An Emergency Fund is designed to cover unexpected personal expenses such as medical bills or car repairs, providing immediate financial stability during everyday crises. In contrast, a Disaster Escape Fund specifically targets large-scale catastrophes like natural disasters, ensuring resources are available for evacuation or long-term recovery. Properly distinguishing between these funds enhances overall money management by safeguarding both short-term emergencies and major unforeseen events.
Table of Comparison
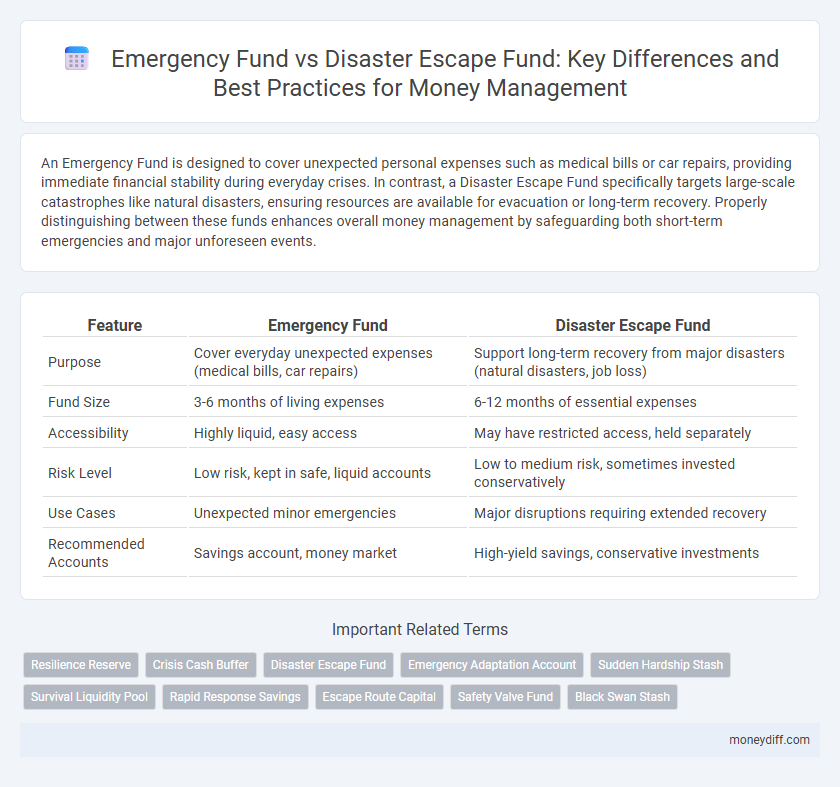
| Feature | Emergency Fund | Disaster Escape Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Cover everyday unexpected expenses (medical bills, car repairs) | Support long-term recovery from major disasters (natural disasters, job loss) |
| Fund Size | 3-6 months of living expenses | 6-12 months of essential expenses |
| Accessibility | Highly liquid, easy access | May have restricted access, held separately |
| Risk Level | Low risk, kept in safe, liquid accounts | Low to medium risk, sometimes invested conservatively |
| Use Cases | Unexpected minor emergencies | Major disruptions requiring extended recovery |
| Recommended Accounts | Savings account, money market | High-yield savings, conservative investments |
Understanding Emergency Funds: Purpose and Importance
Emergency funds are designed to cover unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies, job loss, or urgent car repairs, providing financial stability and peace of mind. Disaster escape funds, on the other hand, are specifically allocated for large-scale emergencies like natural disasters or long-term displacement, requiring a larger reserve. Understanding the distinct purposes helps prioritize savings strategies, ensuring both short-term liquidity and long-term security in money management.
What is a Disaster Escape Fund?
A Disaster Escape Fund is a specialized savings resource designed to provide immediate financial support during natural disasters or catastrophic emergencies, distinct from a general emergency fund which covers everyday unforeseen expenses. This fund typically prioritizes liquidity and accessibility to ensure quick withdrawal when evacuation, repairs, or urgent supplies are necessary. Allocating a separate Disaster Escape Fund allows for targeted readiness against events such as hurricanes, floods, or wildfires, minimizing the financial disruption specific to these crises.
