An Emergency Fund serves as a dedicated stash of cash specifically for unexpected expenses, providing immediate financial security without the need to borrow. Safety Net 2.0 expands this concept by integrating digital tools, multiple income streams, and flexible access to funds, enhancing money management and resilience. Prioritizing an Emergency Fund ensures foundational protection, while Safety Net 2.0 offers a dynamic approach to safeguard against financial shocks.
Table of Comparison
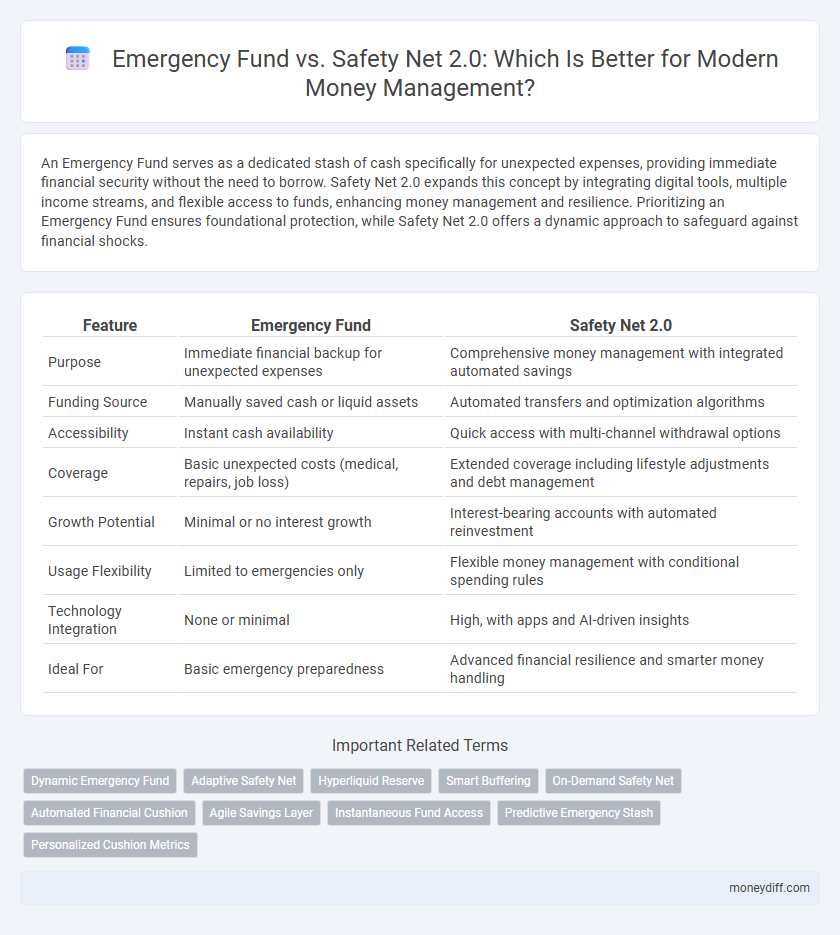
| Feature | Emergency Fund | Safety Net 2.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Immediate financial backup for unexpected expenses | Comprehensive money management with integrated automated savings |
| Funding Source | Manually saved cash or liquid assets | Automated transfers and optimization algorithms |
| Accessibility | Instant cash availability | Quick access with multi-channel withdrawal options |
| Coverage | Basic unexpected costs (medical, repairs, job loss) | Extended coverage including lifestyle adjustments and debt management |
| Growth Potential | Minimal or no interest growth | Interest-bearing accounts with automated reinvestment |
| Usage Flexibility | Limited to emergencies only | Flexible money management with conditional spending rules |
| Technology Integration | None or minimal | High, with apps and AI-driven insights |
| Ideal For | Basic emergency preparedness | Advanced financial resilience and smarter money handling |
Understanding Emergency Funds: Basics and Benefits
Emergency funds are liquid savings specifically reserved to cover unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies, car repairs, or job loss, providing financial stability and peace of mind. A well-funded emergency fund typically covers three to six months' worth of essential living expenses, ensuring you avoid high-interest debt during crises. Unlike Safety Net 2.0, which emphasizes a broader financial ecosystem including insurance and diversified income sources, emergency funds focus on immediate accessibility and risk mitigation.
