Expense refers to planned or expected costs that are accounted for within a budget, providing a clear framework for money management and financial planning. Unbudgeted outflows occur unexpectedly and can disrupt cash flow, requiring immediate adjustments to maintain financial stability. Effective money management involves distinguishing between these two to prioritize spending and prepare contingency funds.
Table of Comparison
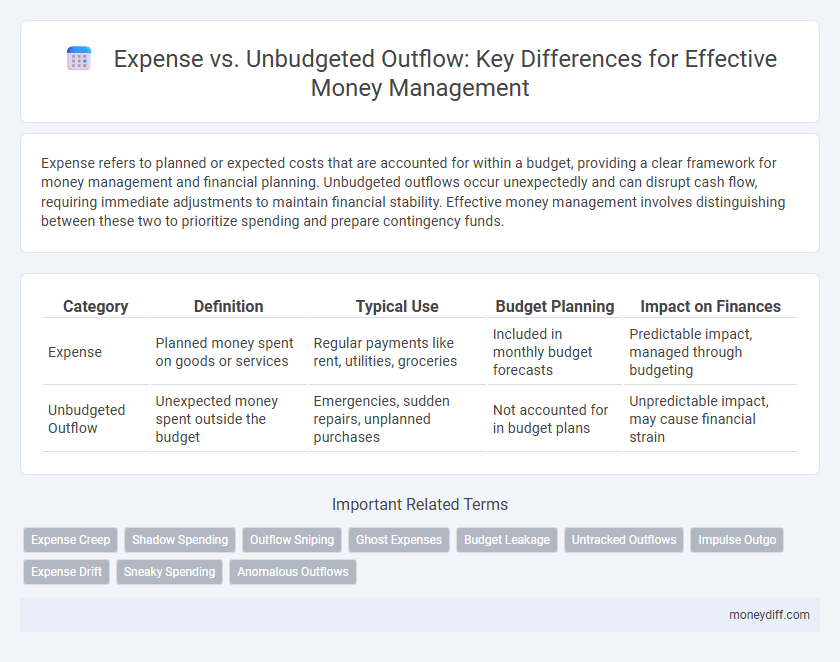
| Category | Definition | Typical Use | Budget Planning | Impact on Finances |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expense | Planned money spent on goods or services | Regular payments like rent, utilities, groceries | Included in monthly budget forecasts | Predictable impact, managed through budgeting |
| Unbudgeted Outflow | Unexpected money spent outside the budget | Emergencies, sudden repairs, unplanned purchases | Not accounted for in budget plans | Unpredictable impact, may cause financial strain |
Understanding Expenses in Money Management
Expenses represent planned and tracked costs within a budget, allowing for effective money management and financial forecasting. Unbudgeted outflows are unexpected or irregular payments that disrupt financial plans and require immediate adjustment to avoid cash flow issues. Differentiating between regular expenses and unbudgeted outflows helps maintain budget accuracy and improves overall financial control.
Defining Unbudgeted Outflows
Unbudgeted outflows refer to financial expenditures that occur unexpectedly and are not accounted for in the planned budget, distinguishing them from regular expenses that are anticipated and allocated for. These unplanned costs can disrupt cash flow management and require immediate reallocation of resources or emergency funds. Properly identifying unbudgeted outflows is essential for maintaining financial stability and improving future budget accuracy.
Key Differences: Expense vs Unbudgeted Outflow
Expenses are planned and recorded costs aligned with a budget, representing predictable financial outflows for goods or services. Unbudgeted outflows refer to unexpected or unplanned expenditures that fall outside the budget, often requiring immediate attention and adjustments. Understanding the distinction ensures effective money management by maintaining budget control while preparing for unforeseen financial demands.
The Role of Budgeting in Expense Control
Budgeting plays a crucial role in distinguishing regular expenses from unbudgeted outflows by setting clear financial limits that guide spending decisions. By establishing predefined categories and spending thresholds, budgeting helps prevent unexpected expenditures from disrupting overall money management. Effective budget control enables timely identification of variances, ensuring proactive adjustments to maintain financial stability.
Common Causes of Unbudgeted Outflows
Unbudgeted outflows often arise from emergency repairs, medical expenses, or unexpected travel costs, disrupting planned financial allocations. Expenses like sudden car breakdowns, urgent home maintenance, or unforeseen health treatments typically exceed budget forecasts. These unplanned costs require careful monitoring to maintain effective money management and avoid financial strain.
