An Emergency Fund is specifically designated for unexpected expenses like urgent pet medical care, providing immediate financial relief without disrupting regular budgeting. A Safety Net Fund serves as a broader financial cushion, covering longer-term disruptions such as job loss or extended income reduction. Prioritizing an Emergency Fund for pet-related expenses ensures quick access to critical funds, while the Safety Net Fund offers a more comprehensive financial security layer.
Table of Comparison
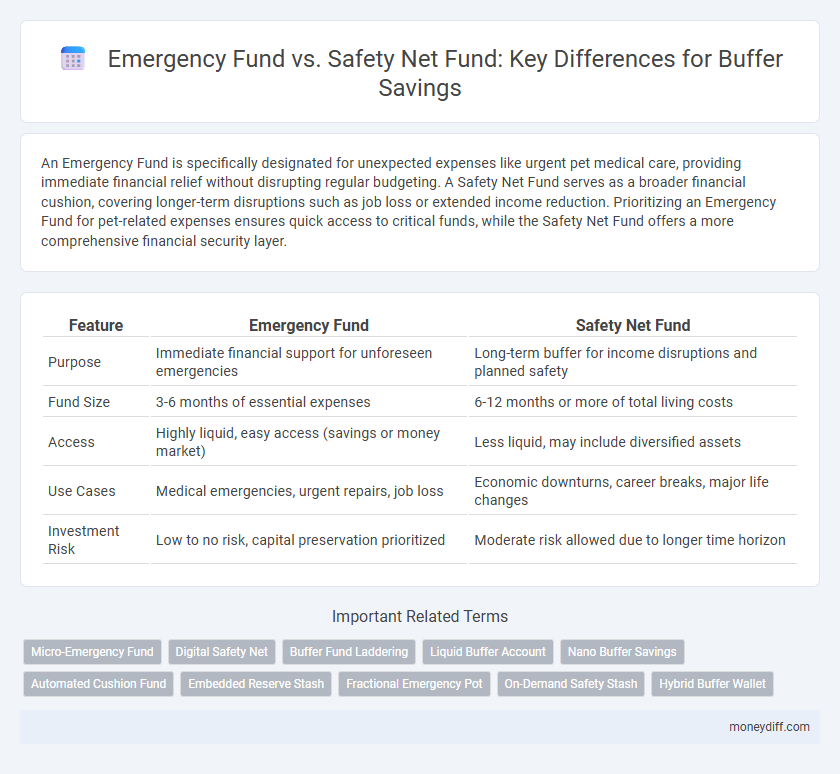
| Feature | Emergency Fund | Safety Net Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Immediate financial support for unforeseen emergencies | Long-term buffer for income disruptions and planned safety |
| Fund Size | 3-6 months of essential expenses | 6-12 months or more of total living costs |
| Access | Highly liquid, easy access (savings or money market) | Less liquid, may include diversified assets |
| Use Cases | Medical emergencies, urgent repairs, job loss | Economic downturns, career breaks, major life changes |
| Investment Risk | Low to no risk, capital preservation prioritized | Moderate risk allowed due to longer time horizon |
Understanding Emergency Funds and Safety Net Funds
Emergency funds typically cover immediate, unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies or urgent home repairs, while safety net funds provide a broader financial cushion for longer-term disruptions like job loss or economic downturns. Both funds are essential components of financial planning, with emergency funds ideally covering three to six months of essential living expenses and safety net funds extending beyond that timeframe for sustained security. Understanding the distinct purposes and optimal balance between these funds helps individuals maintain financial resilience during varying levels of financial stress.
Key Differences Between Emergency Fund and Safety Net Fund
An Emergency Fund is a dedicated savings pool specifically designed to cover unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies, job loss, or urgent home repairs, typically covering three to six months of essential living costs. Safety Net Fund, on the other hand, serves as a broader financial cushion that includes insurance policies, access to credit, and other resources to support long-term financial stability beyond immediate emergencies. Key differences lie in the scope and purpose: Emergency Funds provide immediate liquidity for urgent needs, while Safety Net Funds encompass a larger financial ecosystem aimed at sustained security.
Why You Need a Buffer: Emergency Fund Explained
An emergency fund is a dedicated savings buffer designed to cover unexpected expenses such as medical bills, job loss, or urgent home repairs, typically amounting to three to six months of living expenses. Unlike a safety net fund, which may serve broader financial stability goals, the emergency fund provides immediate liquidity and peace of mind during financial crises. Maintaining this fund reduces reliance on high-interest debt and supports long-term financial security by ensuring readiness for unforeseen challenges.
What Makes a Safety Net Fund Unique?
A Safety Net Fund is unique because it serves as a comprehensive financial buffer specifically designed to cover unexpected life events like job loss, major health expenses, or sudden home repairs, whereas an Emergency Fund typically focuses on short-term, immediate needs. This fund often includes a larger amount, sometimes six to twelve months' worth of living expenses, ensuring greater financial resilience. Its holistic approach provides a broader safety cushion, reducing the risk of debt during prolonged financial disruptions.
Setting Savings Goals: Emergency vs Safety Net Fund
Setting savings goals for an Emergency Fund involves targeting three to six months of essential living expenses to cover unexpected financial crises such as job loss or medical emergencies. A Safety Net Fund, however, focuses on a smaller, more flexible buffer designed to handle short-term disruptions like delayed paychecks or minor car repairs. Defining clear objectives for each fund ensures tailored contributions and effective financial preparedness.
How Much Should You Save in Each Fund?
