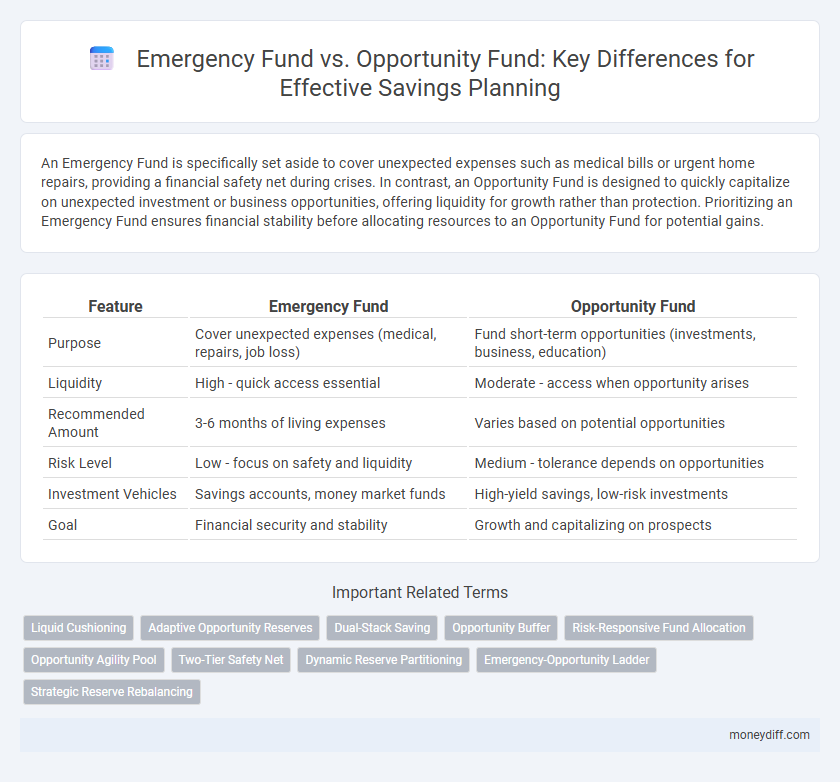
An Emergency Fund is specifically set aside to cover unexpected expenses such as medical bills or urgent home repairs, providing a financial safety net during crises. In contrast, an Opportunity Fund is designed to quickly capitalize on unexpected investment or business opportunities, offering liquidity for growth rather than protection. Prioritizing an Emergency Fund ensures financial stability before allocating resources to an Opportunity Fund for potential gains.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Emergency Fund | Opportunity Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Cover unexpected expenses (medical, repairs, job loss) | Fund short-term opportunities (investments, business, education) |
| Liquidity | High - quick access essential | Moderate - access when opportunity arises |
| Recommended Amount | 3-6 months of living expenses | Varies based on potential opportunities |
| Risk Level | Low - focus on safety and liquidity | Medium - tolerance depends on opportunities |
| Investment Vehicles | Savings accounts, money market funds | High-yield savings, low-risk investments |
| Goal | Financial security and stability | Growth and capitalizing on prospects |
Understanding Emergency Funds: A Financial Safety Net
An Emergency Fund is a dedicated savings reserve designed to cover unforeseen expenses such as medical emergencies, car repairs, or sudden job loss, typically amounting to three to six months of living expenses. Unlike an Opportunity Fund, which targets potential investments or spontaneous financial opportunities, the Emergency Fund prioritizes liquidity and quick access to ensure financial stability during crises. Maintaining a well-funded Emergency Fund reduces reliance on high-interest debt and provides a crucial safety net that supports long-term financial resilience.
What is an Opportunity Fund?
An Opportunity Fund is a savings reserve specifically set aside to capitalize on unexpected investment or financial opportunities that arise, distinct from an Emergency Fund which covers unforeseen expenses or financial hardships. Unlike Emergency Funds that prioritize liquidity and safety, Opportunity Funds aim for growth potential by allowing more flexible investment options. Properly balancing both funds can enhance financial resilience while enabling strategic wealth-building opportunities.
Key Differences Between Emergency and Opportunity Funds
Emergency funds prioritize liquidity and stability, reserved for unexpected expenses like medical emergencies or urgent home repairs, ensuring immediate access without risk of loss. Opportunity funds focus on growth potential, allocated to seize investment opportunities or large purchases, accepting higher risk and less immediate liquidity. Distinguishing between the two helps optimize savings strategy by balancing readiness for unforeseen needs with potential financial gains.
When to Use an Emergency Fund
An Emergency Fund should be used exclusively for unexpected, urgent expenses such as medical emergencies, car repairs, or sudden job loss to ensure financial stability. Unlike an Opportunity Fund, which is reserved for strategic investments or spontaneous chances to grow wealth, the Emergency Fund provides a secure financial cushion during critical times. Proper timing in using this fund preserves your long-term savings goals and prevents financial distress.
Opportunity Fund: Leveraging Savings for Growth
An Opportunity Fund focuses on leveraging savings to capture high-return investments, differentiating itself from the conservative nature of an Emergency Fund. By allocating a portion of savings to growth-oriented assets such as stocks, mutual funds, or real estate, individuals can potentially increase their financial gains over time. This strategic approach balances risk and reward, complementing the liquidity and safety provided by an Emergency Fund in a comprehensive savings plan.
