Recurring expenses provide predictable, fixed costs that simplify budget allocation by ensuring consistent cash flow management. Discretionary microsplitting allows for flexible distribution of funds across minor, variable expenses, enabling more precise control over discretionary spending categories. Combining both strategies enhances financial planning by balancing stability with adaptability in budget management.
Table of Comparison
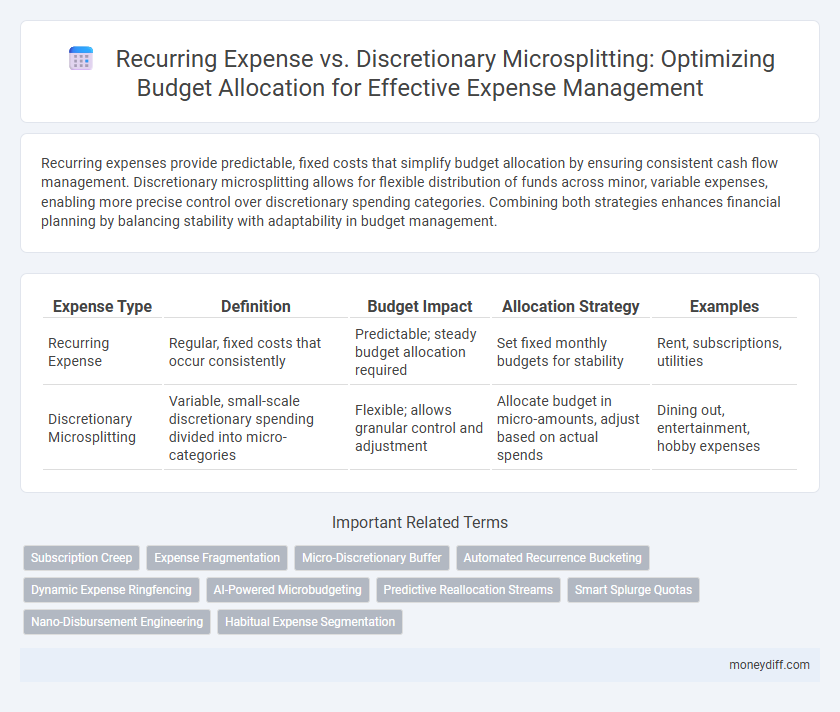
| Expense Type | Definition | Budget Impact | Allocation Strategy | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recurring Expense | Regular, fixed costs that occur consistently | Predictable; steady budget allocation required | Set fixed monthly budgets for stability | Rent, subscriptions, utilities |
| Discretionary Microsplitting | Variable, small-scale discretionary spending divided into micro-categories | Flexible; allows granular control and adjustment | Allocate budget in micro-amounts, adjust based on actual spends | Dining out, entertainment, hobby expenses |
Understanding Recurring vs Discretionary Expenses
Recurring expenses, such as rent, utilities, and subscriptions, represent fixed costs that occur regularly and are essential for maintaining operations. Discretionary microsplitting involves breaking down variable, non-essential expenses like entertainment or dining into smaller categories to optimize budget control. Understanding the distinction between these two types of expenses helps in accurate allocation, ensuring fixed obligations are met while allowing flexible spending adjustments.
The Basics of Microsplitting Budget Categories
Microsplitting budget categories involves dividing expenses into smaller, precise segments, enhancing control over both recurring expenses and discretionary spending. Recurring expenses, such as rent and subscriptions, are allocated fixed amounts regularly, ensuring consistent coverage, while discretionary microsplitting allows flexible budgeting for non-essential items like dining or entertainment, improving financial agility. This method optimizes budget allocation by providing detailed visibility and enabling targeted adjustments to spending habits.
Why Split Your Discretionary Spending?
Splitting discretionary spending into smaller, manageable microsplits enhances budget accuracy and control, making it easier to track specific categories and identify spending patterns. Unlike recurring expenses that are fixed and predictable, discretionary microsplitting allows for dynamic allocation tailored to fluctuating financial priorities. This targeted approach reduces overspending risks and improves overall financial health by promoting disciplined discretionary fund management.
Identifying Fixed Recurring Expenses in Your Budget
Fixed recurring expenses such as rent, utilities, and subscription services form the backbone of budget allocation by providing predictable monthly costs that require consistent funding. Discretionary microsplitting breaks down flexible spending categories into smaller, manageable amounts, allowing for precise control over variable expenses while ensuring that essential fixed costs are prioritized. Identifying and categorizing these fixed recurring expenses is crucial for maintaining financial stability and optimizing overall budget management.
Advantages of Microsplitting Discretionary Funds
Microsplitting discretionary funds enables precise allocation to diverse small-scale expenses, enhancing budget flexibility and control. This granular approach improves tracking of spending patterns, allowing adjustments that optimize overall financial health. It reduces the risk of overspending by setting limits on minor expenses, supporting more disciplined budget management compared to broad recurring expense categories.
Common Mistakes in Budget Allocation
Common mistakes in budget allocation include misclassifying recurring expenses as discretionary, leading to underestimating fixed financial obligations. Microsplitting discretionary spending without clear criteria can result in fragmented budgets that obscure actual spending patterns. Accurate categorization between recurring expenses and discretionary microsplitting enhances budget clarity and financial planning efficiency.