Emergency funds should ideally cover three to six months of essential living expenses, ensuring financial stability during unexpected events like job loss or medical emergencies. Safety net funds act as an additional buffer, typically amounting to one to two months of discretionary spending, designed to handle minor financial setbacks without disrupting the emergency fund. Balancing savings between these two funds provides a comprehensive financial cushion tailored to both major crises and smaller, day-to-day uncertainties.
When to Use Your Emergency Fund vs Safety Net Fund
Use your emergency fund exclusively for unexpected, urgent expenses such as medical emergencies, car repairs, or job loss, ensuring it remains intact for true financial crises. Tap into your safety net fund for less immediate financial shortfalls like temporary income gaps or planned but uncertain expenses, offering a broader cushion without depleting critical emergency savings. Maintaining clear distinctions between these funds enhances financial resilience and prevents premature depletion of resources intended for life-threatening or severe financial disruptions.
Building Your Buffer: Step-by-Step Savings Strategy
Emergency funds are specifically designated savings to cover unexpected financial emergencies like medical bills or car repairs, while safety net funds offer a broader buffer, including ongoing expenses during prolonged income disruptions. Building your buffer involves setting clear savings goals, automating monthly contributions, and gradually increasing the fund to cover three to six months of essential living costs. Prioritizing consistent savings growth ensures readiness for both sudden emergencies and extended financial challenges, enhancing overall financial stability.
Common Mistakes in Creating Buffer Savings
Failing to clearly distinguish between an emergency fund and a safety net fund leads to misallocated savings, reducing financial effectiveness during crises. Many people mistake buffer savings as a one-size-fits-all solution, neglecting to tailor emergency funds for unexpected expenses like medical emergencies or job loss while safety net funds cover longer-term financial stability. Overlooking the importance of setting specific target amounts and liquidity in each fund increases the risk of insufficient coverage when urgent financial needs arise.
Choosing the Right Fund for Financial Security
An Emergency Fund typically covers 3 to 6 months of essential expenses and is designed for sudden, unexpected financial crises like job loss or medical emergencies. A Safety Net Fund, while broader, incorporates additional savings for less urgent but potential risks such as home repairs or major car maintenance, offering a more flexible financial buffer. Selecting the right fund depends on personal financial stability, risk tolerance, and the likelihood of various emergencies, ensuring an optimized strategy for long-term financial security.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Emergency Fund
A Micro-Emergency Fund serves as an immediate financial buffer, covering small, unexpected expenses without depleting broader Safety Net Funds designed for larger, long-term emergencies. Prioritizing a Micro-Emergency Fund enhances financial resilience by ensuring quick access to cash for minor crises, preserving the integrity of primary safety reserves.
Digital Safety Net
An Emergency Fund typically covers short-term, unexpected expenses like medical emergencies or urgent repairs, ensuring immediate financial stability. A Digital Safety Net Fund expands this concept by incorporating online financial tools and platforms, offering seamless access and management of buffer savings during crises.
Buffer Fund Laddering
Emergency Fund prioritizes immediate liquidity for unforeseen expenses, while Safety Net Fund extends to longer-term financial stability; Buffer Fund Laddering strategically allocates savings across these funds to optimize accessibility and growth. Layering savings into a laddered structure enhances financial resilience by ensuring funds are both readily available and invested to preserve or increase value.
Liquid Buffer Account
An Emergency Fund serves as a readily accessible financial resource covering unexpected expenses, while a Safety Net Fund provides broader support for prolonged financial instability. A Liquid Buffer Account enhances these savings by offering immediate liquidity through easily convertible assets, ensuring quick access to cash without penalties or delays.
Nano Buffer Savings
Nano Buffer Savings serve as a more agile alternative to traditional Emergency Funds by providing a quick-access financial cushion for minor unexpected expenses, whereas Safety Net Funds focus on comprehensive coverage for major emergencies. This micro-level savings strategy enhances liquidity and reduces the risk of depleting larger, long-term savings reserved for significant financial disruptions.
Automated Cushion Fund
An Emergency Fund is a dedicated savings reserved for unexpected expenses, such as medical emergencies or job loss, whereas a Safety Net Fund often includes broader financial buffers covering planned but irregular expenses. Automated Cushion Funds leverage technology to regularly and systematically allocate small amounts into these reserves, ensuring consistent growth without requiring active management.
Embedded Reserve Stash
An Emergency Fund primarily covers immediate, unforeseen expenses like medical bills and urgent repairs, whereas a Safety Net Fund offers broader financial stability by supporting ongoing needs such as job loss or extended income gaps. Embedded Reserve Stash acts as a strategic buffer within these funds, ensuring liquidity and quick access to cash while optimizing financial resilience for various emergencies.
Fractional Emergency Pot
A Fractional Emergency Pot serves as a strategic subset of a larger Emergency Fund, offering immediate access to critical cash while the Safety Net Fund provides broader financial stability during prolonged hardship. This layered approach enhances liquidity management, ensuring essential expenses are covered quickly without depleting more comprehensive reserves reserved for longer-term crises.
On-Demand Safety Stash
An Emergency Fund is designed specifically to cover unexpected, high-priority expenses like medical emergencies or urgent home repairs, ensuring immediate liquidity. In contrast, an On-Demand Safety Stash serves as a flexible buffer savings for less critical, everyday financial disruptions, providing quick access without derailing long-term financial goals.
Hybrid Buffer Wallet
A Hybrid Buffer Wallet combines the advantages of both an Emergency Fund and a Safety Net Fund by providing immediate access to liquid savings for unexpected expenses while also maintaining a reserve for longer-term financial stability. This strategic approach optimizes cash flow management, ensuring sufficient coverage for sudden emergencies and extended income disruptions without compromising overall financial security.
Emergency Fund vs Safety Net Fund for buffer savings. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com