Key Differences: Emergency Fund vs Disaster Escape Fund
An Emergency Fund typically covers short-term, unexpected expenses like medical bills, car repairs, or job loss, providing immediate financial stability. A Disaster Escape Fund is designed for long-term crises such as natural disasters or forced relocations, aiming to support survival and recovery phases. The key difference lies in the scope and duration, with Emergency Funds serving everyday emergencies and Disaster Escape Funds addressing catastrophic, large-scale events.
When to Use an Emergency Fund
An Emergency Fund is designed for unexpected personal financial setbacks such as medical expenses, car repairs, or sudden job loss, ensuring liquidity without incurring debt. A Disaster Escape Fund is specifically reserved for larger-scale crises like natural disasters, providing ample resources dedicated to survival and urgent relocation costs. Use the Emergency Fund first for short-term, urgent needs to maintain financial stability before tapping into more substantial disaster reserves.
Situations Calling for a Disaster Escape Fund
A Disaster Escape Fund is specifically designed for urgent, large-scale crises such as natural disasters, forced evacuations, or sudden loss of home, whereas an Emergency Fund covers everyday financial surprises like medical bills or car repairs. Situations calling for a Disaster Escape Fund often involve immediate relocation costs, temporary housing expenses, and essential survival needs that exceed the scope of a general Emergency Fund. Properly distinguishing between these funds ensures targeted financial preparedness and quicker recovery during catastrophic events.
How Much to Save: Emergency vs Disaster Escape
An Emergency Fund typically covers three to six months of essential living expenses, ensuring financial stability during unexpected events such as job loss or medical emergencies. In contrast, a Disaster Escape Fund requires a larger sum, often equating to six to twelve months of expenses, designed to support long-term displacement or recovery from natural disasters. Prioritizing the appropriate fund amount depends on individual risk factors and local disaster probabilities, with both funds serving distinct but complementary roles in comprehensive money management.
Building Your Emergency Fund: Practical Steps
Building your emergency fund involves setting aside three to six months' worth of living expenses in a highly liquid, easily accessible account to cover unexpected costs like job loss or medical emergencies. Disaster escape funds, by contrast, are specifically allocated for large-scale catastrophes such as natural disasters or severe financial crises, requiring a larger reserve often stored separately from general savings. Prioritize automating monthly contributions and cutting non-essential expenses to steadily increase your emergency fund, ensuring financial stability during unforeseen personal emergencies.
Establishing a Disaster Escape Fund: Essential Strategies
Establishing a disaster escape fund requires setting aside liquid assets specifically for unexpected catastrophes like natural disasters or severe personal emergencies, ensuring immediate access to funds without disrupting long-term savings. Prioritizing contributions that exceed a standard emergency fund, typically covering at least six months of expenses, provides a financial buffer tailored for high-risk scenarios. Strategic allocation into accessible accounts such as high-yield savings or money market funds enhances readiness while maintaining financial flexibility during crises.
Prioritizing Savings: Balancing Both Funds
Prioritizing savings between an Emergency Fund and a Disaster Escape Fund requires assessing immediate liquidity needs versus long-term crisis scenarios. An Emergency Fund typically covers 3 to 6 months of essential expenses, ensuring financial stability during job loss or unexpected bills. Simultaneously allocating resources to a Disaster Escape Fund, which addresses large-scale events like natural disasters or pandemics, enhances overall preparedness without compromising day-to-day security.
Integrating Both Funds in a Comprehensive Money Management Plan
An integrated money management plan combines an Emergency Fund, typically covering 3-6 months of essential expenses, with a Disaster Escape Fund dedicated to unforeseen large-scale events like natural disasters or economic crises. Allocating resources into both funds enhances financial resilience by addressing immediate personal needs and long-term recovery contingencies. This dual-fund strategy ensures liquidity for urgent demands while safeguarding against extraordinary disruptions, optimizing overall financial security.