What is a Safety Net 2.0?
A Safety Net 2.0 expands the traditional emergency fund by incorporating diversified financial resources, including accessible credit lines, insurance policies, and investment liquidity, to provide a more comprehensive buffer against unexpected expenses. Unlike a standard emergency fund that relies solely on cash savings, Safety Net 2.0 leverages multiple financial tools to enhance stability and reduce reliance on limited cash reserves. This approach optimizes money management by balancing immediate liquidity with long-term financial resilience.
Key Differences: Emergency Fund vs Safety Net 2.0
An Emergency Fund typically consists of three to six months' worth of essential living expenses saved in a liquid, low-risk account to cover unexpected financial hardships. Safety Net 2.0 extends beyond traditional savings by integrating dynamic financial tools like credit lines, insurance products, and diverse liquid assets to provide more flexible and comprehensive protection. Key differences include the scope of coverage, liquidity options, and the proactive use of financial instruments designed to optimize resilience against a broader range of financial emergencies.
Why an Emergency Fund Isn’t Enough in 2024
An Emergency Fund typically covers three to six months of essential expenses but may fall short in 2024 due to rising inflation, unexpected healthcare costs, and economic volatility. Safety Net 2.0 integrates diversified financial tools like short-term investments, insurance policies, and flexible credit options to provide more comprehensive protection against financial shocks. Relying solely on an Emergency Fund limits adaptability and may not safeguard against prolonged unemployment or large-scale emergencies in today's unpredictable economy.
Components of a Robust Safety Net 2.0
A robust Safety Net 2.0 for money management includes multiple components such as a fully funded emergency fund covering 3 to 6 months of essential expenses, diversified income streams to mitigate job loss risks, and access to short-term credit facilities for unexpected large expenses. Integrating insurance policies--health, disability, and critical illness--strengthens financial resilience beyond the basic emergency fund. Regularly updating and testing these components ensures the Safety Net 2.0 adapts to changing economic conditions and personal circumstances, providing comprehensive protection.
How to Structure an Emergency Fund
An Emergency Fund should cover three to six months of essential living expenses, stored in a liquid, easily accessible account such as a high-yield savings or money market account. Safety Net 2.0 expands beyond this by incorporating flexible savings, short-term investments, and insurance products to provide layered financial protection against diverse risks. Structuring an Emergency Fund involves prioritizing liquidity, regular contributions, and periodic reassessment aligned with changing income, expenses, and risk factors.
Building a Next-Level Financial Safety Net
Building a next-level financial safety net involves integrating a robust emergency fund with advanced money management strategies tailored to cover unexpected expenses and income disruptions. A comprehensive safety net 2.0 extends beyond traditional emergency savings by incorporating investments, insurance, and flexible budgeting tools to optimize liquidity and growth potential. Prioritizing diversified financial resources enhances resilience against economic uncertainties while ensuring long-term financial stability.
When Should You Rely on Your Emergency Fund?
Rely on your emergency fund exclusively for unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies, job loss, or urgent home repairs to maintain financial stability. Safety Net 2.0, which includes diversified income streams, insurance, and investments, provides additional layers of protection but should not replace the liquidity and immediacy of an emergency fund. Using your emergency fund only during true financial crises ensures it remains intact for critical, unforeseen events.
Integrating Insurance and Investments into Safety Net 2.0
Safety Net 2.0 enhances traditional emergency funds by integrating insurance policies and diversified investments to provide a more robust financial cushion. Combining health, disability, and property insurance with liquid assets and growth-oriented investments ensures comprehensive coverage against unforeseen expenses. This approach not only safeguards against immediate financial shocks but also supports long-term wealth preservation and growth.