Tools for Tracking Recurring and Discretionary Expenses
Effective budget allocation requires precise tools to track both recurring expenses and discretionary microsplitting. Software like Mint and YNAB offers automated categorization and detailed reporting to monitor consistent bills and variable spending. Utilizing apps with real-time notifications and customizable labels enhances visibility and ensures disciplined financial management across all expense types.
Balancing Stability and Flexibility in Monthly Budgets
Recurring expenses provide stability in monthly budgets by covering fixed costs such as rent, utilities, and subscriptions, ensuring predictable cash flow management. Discretionary microsplitting allocates flexible funds to variable spending categories like dining, entertainment, and hobbies, allowing for adaptability and personalized financial control. Balancing these approaches optimizes budget allocation by maintaining essential commitments while enabling adjustments that respond to changing financial priorities.
Practical Examples of Microsplitting Discretionary Spending
Microsplitting discretionary spending involves breaking down flexible budget categories like entertainment or dining out into smaller, specific subcategories such as movies, concerts, or cafes, enabling precise tracking and control. For example, allocating $50 monthly for dining can be microsplit into $20 for coffee shops, $15 for casual dinners, and $15 for snacks, which helps identify spending patterns and adjust allocations effectively. Compared to recurring expenses like rent or subscriptions, which remain fixed, microsplitting discretionary expenses provides granular insights essential for optimizing budget flexibility.
Optimizing Budget Allocation for Financial Goals
Recurring expenses provide a stable framework for budget allocation, ensuring essential costs such as rent, utilities, and subscriptions are consistently covered. Discretionary microsplitting allows for flexible allocation of smaller discretionary funds across various categories, enhancing control over non-essential spending. Optimizing budget allocation by balancing recurring expenses with discretionary microsplitting supports achieving financial goals through disciplined yet adaptable financial planning.
Related Important Terms
Subscription Creep
Recurring expenses are predictable costs such as subscriptions, which can accumulate unnoticed, a phenomenon known as subscription creep that significantly impacts budget allocation. Discretionary microsplitting involves breaking down variable expenses into smaller, manageable categories to better control spending and identify opportunities for cost reduction.
Expense Fragmentation
Recurring expenses ensure steady budget allocation through fixed, predictable payments, while discretionary microsplitting fragments spending into smaller, variable components allowing granular control and flexible adjustment. This expense fragmentation enhances financial visibility and precision in resource distribution across diverse budget categories.
Micro-Discretionary Buffer
Micro-Discretionary Buffer enhances budget allocation by allowing flexible adjustments within discretionary spending categories, optimizing cash flow without impacting essential recurring expenses. This approach improves financial agility by minimizing the risk of overspending while ensuring recurring expenses remain fully funded.
Automated Recurrence Bucketing
Automated Recurrence Bucketing enhances budget allocation by systematically categorizing recurring expenses, ensuring consistent tracking and forecasting without manual intervention. This contrasts with discretionary microsplitting, which requires granular analysis of variable spending, making it less efficient for managing predictable financial outflows.
Dynamic Expense Ringfencing
Dynamic Expense Ringfencing enhances budget allocation by segregating recurring expenses from discretionary microsplitting, ensuring predictable costs are prioritized while allowing flexibility in discretionary spending. This method optimizes cash flow management by dynamically adjusting spend limits based on real-time expense patterns and predefined financial goals.
AI-Powered Microbudgeting
AI-powered microbudgeting leverages machine learning algorithms to distinguish between recurring expenses and discretionary microsplitting, optimizing budget allocation by predicting spending patterns with high accuracy. This approach enables granular control over discretionary spending while ensuring fixed costs are consistently managed, enhancing overall financial efficiency.
Predictive Reallocation Streams
Recurring expenses provide stable cash flow predictions essential for Predictive Reallocation Streams, enabling automated budget adjustments with high accuracy. Discretionary Microsplitting enhances this model by dynamically reallocating smaller budget segments, optimizing funds for variable priorities without disrupting core financial commitments.
Smart Splurge Quotas
Smart Splurge Quotas enable precise budget allocation by differentiating between Recurring Expenses, which are fixed and predictable, and Discretionary Microsplitting, allowing flexible, controlled spending on variable items. This method enhances financial management by balancing essential recurring costs with adjustable discretionary spending limits tailored to personal or organizational priorities.
Nano-Disbursement Engineering
Recurring expenses ensure predictable financial commitments while discretionary microsplitting leverages nano-disbursement engineering to allocate budget dynamically across micro-categories, optimizing cash flow and enhancing granular expense tracking. This approach enables precise control over spending patterns, reducing waste and improving financial agility through automated, data-driven budget adjustments.
Habitual Expense Segmentation
Habitual expense segmentation distinguishes recurring expenses, which are predictable and essential like rent and subscriptions, from discretionary microsplitting that breaks down variable expenses into smaller, controlled categories to enhance budget flexibility. This method improves financial management by ensuring steady allocation for fixed costs while enabling precise tracking and adjustment of flexible spending habits.
Recurring Expense vs Discretionary Microsplitting for budget allocation. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com