Related Important Terms
Resilience Reserve
An Emergency Fund is a financial buffer for unexpected expenses such as medical bills or car repairs, ensuring immediate stability, while a Disaster Escape Fund is specifically allocated for large-scale crises like natural disasters or job loss, emphasizing long-term survival. Prioritizing a Resilience Reserve combines both concepts, creating a comprehensive safety net that supports both short-term emergencies and extended financial disruptions.
Crisis Cash Buffer
A Crisis Cash Buffer serves as a more flexible component of an Emergency Fund, designed specifically for immediate access during unforeseen disasters, such as natural calamities or sudden economic shocks. Unlike a standard Emergency Fund that covers daily living expenses during short-term income loss, the Disaster Escape Fund prioritizes liquidity and rapid availability to manage large-scale crises effectively.
Disaster Escape Fund
A Disaster Escape Fund is a specialized financial reserve designed to cover immediate evacuation, temporary shelter, and essential supplies during natural disasters, distinct from a general Emergency Fund that addresses broader unexpected expenses. Prioritizing a Disaster Escape Fund enhances preparedness for hurricanes, floods, or wildfires by ensuring access to liquidity for quick, critical decisions and safety measures in high-risk situations.
Emergency Adaptation Account
An Emergency Adaptation Account is a flexible financial tool designed to bridge immediate needs during unforeseen events, distinct from a Disaster Escape Fund that targets large-scale crises like natural disasters. Prioritizing liquidity and rapid access, this account supports adaptive money management for everyday emergencies, ensuring stability without depleting long-term savings.
Sudden Hardship Stash
A Sudden Hardship Stash is a targeted subset of an Emergency Fund designed specifically for immediate access during unexpected financial shocks like job loss or urgent medical expenses. Unlike a broader Disaster Escape Fund that covers large-scale crises, this stash prioritizes liquidity and quick availability to manage short-term hardships effectively.
Survival Liquidity Pool
An Emergency Fund provides immediate access to essential cash for unforeseen personal expenses, while a Disaster Escape Fund is a larger reserve designed to sustain extended financial disruptions caused by major crises, both forming critical components of a Survival Liquidity Pool. Prioritizing the Survival Liquidity Pool ensures continuous cash flow to cover necessities such as food, shelter, and utilities during emergencies, optimizing money management strategies.
Rapid Response Savings
Emergency Fund focuses on covering everyday unexpected expenses like medical bills or car repairs, while Disaster Escape Fund is designed for larger-scale crises such as natural disasters, providing rapid response savings to maintain financial stability during emergencies. Prioritizing a Rapid Response Savings approach ensures immediate access to liquid funds, minimizing the impact of sudden, high-cost events.
Escape Route Capital
An Emergency Fund provides immediate financial backup for unexpected expenses, while a Disaster Escape Fund specifically allocates capital to secure safe evacuation and shelter during catastrophic events. Prioritizing Escape Route Capital ensures swift, planned exits from disaster zones, safeguarding both safety and assets in extreme scenarios.
Safety Valve Fund
An Emergency Fund acts as a safety valve fund designed to cover unexpected personal expenses such as medical emergencies or job loss, ensuring immediate financial stability. In contrast, a Disaster Escape Fund is typically larger, aimed at long-term recovery from major disruptions like natural disasters, requiring strategic planning beyond the scope of regular emergency savings.
Black Swan Stash
An Emergency Fund typically covers unexpected everyday financial crises like medical bills or car repairs, while a Disaster Escape Fund is a larger reserve designed for rare, high-impact Black Swan events such as natural disasters or economic collapse. Prioritizing a Black Swan Stash within your Disaster Escape Fund ensures you have sufficient resources to survive and recover from extreme situations beyond routine emergencies.
Emergency Fund vs Disaster Escape Fund for money management Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com