How Much to Save: Emergency vs Opportunity Fund
An emergency fund typically requires saving three to six months' worth of essential living expenses to cover unexpected financial setbacks, providing a liquidity cushion for immediate needs. In contrast, an opportunity fund is more flexible, often targeting a smaller amount tailored to capitalize on sudden investment or business opportunities, generally ranging from one to three months' worth of discretionary spending. Prioritizing an adequately funded emergency fund ensures financial stability before allocating resources to an opportunity fund for strategic growth potential.
Assessing Your Financial Priorities
Assessing your financial priorities involves distinguishing between an emergency fund and an opportunity fund, where the emergency fund covers unexpected expenses like medical bills or job loss, ensuring financial stability. An opportunity fund, on the other hand, is allocated for potential investments or purchases that could enhance your financial growth. Prioritizing an emergency fund first creates a safety net, while an opportunity fund supports proactive wealth-building strategies.
Building and Funding Both Accounts
Building and funding an emergency fund requires prioritizing liquidity and quick access to cover unexpected expenses, ideally maintaining three to six months' worth of living costs in a high-yield savings account. Opportunity funds, by contrast, are designed for seizing investment or business opportunities and can be funded with surplus savings allocated to higher-risk, higher-return vehicles like stocks or mutual funds. Balancing contributions between both accounts ensures financial security while enabling growth potential, optimizing overall savings planning strategies.
Common Mistakes in Savings Planning
Common mistakes in savings planning include confusing an emergency fund with an opportunity fund, which leads to inadequate financial protection during unexpected crises. Emergency funds should cover 3 to 6 months of essential living expenses, while opportunity funds target investment or spontaneous opportunities without risking financial stability. Mixing these funds often results in depleted reserves during emergencies or missed investment chances, undermining long-term financial goals.
Creating a Balanced Savings Strategy
An Emergency Fund provides immediate financial security by covering unexpected expenses, while an Opportunity Fund targets potential investments and growth opportunities. Balancing both funds ensures liquidity for crises without sacrificing long-term wealth accumulation. Allocating savings proportionally based on risk tolerance and financial goals optimizes overall financial resilience and flexibility.
Related Important Terms
Liquid Cushioning
An Emergency Fund provides a liquid cushioning by holding readily accessible cash to cover unforeseen expenses, ensuring financial stability during crises. In contrast, an Opportunity Fund is designed for quick access to capitalize on investments or opportunities without compromising essential liquidity.
Adaptive Opportunity Reserves
Adaptive Opportunity Reserves strategically balance liquidity and growth by allocating funds for emerging investment opportunities without compromising immediate access needed for emergencies. This approach enhances savings planning by integrating a flexible allocation between traditional Emergency Funds and Opportunity Funds, optimizing financial resilience and potential gains.
Dual-Stack Saving
Emergency funds provide liquid financial security against unexpected expenses, while opportunity funds focus on growth potential through calculated investments. Dual-stack saving balances these by maintaining a readily accessible emergency fund alongside a strategically invested opportunity fund to optimize both safety and wealth accumulation.
Opportunity Buffer
An Emergency Fund is designed to cover unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies or job loss, typically holding three to six months' worth of living expenses in easily accessible accounts. In contrast, an Opportunity Fund, or Opportunity Buffer, is a flexible savings reserve intended to seize timely investments or career opportunities, providing liquidity without disrupting long-term financial goals.
Risk-Responsive Fund Allocation
Emergency funds provide immediate financial security by covering essential expenses during unexpected crises, whereas opportunity funds focus on capitalizing growth prospects, balancing risk by allocating savings to liquidity versus potential returns. Risk-responsive fund allocation strategically divides savings to ensure sufficient emergency reserves while enabling investment in higher-yield opportunities without jeopardizing financial stability.
Opportunity Agility Pool
An Emergency Fund provides immediate financial security for unexpected expenses, typically equal to three to six months of living costs, while an Opportunity Fund, often called an Opportunity Agility Pool, is designed for seizing short-term investments or business opportunities with higher risk tolerance. The Opportunity Agility Pool enhances savings planning by maintaining liquidity and flexibility, allowing individuals to capitalize on market or personal growth opportunities without depleting essential emergency reserves.
Two-Tier Safety Net
An Emergency Fund acts as the first tier of a two-tier safety net, providing immediate financial protection against unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies or job loss. The Opportunity Fund serves as the second tier, enabling strategic investments or purchases that capitalize on sudden opportunities without jeopardizing essential savings.
Dynamic Reserve Partitioning
Dynamic Reserve Partitioning enhances savings planning by allocating funds between an Emergency Fund, covering 3-6 months of essential expenses for unplanned crises, and an Opportunity Fund, which captures growth opportunities without risking financial security. This strategy ensures liquidity for urgent needs while optimizing capital for investments, balancing risk management and wealth accumulation effectively.
Emergency-Opportunity Ladder
An Emergency Fund provides immediate financial security by covering unexpected expenses such as medical bills or job loss, while an Opportunity Fund is designed for seizing timely investments or business opportunities without jeopardizing essential savings. The Emergency-Opportunity Ladder strategy prioritizes building a solid Emergency Fund first, then gradually shifting surplus savings towards an Opportunity Fund to balance risk management with growth potential.
Strategic Reserve Rebalancing
Strategic Reserve Rebalancing involves regularly adjusting the allocation between an Emergency Fund and an Opportunity Fund to maintain optimal liquidity and growth potential. This approach ensures that immediate financial security is preserved while capitalizing on investment opportunities to enhance long-term savings performance.
Emergency Fund vs Opportunity Fund for savings planning. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com