A monthly budget sets fixed spending limits for each calendar month, providing clear short-term financial targets and control. A rolling budget continually updates by adding a new month as the current month ends, allowing for more flexible adjustments based on recent financial performance. This dynamic approach helps manage cash flow more effectively, adapting to changing expenses and income patterns over time.
Table of Comparison
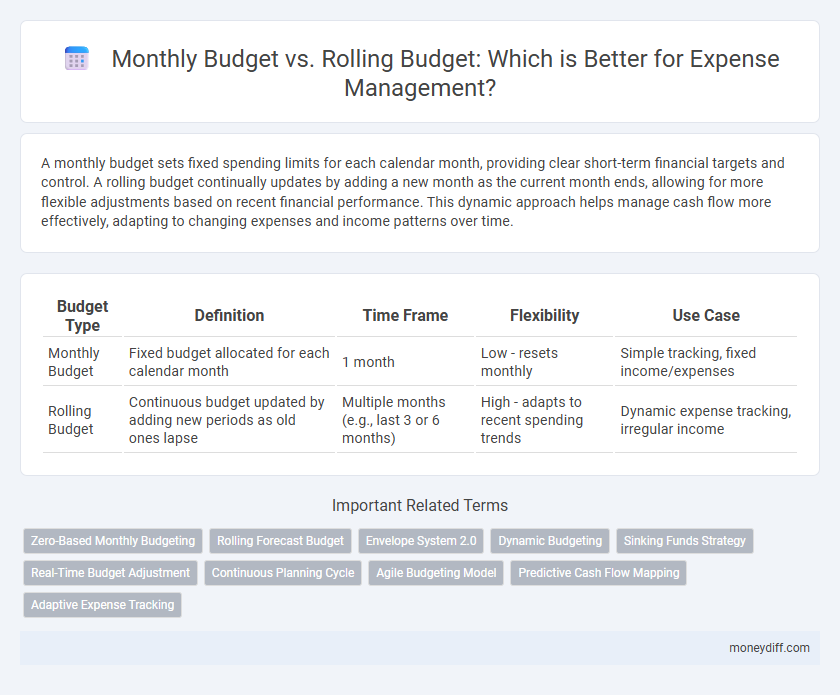
| Budget Type | Definition | Time Frame | Flexibility | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monthly Budget | Fixed budget allocated for each calendar month | 1 month | Low - resets monthly | Simple tracking, fixed income/expenses |
| Rolling Budget | Continuous budget updated by adding new periods as old ones lapse | Multiple months (e.g., last 3 or 6 months) | High - adapts to recent spending trends | Dynamic expense tracking, irregular income |
Introduction to Budgeting Methods
Monthly budgets set fixed spending limits based on anticipated income and expenses over a specific calendar month, enabling precise control of cash flow and expense tracking. Rolling budgets continuously update financial plans by adding a new budget period as the current period ends, allowing for flexible adjustments based on real-time financial data and trends. Both methods serve distinct money management goals, with monthly budgets emphasizing structure and discipline, while rolling budgets prioritize adaptability and ongoing financial forecasting.
What is a Monthly Budget?
A monthly budget is a detailed financial plan that allocates income towards expenses, savings, and debt payments within a 30-day period. It helps individuals or households track spending, control costs, and prioritize financial goals for predictable cash flow management. By setting fixed limits for categories such as rent, groceries, and utilities, a monthly budget enhances accountability and reduces the risk of overspending.
What is a Rolling Budget?
A rolling budget continuously updates by adding a new budget period as the current period ends, maintaining a constant planning horizon and enhancing financial flexibility. It allows businesses to adapt their expense forecasts and resource allocation based on real-time financial data and changing market conditions. This dynamic approach improves accuracy in cash flow management compared to static monthly budgets, which are fixed for a set period without ongoing adjustments.
Key Differences Between Monthly and Rolling Budgets
Monthly budgets allocate fixed spending limits for each calendar month, enabling straightforward tracking and comparison against actual expenses. Rolling budgets continuously update projections by adding a new month as the current month ends, providing a dynamic forecast extending over the next 12 months. The key difference lies in flexibility: monthly budgets offer static targets while rolling budgets adjust in real-time to reflect changes in income and expenditure patterns.
Advantages of Monthly Budgeting
Monthly budgeting provides clear, fixed financial targets that help control expenses and improve cash flow management. It simplifies tracking by offering a consistent timeframe for analyzing spending patterns and making informed adjustments. This approach enhances accountability, enabling individuals to promptly identify overspending and prioritize essential costs effectively.
Benefits of Rolling Budgeting
Rolling budgeting enhances financial flexibility by continuously updating forecasts based on real-time expense data, allowing more accurate money management. It improves responsiveness to changing market conditions and unexpected costs, ensuring better control over monthly budgets and optimized resource allocation. This approach supports proactive decision-making and reduces the risk of budget overruns by maintaining a dynamic overview of expenses.