Choosing the Best Money Management Strategy for You
Choosing the best money management strategy depends on your financial goals and risk tolerance, where an Emergency Fund provides immediate liquidity for unexpected expenses, typically covering 3-6 months of essential costs. Safety Net 2.0 expands on this by integrating diversified income streams, investments, and insurance to create a more resilient financial buffer against long-term uncertainties. Assessing personal cash flow stability and future financial commitments helps determine whether a traditional Emergency Fund or a comprehensive Safety Net 2.0 approach best secures your financial well-being.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Emergency Fund
A Dynamic Emergency Fund adjusts its balance based on changing life circumstances and financial responsibilities, offering more flexibility than a traditional static Emergency Fund. Unlike Safety Net 2.0, which focuses on long-term resilience through diversified savings and investment strategies, a Dynamic Emergency Fund prioritizes immediate liquidity and adaptive allocation to cover unexpected expenses effectively.
Adaptive Safety Net
The Adaptive Safety Net integrates real-time financial data and flexible spending limits to enhance traditional Emergency Fund strategies, providing dynamic coverage that adjusts to evolving economic conditions and personal income fluctuations. This approach ensures more resilient money management by proactively bridging gaps before reaching critical thresholds typically covered by static Emergency Funds.
Hyperliquid Reserve
An Emergency Fund serves as a dedicated Hyperliquid Reserve, offering immediate access to cash for unforeseen expenses without dipping into long-term investments, whereas Safety Net 2.0 expands this concept by integrating diversified liquid assets and credit lines to enhance financial flexibility. Prioritizing an Emergency Fund ensures rapid availability of funds, while Safety Net 2.0 provides a robust, multilayered approach to money management in times of crisis.
Smart Buffering
Smart Buffering in Emergency Fund management enhances financial resilience by allocating flexible reserves that adapt to unexpected expenses, unlike traditional Safety Net 2.0 approaches which often rely on fixed, less dynamic savings. This strategy optimizes liquidity and minimizes financial stress by balancing immediate accessibility with long-term growth potential.
On-Demand Safety Net
An Emergency Fund provides a fixed cash reserve for unexpected expenses, while Safety Net 2.0 introduces an On-Demand Safety Net that leverages flexible credit lines and digital financial tools to offer instant liquidity without depleting savings. This dynamic approach to money management enhances financial resilience by combining immediate access to funds with strategic cash flow optimization.
Automated Financial Cushion
An Emergency Fund serves as a traditional financial buffer, typically three to six months of expenses saved manually, while Safety Net 2.0 leverages automated financial tools like high-yield savings accounts, automated transfers, and AI-driven budgeting apps to create a dynamic, self-sustaining financial cushion. This automated approach enhances liquidity management, reduces manual intervention, and optimizes fund allocation for unforeseen expenses.
Agile Savings Layer
The Emergency Fund serves as a foundational financial buffer, typically covering three to six months of essential expenses, while Safety Net 2.0 incorporates the Agile Savings Layer, a dynamic and flexible strategy that adapts savings based on real-time needs and cash flow changes. This agile approach enhances money management by allowing quicker access to funds for unexpected expenses, optimizing liquidity without sacrificing long-term financial stability.
Instantaneous Fund Access
Emergency Fund offers immediate access to cash for unforeseen expenses, ensuring quick financial relief without delays. In contrast, Safety Net 2.0 integrates instant fund accessibility with digital tools like mobile wallets and automated transfers, enhancing responsiveness in money management.
Predictive Emergency Stash
Predictive Emergency Stash leverages data analytics and AI to forecast potential financial emergencies, enabling proactive fund allocation compared to traditional Emergency Funds that rely on fixed savings. Unlike Safety Net 2.0, which emphasizes immediate liquidity, Predictive Emergency Stash optimizes cash flow by dynamically adjusting reserves based on predictive risk models, enhancing money management efficiency.
Personalized Cushion Metrics
Emergency Fund strategies prioritize a fixed cash reserve covering 3-6 months of essential expenses, while Safety Net 2.0 employs Personalized Cushion Metrics that adapt liquidity based on individual risk factors, spending habits, and income volatility. This tailored approach enhances financial resilience by optimizing reserve size and accessibility to match unique financial profiles.
Emergency Fund vs Safety Net 2.0 for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com