Impact of Unbudgeted Outflows on Financial Stability
Unbudgeted outflows significantly disrupt financial stability by creating unexpected cash shortages that strain liquidity and hinder effective money management. Unlike planned expenses, these unforeseen payments force individuals or businesses to reallocate funds abruptly, risking the depletion of emergency savings or the accumulation of debt. Managing unbudgeted outflows requires proactive strategies to maintain cash flow balance and safeguard long-term financial health.
Strategies to Minimize Unbudgeted Outflows
Implementing strict budget tracking and using expense forecasting tools significantly reduce unbudgeted outflows by enhancing financial visibility. Establishing emergency funds and setting spending limits for discretionary purchases prevent unexpected expenses from disrupting cash flow. Regularly reviewing and adjusting budget categories ensures alignment with actual spending patterns, minimizing the risk of unplanned financial shortfalls.
Tracking and Categorizing Expenses Effectively
Tracking expenses meticulously enables accurate differentiation between planned expenses and unbudgeted outflows, enhancing money management precision. Categorizing expenses into fixed, variable, and discretionary segments allows for targeted monitoring and analysis, facilitating better financial control. Utilizing expense management tools with real-time reporting streamlines the identification of unexpected outflows, supporting proactive budgeting adjustments.
Benefits of Differentiating Expenses and Unbudgeted Outflows
Differentiating expenses from unbudgeted outflows enhances financial clarity by categorizing planned versus unexpected spending, allowing for precise budget tracking and improved cash flow management. This distinction enables organizations to identify cost-saving opportunities within regular expenses while quickly addressing and mitigating the impact of unforeseen expenditures. Accurate classification supports strategic financial planning, ensuring resources are allocated effectively to maintain financial stability and achieve long-term goals.
Building Resilience Against Unbudgeted Outflows
Effective money management prioritizes distinguishing regular expenses from unbudgeted outflows to build financial resilience. Tracking predictable expenses helps maintain cash flow stability, while allocating emergency funds prepares for unexpected costs such as medical bills or urgent repairs. Establishing a clear separation between these categories reduces financial stress and ensures uninterrupted progress toward long-term savings goals.
Related Important Terms
Expense Creep
Expense creep occurs when small, unbudgeted outflows gradually increase overall spending, undermining financial discipline and leading to budget overruns. Monitoring and controlling these incremental expenses is essential for effective money management and maintaining long-term financial stability.
Shadow Spending
Shadow spending refers to unbudgeted outflows that occur outside the planned expense categories, often leading to financial discrepancies and reduced savings. Monitoring and categorizing these hidden expenses helps improve cash flow visibility and enhances overall money management effectiveness.
Outflow Sniping
Outflow Sniping targets unbudgeted outflows by identifying and categorizing unexpected expenses to maintain strict control over overall cash flow. Effective money management relies on distinguishing routine expenses from outflow sniping cases to prevent financial overruns and optimize budget adherence.
Ghost Expenses
Ghost expenses, often overlooked unbudgeted outflows, silently erode your financial stability by draining funds without clear documentation or planning. Identifying and tracking these hidden costs are crucial for accurate money management and preventing unexpected budget deficits.
Budget Leakage
Expense represents planned financial outflows aligned with budget allocations, whereas unbudgeted outflow indicates unexpected spending that contributes directly to budget leakage by eroding reserved funds. Effective money management requires monitoring these discrepancies to prevent budget overruns and ensure financial discipline.
Untracked Outflows
Untracked outflows represent money spent without prior documentation or allocation in the budget, posing significant risks to accurate money management by obscuring the true financial picture. Unlike planned expenses, these unbudgeted outflows can lead to cash flow shortages and hinder effective forecasting, making it essential to implement tracking systems for comprehensive expense oversight.
Impulse Outgo
Impulse outgo refers to unplanned expenses that arise spontaneously, often leading to unbudgeted outflows that disrupt financial stability. Tracking impulse spending and categorizing these outflows separately from regular expenses enables more accurate budgeting and improved money management.
Expense Drift
Expense drift occurs when actual expenses gradually exceed budgeted amounts, leading to unbudgeted outflows that disrupt financial plans and cash flow stability. Monitoring expense drift through real-time tracking and variance analysis helps organizations identify and correct spending patterns before they escalate into significant budget overruns.
Sneaky Spending
Sneaky spending often disguises itself as minor expenses, gradually escalating unbudgeted outflows and disrupting financial control. Careful tracking of every expense, including small or irregular purchases, is essential to prevent unnoticed leakage from money management plans.
Anomalous Outflows
Anomalous outflows represent unbudgeted expenses that deviate significantly from planned allocations, disrupting accurate financial forecasting and cash flow management. Identifying and categorizing these unexpected expenditures enables more precise budget adjustments and mitigates risks associated with overspending.
Expense vs Unbudgeted Outflow for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com