximization, reflecting a conscious effort to align purchases with personal goals and financial constraints. Psychological factors such as self-control, future orientation, and mindful consumption play critical roles in guiding buyers to prioritize quality over quantity and avoid impulsive buying. Understanding these cognitive mechanisms helps businesses tailor marketing strategies that resonate with consumers seeking purposeful and reflective purchasing experiences.
Key Differences: Impulse Buying vs Intentional Purchasing
Impulse purchases occur spontaneously without pre-planning, driven by immediate emotions or external triggers such as sales promotions, whereas intentional spending involves deliberate decision-making based on needs, budget, and long-term goals. Impulse buyers often experience regret and overspending, impacting financial stability, while intentional purchasers exhibit greater control and alignment with financial priorities. Key differences include the level of premeditation, emotional influence, and the impact on overall financial health.
Emotional Triggers in Impulse Shopping
Impulse purchases often stem from strong emotional triggers such as excitement, stress relief, or the desire for instant gratification, influencing buyers to make spontaneous decisions without thorough evaluation. Intentional spending, however, is characterized by careful planning and prioritization aligned with budget goals or personal values, minimizing emotional interference. Understanding these emotional drivers is crucial for retailers aiming to optimize marketing strategies that tap into momentary buyer impulses effectively.
Long-Term Financial Impact of Impulse Purchases
Impulse purchases often lead to unplanned expenses that can accumulate, negatively affecting long-term financial stability by reducing available savings and increasing debt. Over time, habitual impulsive spending can erode budget discipline, diminishing the ability to invest in essential goals such as retirement or education. Intentional spending, driven by careful planning and consideration, promotes better financial outcomes by aligning purchases with long-term priorities and mitigating unnecessary financial strain.
Benefits of Practicing Intentional Spending
Intentional spending enhances financial control by promoting thoughtful decision-making and reducing unnecessary impulse purchases. This approach improves budget adherence and increases savings potential, fostering long-term financial stability. Consumers who practice intentional spending often experience greater satisfaction with their purchases and a clearer sense of financial priorities.
Strategies to Reduce Impulse Buying Habits
Implementing strategies to reduce impulse buying habits enhances budget control and supports intentional spending. Techniques such as setting strict shopping lists, employing mindfulness practices before purchases, and delaying non-essential buys by 24 hours significantly curb impulsive expenditure. Leveraging mobile apps that track and categorize expenses also promotes awareness and disciplined buyer behavior.
Building Mindful Money Habits for Better Expense Control
Impulse purchases often lead to unplanned expenses that disrupt budget goals, whereas intentional spending aligns with financial priorities and promotes better expense control. Cultivating mindful money habits involves tracking expenses, setting clear financial goals, and practicing pause-and-reflect techniques before purchases. Leveraging tools like budgeting apps and expense trackers enhances awareness and reduces impulsive buying tendencies, fostering sustainable financial health.
Real-Life Examples: From Impulse Shopper to Conscious Consumer
Impulse purchases, such as grabbing a candy bar at the checkout or buying a trending gadget on a whim, highlight the often spontaneous nature of consumer behavior driven by immediate desire rather than necessity. Intentional spending reflects a more deliberate decision-making process, as seen when consumers research and compare prices before investing in high-value items like electronics or furniture. Transitioning from impulse shopper to conscious consumer involves recognizing triggers, setting budgets, and prioritizing long-term satisfaction over short-term gratification in everyday expense management.
Creating a Personal Action Plan for Intentional Spending
Analyzing impulse purchase triggers and identifying spending patterns enable consumers to design a personal action plan that prioritizes intentional spending. Setting specific financial goals and establishing budget thresholds help maintain control over discretionary expenses and minimize unplanned purchases. Regularly reviewing expenses encourages mindful decision-making, fostering long-term financial discipline and improved budget adherence.
Related Important Terms
Dopamine-Driven Spending
Dopamine-driven spending often fuels impulse purchases, triggering immediate reward sensations that overshadow long-term financial goals. Intentional spending, contrastingly, involves deliberate decision-making processes that reduce emotional triggers and promote sustained budgeting discipline.
Cart Abandonment Psychology
Impulse purchases often trigger cart abandonment due to sudden buyer hesitation and lack of preparedness, while intentional spending reflects deliberate decision-making that reduces the likelihood of leaving items unpurchased. Understanding the psychological tension between spontaneous desire and rational evaluation helps retailers design strategies to minimize cart abandonment by fostering commitment and clear purchase intent.
FOMO Purchases (Fear of Missing Out)
Impulse purchases driven by FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) often result in buyers making unplanned, emotionally charged spending decisions, contrasting intentional spending where purchases are deliberate and budgeted. Consumers influenced by FOMO prioritize immediate gratification and social inclusion, leading to higher instances of buyer's remorse and financial strain compared to mindful, intentional expenditure.
Deliberate Consumption Pathways
Impulse purchases typically occur without premeditation, driven by immediate emotions or external stimuli, contrasting with intentional spending where buyers follow deliberate consumption pathways characterized by researched decision-making and specific needs assessment. Understanding these distinct behaviors enables marketers to tailor strategies that either capitalize on spontaneous desires or support informed purchasing journeys.
Micro-Justification Buying
Micro-justification buying occurs when consumers rationalize impulse purchases through small, personal reasons that align with their values or emotional needs, blurring the line between impulse and intentional spending. This behavior highlights how buyers often create mental justifications to legitimize spontaneous expenses, influencing overall buyer behavior and expense management.
Conscious Checkout Moments
Impulse purchases often occur during unconscious checkout moments driven by emotional triggers, whereas intentional spending reflects a deliberate decision-making process aligned with budget and value considerations. Understanding these distinct buyer behaviors enables retailers to optimize marketing strategies and enhance customer engagement through targeted messaging and personalized offers at points of sale.
Wishlist Cultivation
Impulse purchases often bypass wishlist cultivation, driven by spontaneous emotions rather than planned needs, resulting in higher chances of buyer's remorse. Intentional spending involves careful wishlist curation, enabling consumers to evaluate priorities and budget constraints before making well-considered purchases.
Decision Fatigue Buying
Decision fatigue significantly influences impulse purchases by depleting cognitive resources, leading buyers to opt for immediate gratification rather than deliberate, intentional spending. Consumers experiencing decision fatigue are more susceptible to spontaneous buying choices, often resulting in unplanned expenses that contrast with carefully planned purchases.
Mindful Spending Cues
Impulse purchases often bypass rational decision-making, driven by immediate emotional triggers and unplanned desires, whereas intentional spending involves deliberate evaluation of needs and long-term value. Recognizing mindful spending cues such as budget limits, product necessity, and personal financial goals helps buyers cultivate disciplined purchasing habits and reduce impulsive expenses.
Social Influence Trigger Buys
Impulse purchases triggered by social influence often result from exposure to peers' buying behaviors and targeted social media advertising, leading consumers to make spontaneous decisions without prior intention. Intentional spending, in contrast, involves deliberate planning and prioritization of needs, reducing the impact of social triggers on purchasing behavior.
Impulse Purchase vs Intentional Spending for buyer behavior. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com