Challenges of Monthly Budgets
Monthly budgets often struggle with flexibility, as fixed expense categories can't easily adapt to irregular income or unexpected costs, leading to overspending or underfunding critical needs. They lack real-time responsiveness, making it difficult to accommodate fluctuating expenses or sudden financial changes. This rigidity can cause stress and reduce the effectiveness of money management compared to rolling budgets that continuously update based on actual spending patterns.
Drawbacks of Rolling Budgets
Rolling budgets often require continuous updates, which can lead to increased administrative workload and complexity. This constant revision may cause confusion among departments, impairing clear financial planning and accountability. Businesses might struggle with short-term focus, neglecting long-term strategic goals due to frequent budget changes.
Choosing the Right Budget for Your Financial Goals
Monthly budgets provide a fixed spending limit based on predicted income and expenses within a specific month, ideal for short-term financial control and immediate goal tracking. Rolling budgets continuously update based on actual spending and income, offering flexibility to adjust plans dynamically for long-term financial stability. Selecting the right budget depends on your financial goals, where monthly budgets suit those needing strict discipline, while rolling budgets benefit individuals seeking adaptive money management.
Tips for Effective Money Management Using Budgets
Comparing monthly budgets and rolling budgets reveals key strategies for effective money management: monthly budgets offer fixed financial targets within set periods, aiding disciplined spending tracking, while rolling budgets provide adaptive, continuous updates reflecting real-time expenses and income fluctuations. Using a rolling budget helps anticipate cash flow changes more accurately, enabling proactive adjustments that reduce financial stress. Combining these approaches by setting a monthly base budget and adjusting with a rolling forecast improves overall budgeting precision and financial stability.
Related Important Terms
Zero-Based Monthly Budgeting
Zero-based monthly budgeting requires allocating every dollar of income to specific expenses, savings, or debt repayment, ensuring no funds remain unassigned each month. Unlike rolling budgets that adjust based on previous months' spending, zero-based budgeting demands precise planning to optimize cash flow and control expenses effectively.
Rolling Forecast Budget
A rolling forecast budget continuously updates financial projections by incorporating real-time expense data and adjusting future periods based on current trends, enhancing accuracy in money management. This flexible approach contrasts with a fixed monthly budget, allowing businesses to respond dynamically to changing costs and optimize cash flow.
Envelope System 2.0
The Envelope System 2.0 enhances money management by integrating a rolling budget that adjusts continuously based on actual expenses, offering more flexibility than a fixed monthly budget. This dynamic approach allocates funds to spending categories as needed, preventing overspending and ensuring optimized control over cash flow.
Dynamic Budgeting
Dynamic budgeting adapts the monthly budget by continuously updating financial allocations based on real-time expenses and income fluctuations, unlike fixed monthly budgets that remain static throughout the period. Rolling budgets extend this flexibility by adding a new budget period as the current one ends, enabling ongoing adjustments that improve cash flow management and responsiveness to changing financial conditions.
Sinking Funds Strategy
A monthly budget allocates fixed amounts for expenses each month, while a rolling budget continuously updates to reflect changing financial needs, enhancing flexibility in money management. Employing a sinking funds strategy within a rolling budget allows for systematic savings toward future expenses, ensuring funds are available when needed without disrupting other financial goals.
Real-Time Budget Adjustment
Monthly budget allocates fixed amounts for expenses within set periods, while rolling budget continuously updates financial plans based on real-time expense tracking and income changes. Real-time budget adjustment enhances money management by allowing immediate response to fluctuating cash flows, ensuring more accurate control over spending and savings.
Continuous Planning Cycle
A rolling budget ensures continuous financial planning by updating projections monthly to reflect actual expenses and revenue changes, promoting agility in money management. In contrast, a monthly budget sets fixed spending limits for a single period, limiting responsiveness to dynamic financial conditions.
Agile Budgeting Model
The Agile Budgeting Model prioritizes flexibility by using rolling budgets that are continuously updated based on real-time financial data, enabling more adaptive and responsive money management compared to static monthly budgets. This dynamic approach improves expense control by allowing businesses to adjust spending and resource allocation frequently in response to market fluctuations and organizational priorities.
Predictive Cash Flow Mapping
Monthly budgets offer fixed spending limits based on historical data, while rolling budgets continuously update projections to reflect real-time financial changes. Predictive cash flow mapping enhances rolling budgets by forecasting future cash inflows and outflows, enabling more accurate and dynamic expense management.
Adaptive Expense Tracking
Monthly budgets set fixed spending limits for each month, providing clear expense boundaries, while rolling budgets continuously update based on actual spending trends to offer dynamic financial insights. Adaptive expense tracking leverages rolling budgets to adjust allocations in real-time, improving accuracy and responsiveness in money management.
Monthly budget vs Rolling budget for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com